

International tourism, number of arrivals - Albania

Selected Countries and Economies
All countries and economies.
- Privacy Notice
- Access to Information
This site uses cookies to optimize functionality and give you the best possible experience. If you continue to navigate this website beyond this page, cookies will be placed on your browser. To learn more about cookies, click here.

Tourism in Albania
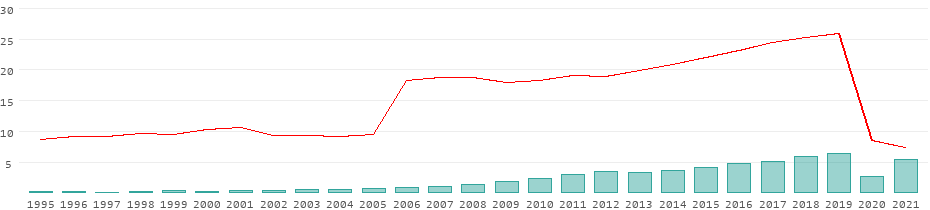
Development of the tourism sector in albania from 1995 to 2021.
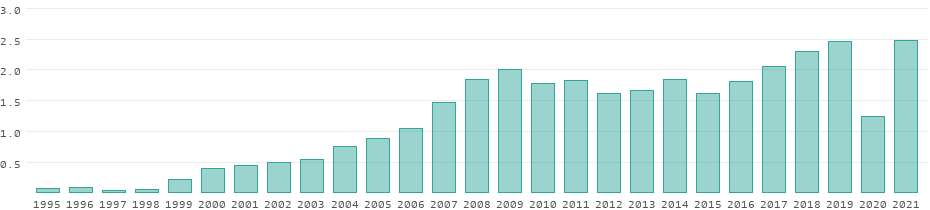
Revenues from tourism
All data for Albania in detail

Tourism in Figures - Albania 2021
Albania - International tourism, number of arrivals
The value for International tourism, number of arrivals in Albania was 2,658,000 as of 2020. As the graph below shows, over the past 25 years this indicator reached a maximum value of 6,406,000 in 2019 and a minimum value of 119,000 in 1997.
Definition: International inbound tourists (overnight visitors) are the number of tourists who travel to a country other than that in which they have their usual residence, but outside their usual environment, for a period not exceeding 12 months and whose main purpose in visiting is other than an activity remunerated from within the country visited. When data on number of tourists are not available, the number of visitors, which includes tourists, same-day visitors, cruise passengers, and crew members, is shown instead. Sources and collection methods for arrivals differ across countries. In some cases data are from border statistics (police, immigration, and the like) and supplemented by border surveys. In other cases data are from tourism accommodation establishments. For some countries number of arrivals is limited to arrivals by air and for others to arrivals staying in hotels. Some countries include arrivals of nationals residing abroad while others do not. Caution should thus be used in comparing arrivals across countries. The data on inbound tourists refer to the number of arrivals, not to the number of people traveling. Thus a person who makes several trips to a country during a given period is counted each time as a new arrival.
Source: World Tourism Organization, Yearbook of Tourism Statistics, Compendium of Tourism Statistics and data files.
- Thematic map
- Country comparison
- Country ranking
- Download data to Excel
Development Relevance: Tourism is officially recognized as a directly measurable activity, enabling more accurate analysis and more effective policy. Whereas previously the sector relied mostly on approximations from related areas of measurement (e.g. Balance of Payments statistics), tourism today possesses a range of instruments to track its productive activities and the activities of the consumers that drive them: visitors (both tourists and excursionists). An increasing number of countries have opened up and invested in tourism development, making tourism a key driver of socio-economic progress through export revenues, the creation of jobs and enterprises, and infrastructure development. As an internationally traded service, inbound tourism has become one of the world's major trade categories. For many developing countries it is one of the main sources of foreign exchange income and a major component of exports, creating much needed employment and development opportunities.
Limitations and Exceptions: Tourism can be either domestic or international. The data refers to international tourism, where the traveler's country of residence differs from the visiting country. International tourism consists of inbound (arrival) and outbound (departures) tourism. The data are from the World Tourism Organization (WTO), a United Nations agency. The data on inbound and outbound tourists refer to the number of arrivals and departures, not to the number of people traveling. Thus a person who makes several trips to a country during a given period is counted each time as a new arrival. The data on inbound tourism show the arrivals of nonresident tourists (overnight visitors) at national borders. When data on international tourists are unavailable or incomplete, the data show the arrivals of international visitors, which include tourists, same-day visitors, cruise passengers, and crew members. Sources and collection methods for arrivals differ across countries. In some cases data are from border statistics (police, immigration, and the like) and supplemented by border surveys. In other cases data are from tourism accommodation establishments. For some countries number of arrivals is limited to arrivals by air and for others to arrivals staying in hotels. Some countries include arrivals of nationals residing abroad while others do not. Caution should thus be used in comparing arrivals across countries.
Statistical Concept and Methodology: Statistical information on tourism is based mainly on data on arrivals and overnight stays along with balance of payments information. These data do not completely capture the economic phenomenon of tourism or provide the information needed for effective public policies and efficient business operations. Data are needed on the scale and significance of tourism. Information on the role of tourism in national economies is particularly deficient. Although the World Tourism Organization reports progress in harmonizing definitions and measurement, differences in national practices still prevent full comparability. Arrivals data measure the flows of international visitors to the country of reference: each arrival corresponds to one in inbound tourism trip. If a person visits several countries during the course of a single trip, his/her arrival in each country is recorded separately. In an accounting period, arrivals are not necessarily equal to the number of persons travelling (when a person visits the same country several times a year, each trip by the same person is counted as a separate arrival). Arrivals data should correspond to inbound visitors by including both tourists and same-day non-resident visitors. All other types of travelers (such as border, seasonal and other short-term workers, long-term students and others) should be excluded as they do not qualify as visitors. Data are obtained from different sources: administrative records (immigration, traffic counts, and other possible types of controls), border surveys or a mix of them. If data are obtained from accommodation surveys, the number of guests is used as estimate of arrival figures; consequently, in this case, breakdowns by regions, main purpose of the trip, modes of transport used or forms of organization of the trip are based on complementary visitor surveys.
Aggregation method: Gap-filled total
Periodicity: Annual
Classification
Topic: Private Sector & Trade Indicators
Sub-Topic: Travel & tourism
Note: This page was last updated on December 28, 2019
Home | About | Search | Site Map | Blog | Indicadores en Español
- Get involved

- Tourism and Hospitality in Albania 2022 An assessment of tourism trends and performance pdf (4.2 MB)
Tourism and Hospitality in Albania 2022
Tourism and Hospitality in Albania 2022 An assessment of tourism trends and performance
December 20, 2022
In the second half of 2022, UNDP in cooperation with the Albanian Tourism Association conducted a study to assess the impact of the war in Ukraine on the tourism sector. The main goal was to collect and analyze data on hospitality and tourism focusing on the main actors from the supply and demand side.
In addition to data from official sources, the study included surveys and focus groups with the hospitality and tourism sector as well as a representative survey with the urban population. Innovative techniques were also used to extract data from online booking platforms. The report summarizes a series of findings and perceptions, conclusions and recommendations that offer a comprehensive picture of tourism in Albania in 2022.
Regions and Countries
Related publications, publications, legal package, a working tool for the needs assessment an....
Legal package for the Needs Assessment and Referral Unit (NARU) was prepared in implementation of the "Empowering Communities (ICR)" Program, financed by USAID ...
Annual Progress Report - Un Joint Programme Leave No One ...
This report covers the main developments and achievements under the ‘Leave no one Behind’ UN Joint Programme (LNB2) during its second year of implementation (Au...
The National Disaster Risk Reduction Strategy
The National Disaster Risk Reduction Strategy, in addition to being one of the legal obligations of Law 45/2019 "On Civil Protection", is included in objective ...
Report On Training Need Assessment of Teachers of Primar...
This report is prepared under “EU4Schools” Programme, funded by the European Union (EU) and implemented by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) in co...
Strengthening the Social Protection Response After the Ea...
The final progress report of ‘Strengthening the Social Protection Response after the Earthquake in Albania’ (ESPR) project, provides a statement of progress mad...
STOCKTAKING REPORT - Qualitative assessment of the SDGs p...
This report presents an overview of the status of the agro-processing sector in Albania, which holds significant value in the nation’s economic landscape, provi...

Tourism 2.0 in Albania: A new opportunity for resilient growth
Raha shahidsaless, fernando blanco, stefka slavova, laureta qorlazja.

In a striking example, Albania has shown how the tourism sector can drive economic development. Following the country’s turbulent economic and political transition in the 1990s, tourism was perched on the sidelines of the Albanian economy. International travel, hospitality and related services essentially catered to returning members of the country’s large diaspora. However, in the 2000s, several major European tourism operators started recognizing Albania’s potential to join the Mediterranean’s thriving, though often overcrowded, sun-and-sand destinations. A surge of investments followed, and, between 2000 and 2019 the number of hotels, rooms, and beds increased more than tenfold.
Over the past two decades, the contribution of Albania’s tourism and travel sector to the country’s gross domestic product (GDP) has steadily increased and reached more than 8%, creating jobs and generating 38% of total exports. Looking back, 2019 was Albania’s best year for tourism, with 6.4 million foreign visitors and $2.3 billion in sectoral earnings. The future looked promising.
Unfortunately, when COVID-19 swept across the world, the number of international arrivals plunged by 60% and the sector’s earnings fell to $1.1 billion with the accommodations subsector shrinking by 75% in the second quarter of 2020. While 10% of Albanian businesses reported shutting down, another 60% earned less than 10% of their 2019 revenue, and more than half the employees in the sector were laid off.
Luckily, as travel restrictions eased and economies launched recovery efforts, the tourism sector bounced back with the arrival of 5.7 million foreign visitors and tourism earnings achieving pre-pandemic levels during the summer of 2021. While the sector was just finding its feet, Russia’s invasion of Ukraine dealt a second blow. The good news is that, despite the war, the summer of 2022 has been even better—as of October, the country received 6.8 million visitors, with projected earnings of more than $3.3 billion.
While the recovery was swift and remarkable, COVID-19 exposed the tourism sector’s vulnerability to external shocks, highlighting the need for a more diversified, resilient, and sustainable tourism sector.
Now, as hotels, restaurants, and operators recover from the economic impacts of the pandemic, they face three major hurdles:
Staffing : While the pandemic’s impact on the number of visitors and earnings has been fully reversed, it has exacerbated the situation regarding the shortage of qualified personnel. Kliton Gerxhani, Chairman of the Albanian Tourism Operators Association (ATOA) and co-owner of Albania Holidays DMC, emphasizes, “With no proper tourism schools, we invested a lot in training our staff on the job over the last five to 10 years. Yet, we were forced to let them go—first the younger staff and then the more experienced ones.”
In 2022, skills shortage continued to take a toll on the industry. While the sector tried to bring back staff following the recovery of tourism in Europe, many had already found jobs in other sectors or moved abroad, leading to reduced service capacity. In response, the provision of training courses for the accommodation sector and also for maritime activities could address the issue of skills shortage through training programs that award recognized international certifications.
The War in Ukraine : While the war has not impacted the total number of visitors to the country, it has triggered logistical and supply issues for the industry. Supply chain disruptions and surging food and oil prices have increased costs, eating into the sector’s revenue share in 2022. COVID-19 and the war in Ukraine have also altered tourist behavior with a higher rate of booking cancellations, impacting planning and logistics of supplies and management of reservations, and underlining the need for digitalization.
Opportunities and Branding : Albania is known as a beach destination for tourists who usually prefer shorter stays with low levels of individual spending—a profile associated with an undiversified tourism value chain with a limited range of attractions and activities.
Unfortunately, Albania’s “blue tourism” subsector, including boating, diving, recreational fishing and aquatic sports, remains largely undeveloped. Additionally, despite Albania’s unique cultural heritage, cultural tourism represents a small fraction of the industry.
Mapping the future
Prepared by IFC and the World Bank, the Albania Country Private Sector Diagnostic ( CPSD ), released in June 2022, highlights massive investment opportunities for the private sector. It also underlines the need for a strong policy roadmap that can set the course for a higher-value-added, more diversified and sustainable tourism sector.
With the pandemic bringing about a shift in tourist preferences—from mass tourism to small group outdoors-based tourism—this could be a good opportunity for Albania. The country can reposition its tourism sector to cater to new markets and rebrand as a destination for niche and high-end tourism.
Further, linking blue tourism in coastal areas to nature-, food-, and culture-oriented tourism in the country’s mountain forests and well-preserved villages could raise average spending, extend the average length of stay, reduce seasonality and ease the pressure on overcrowded tourism hotspots. Implementing the government’s Blue Tourism Strategy could increase international arrivals by 208,000 a year, boosting tourism revenue by over $400 million annually.
However, shifting to a more diverse and sustainable tourism model will require major investments, for example, in marinas and nature-based activities. Albania will need to address critical infrastructure bottlenecks while increasing air connectivity and expanding road networks to develop inland tourism and promote tourist circulation.
Albania will also need investments in water and waste management along with regulations and environmental safeguards to ensure destinations are sustainable. The growth of ecological and cultural tourism will require specialized accommodations and supportive infrastructure for the country’s national parks, inland villages and cultural heritage sites. Additionally, it will be key to develop a skilled workforce, support firms with innovation and technology transfer and improve access to finance for tourism operators.
With strong government support, timely investments in infrastructure and effective policy and regulatory measures, the private sector can contribute to a robust tourism industry, turning Albania into a top tourist destination while preserving its underlying natural and cultural assets.
- Financial Sector
- Jobs & Development
- Europe and Central Asia

Senior Private Specialist

Principal Economist for Europe and Central Asia of the IFC

Lead Economist

IFC Country Officer, Tirana, Albania
Join the Conversation
- Share on mail
- comments added
This website stores cookies on your computer. These cookies are used to collect information about how you interact with our website and allow us to remember you. We use this information in order to improve and customize your browsing experience and for analytics and metrics about our visitors both on this website and other media. To find out more about the cookies we use, see our Cookies Policy .
If you decline, your information won’t be tracked when you visit this website. A single cookie will be used in your browser to remember your preference not to be tracked.
Albania Visitor Arrivals
- Albania Visitor Arrivals recorded 1,778,637 person in Dec 2023, compared with 4,661,112 person in the previous quarter
- Albania Visitor Arrivals data is updated quarterly, available from Mar 2005 to Dec 2023
- The data reached an all-time high of 4,661,112 person in Sep 2023 and a record low of 75,438 person in Mar 2005
View Albania's Visitor Arrivals from Mar 2005 to Dec 2023 in the chart:
What was Albania's Visitor Arrivals in Dec 2023?
Albania Visitor Arrivals recorded 1,778,637 person in Dec 2023, compared with 4,661,112 person in the previous quarter See the table below for more data.
Visitor Arrivals by Country Comparison
Buy selected data, accurate macro & micro economic data you can trust.
Explore the most complete set of 6.6 million time series covering more than 200 economies, 20 industries and 18 macroeconomic sectors.
Albania Key Series
More indicators for albania, request a demo of ceic.
CEIC’s economic databases cover over 200 global markets. Our Platform offers the most reliable macroeconomic data and advanced analytical tools.
Explore our Data

Travel & Tourism - Albania
- Albania is expected to see a significant increase in revenue within the Travel & Tourism market.
- By the year 2024, revenue is projected to reach US$75.49m, with an anticipated annual growth rate of 4.56% from 2024 to 2028.
- This growth will result in a projected market volume of US$90.23m by 2028.
- The largest market within the market is the Hotels market, with a projected market volume of US$32.78m in 2024.
- Furthermore, it is expected that the number of users in Hotels will reach 527.00k users by 2028, with a user penetration rate of 19.7% in 2024, expected to increase to 23.5% by 2028.
- The average revenue per user (ARPU) is projected to amount to US$135.40.
- Additionally, it is anticipated that 80% of the total revenue in the Travel & Tourism market in Albania will be generated through online sales by 2028.
- It is worth noting that, in global comparison, United States is expected to generate the most revenue within the Travel & Tourism market, with a projected revenue of US$199bn in 2024.
- Albania's travel and tourism market is experiencing a rise in popularity due to its stunning coastline and historic landmarks.
Key regions: Malaysia , Europe , Singapore , Vietnam , United States
Definition:
The Travel & Tourism market encompasses a diverse range of accommodation services catering to the needs and preferences of travelers. This dynamic market includes package holidays, hotel accommodations, private vacation rentals, camping experiences, and cruises.
The market consists of five further markets.
- The Cruises market covers multi-day vacation trips on a cruise ship. The Cruises market encompasses exclusively passenger ticket revenues.
- The Vacation Rentals market comprises of private accommodation bookings which includes private holiday homes and houses as well as short-term rental of private rooms or flats.
- The Hotels market includes stays in hotels and professionally run guest houses.
- The Package Holidays market comprises of travel deals that normally contain travel and accommodation sold for one price, although optional further provisions can be included such as catering and tourist services.
- The Camping market includes bookings at camping sites for pitches using tents, campervans, or trailers. These can be associated with big chains or privately managed campsites.
Additional Information:
The main performance indicators of the Travel & Tourism market are revenues, average revenue per user (ARPU), users and user penetration rates. Additionally, online and offline sales channel shares display the distribution of online and offline bookings. The ARPU refers to the average revenue one user generates per year while the revenue represents the total booking volume. Revenues are generated through both online and offline sales channels and include exclusively B2C revenues and users for the above-mentioned markets. Users represent the aggregated number of guests. Each user is only counted once per year. Additional definitions for each market can be found within the respective market pages.
The booking volume includes all booked travels made by users from the selected region, independent of the departure and arrival. The scope includes domestic and outbound travel.
Prominent players in this sector include online travel agencies (OTAs) like Expedia and Opodo, as well as tour operators such as TUI. Specialized platforms like Hotels.com, Booking.com, and Airbnb facilitate the online booking of hotels and private accommodations, contributing significantly to the market's vibrancy.
For further information on the data displayed, refer to the info button right next to each box.
- Bookings directly via the website of the service provider, travel agencies, online travel agencies (OTAs) or telephone
out-of-scope
- Business trips
- Other forms of trips (e.g. excursions, etc.)
Travel & Tourism
- Vacation Rentals
- Package Holidays
- Analyst Opinion
Albania, a country known for its stunning landscapes and rich history, has been experiencing significant growth in its Travel & Tourism market. Customer preferences: Travelers in Albania are increasingly seeking authentic and immersive experiences, driving the demand for cultural and adventure tourism. Tourists are drawn to the country's UNESCO World Heritage sites, pristine beaches, and vibrant local culture. Additionally, there is a growing interest in eco-friendly and sustainable travel options among visitors. Trends in the market: One notable trend in the Albanian Travel & Tourism market is the rise of digital platforms and online booking services, making it easier for travelers to plan their trips and discover hidden gems in the country. The emergence of boutique hotels, homestays, and unique accommodations is also reshaping the hospitality sector in Albania, catering to the diverse preferences of modern tourists. Local special circumstances: Albania's strategic location in the Balkans, with easy access to both the Adriatic and Ionian Seas, has positioned the country as a desirable destination for both leisure and business travelers. The government's efforts to improve infrastructure, promote sustainable tourism practices, and enhance safety and security measures have further boosted the country's appeal among international visitors. Underlying macroeconomic factors: The steady economic growth in Albania, coupled with increasing disposable incomes among the local population, has fueled domestic tourism and encouraged investments in the Travel & Tourism sector. The country's visa liberalization policies and efforts to promote air connectivity have also contributed to the growth of international arrivals, supporting the overall expansion of the market.
- Methodology
Data coverage:
Modeling approach:
Additional notes:
- Sales Channels
- Travel Behavior
- Global Comparison
- Key Market Indicators
Mon - Fri, 9am - 6pm (EST)
Mon - Fri, 9am - 5pm (SGT)
Mon - Fri, 10:00am - 6:00pm (JST)
Mon - Fri, 9:30am - 5pm (GMT)
- Unlimited access to our Market Insights
- Statistics and reports
- Usage and publication rights

© Ilir Tsouko/Lonely Planet
Albania's stunning mountain scenery, crumbling castles, boisterous capital and dreamy beaches rival any in the Mediterranean and continue to enchant.
Best Places to Visit
Spending diaries, your next trip starts here.
Go from dreaming to planning with trip planning options made to help you craft your ideal itinerary.
Attractions
Must-see attractions.

The Albanian Riviera
Early in the morning, before the tourist crowds arrive and when the rocks are still tinged in the yellow dawn light, you might just imagine that the…

The evocative ruins of the ancient Illyiran city of Apollonia sit on a windswept hilltop some 12km west of the city of Fier. While a large part of the…

Hidden behind the crumbling walls of the fortress that crowns the hill above Berat is the whitewashed, village-like neighbourhood of Kala; if you walk…
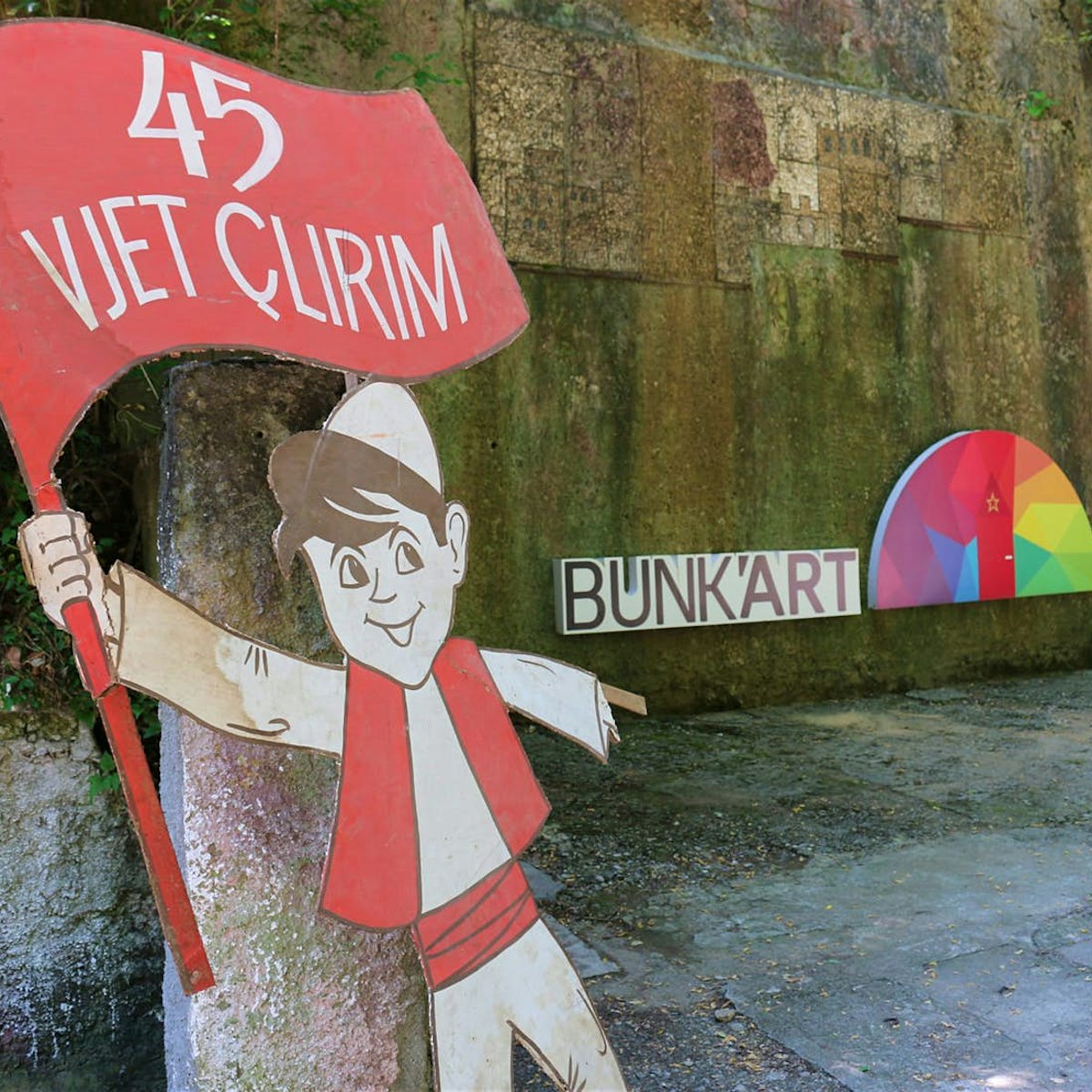

Bunk'Art
This fantastic conversion – from a massive Cold War bunker on the outskirts of Tirana into a history and contemporary art museum – is Albania's most…
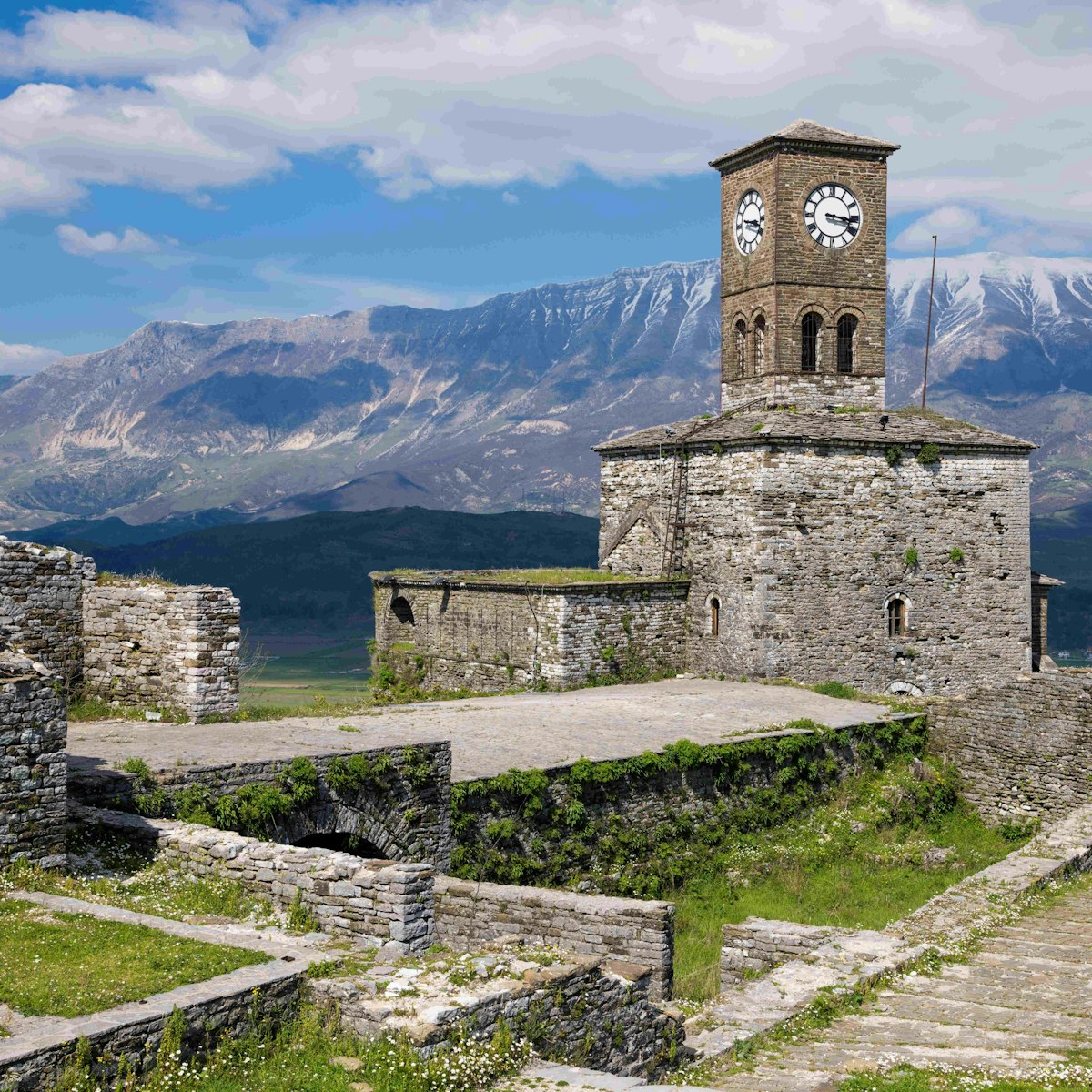

Gjirokastra Castle
Gjirokastra
Gjirokastra's eerie hilltop castle is one of the biggest in the Balkans. There's been a fortress here since the 12th century, although much of what can be…

Onufri Museum
The Onufri Museum is situated in the Kala quarter's biggest church, the Church of the Dormition of St Mary (Kisha Fjetja e Shën Mërisë). The church itself…

Durrës Archaeological Museum
This ultra-modern, well lit and labelled museum just back from the seafront has a breathtaking collection of historical artefacts. Highlights include the…

Gjipe Beach
Between Dhërmi and Vuno is the turn-off for this little-known gem, a gorgeous stretch of isolated white sand and rock backed by big cliffs – and as yet…
Latest stories from Albania
Filter by interest:
- All Interests
- Adventure Travel
- Art & Culture
- Beaches, Coasts & Islands
- Food & Drink

Nov 18, 2023 • 7 min read
Albania is slowly becoming the jewel of the Balkans due to its crystal waters, impressive mountains, and affordability for all types of travelers.

Aug 23, 2023 • 7 min read

Apr 6, 2023 • 3 min read

Nov 15, 2022 • 8 min read

Nov 15, 2022 • 2 min read

Feb 1, 2021 • 5 min read

Nov 12, 2020 • 10 min read

Feb 28, 2020 • 11 min read

Jun 24, 2019 • 4 min read

Sep 19, 2018 • 1 min read
in partnership with getyourguide
Book popular activities in Albania
Purchase our award-winning guidebooks.
Get to the heart of Albania with one of our in-depth, award-winning guidebooks, covering maps, itineraries, and expert guidance.
Albania and beyond

Albania Tourist Arrivals
Tourist arrivals in albania decreased to 1861040 in the fourth quarter of 2023 from 4897668 in the third quarter of 2023. tourist arrivals in albania averaged 831802.70 from 2001 until 2023, reaching an all time high of 4897668.00 in the third quarter of 2023 and a record low of 62116.00 in the second quarter of 2001. source: instituti i statistikave (instat), markets, gdp, labour, prices, money, trade, government, business, consumer, housing, taxes, health, climate.

Tourism in Albania
Disclaimer: Some posts on Tourism Teacher may contain affiliate links. If you appreciate this content, you can show your support by making a purchase through these links or by buying me a coffee . Thank you for your support!
Tourism in Albania is big business! But why is tourism here so important and why does it matter? Read on to find out…
Overview of the Geography of Albania
Statistics about tourism in albania, most popular tourist attractions in albania, most popular types of tourism in albania, impacts of tourism in albania, faqs about tourism in albania, to conclude: tourism in albania.
Albania is a country located in Southeastern Europe on the Balkan Peninsula. It shares borders with Montenegro to the northwest, Kosovo to the northeast, North Macedonia to the east, and Greece to the southeast. To the west, Albania has a coastline along the Adriatic and Ionian Seas, making it the only country in the Balkans with direct access to the Mediterranean Sea.
The geography of Albania is characterized by a diverse landscape that includes coastal areas, mountain ranges, and inland plains. Here are some key features:
- Coastline: Albania’s coastline stretches approximately 476 kilometers (296 miles) along the Adriatic and Ionian Seas. It features numerous picturesque beaches, bays, and rocky cliffs. The Albanian Riviera, located along the Ionian Sea, is known for its stunning beauty and popular tourist destinations.
- Mountains: The Albanian Alps, also known as the Accursed Mountains or Prokletije, dominate the northern part of the country. This mountain range is part of the Dinaric Alps and offers breathtaking scenery, deep canyons, and peaks reaching over 2,500 meters (8,200 feet) in elevation. The Sharr Mountains extend along the border with North Macedonia, while the Korab Mountains mark the border with North Macedonia and Kosovo.
- Inland Plains: The central part of Albania is characterized by several major inland plains, including the Shkumbin River Valley and the Myzeqe Plain. These areas are relatively flat and fertile, supporting agricultural activities such as farming and livestock rearing.
- Lakes and Rivers: Albania is home to several lakes, the most notable being Lake Ohrid and Lake Prespa. Lake Ohrid, shared with North Macedonia, is one of the oldest and deepest lakes in Europe, known for its unique ecosystem and cultural heritage. The country is also traversed by numerous rivers, including the Drin, Vjosa, and Osum, which provide important water resources.
- National Parks: Albania boasts several national parks, showcasing its natural beauty and biodiversity. Some prominent examples include the Theth National Park, located in the Albanian Alps, and Butrint National Park, renowned for its ancient archaeological sites and wetland habitats.
Overall, Albania’s geography offers a combination of stunning coastal areas, towering mountain ranges, and fertile plains, providing diverse opportunities for tourism, outdoor activities, and ecological exploration.
The tourism industry plays a vital role in economic development and cultural exchange worldwide. Albania, a country situated in Southeastern Europe, has emerged as an intriguing destination for international travelers due to its unique blend of natural beauty, historical sites, and cultural heritage. Lets look at some of the most noteworthy aspects of tourism in Albania:

- Geographical Features: Albania’s geographical location offers a diverse array of landscapes, ranging from stunning coastline along the Adriatic and Ionian Seas to rugged mountains and pristine lakes. The country boasts three national parks, including the renowned Butrint National Park and the Albanian Alps, providing ample opportunities for outdoor activities such as hiking, camping, and wildlife observation. The pristine beaches of the Albanian Riviera and the historical city of Berat, recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage site, further enhance the country’s appeal to tourists.
- Cultural Heritage: Albania’s rich cultural heritage reflects its historical influences from Illyrians, Greeks, Romans, Byzantines, and Ottomans. The country houses numerous archaeological sites, ancient ruins, and medieval castles that attract history enthusiasts and cultural explorers. The city of Gjirokastër, another UNESCO World Heritage site, offers a glimpse into Ottoman-era architecture, while the ancient city of Butrint showcases remnants of Roman and Greek civilizations. These cultural treasures provide visitors with a deeper understanding of Albania’s past and contribute to its allure as a tourism destination.
- Tourism Development and Promotion: Albania has made significant strides in developing its tourism industry in recent years. Recognizing the economic potential of tourism, the Albanian government has implemented various initiatives to promote the country as an attractive destination. These efforts include infrastructure improvements, such as expanding airport facilities and enhancing road networks, as well as marketing campaigns targeting international audiences. Additionally, the country has simplified visa procedures and introduced incentives for foreign investment in the tourism sector, aiming to facilitate visitor arrivals and stimulate industry growth.
- Challenges and Opportunities: While Albania’s tourism industry shows promising growth, it also faces challenges that need to be addressed. These challenges include limited awareness of Albania as a tourist destination, inadequate infrastructure in some regions, and the need to improve the quality and diversity of tourism services. Furthermore, sustainable tourism practices must be prioritized to preserve the country’s natural and cultural assets for future generations. By leveraging its unique offerings, Albania has the opportunity to position itself as a sustainable tourism destination, attracting travelers seeking authentic experiences and fostering long-term socio-economic benefits.
- Conclusion: Albania’s tourism industry exhibits considerable potential as it capitalizes on its diverse landscapes, cultural heritage, and recent development efforts. With its pristine beaches, stunning mountains, and historical sites, Albania offers a captivating experience for travelers seeking a blend of natural beauty and cultural immersion. However, sustainable tourism practices, infrastructure improvements, and targeted marketing campaigns remain crucial for the industry’s continued success. By balancing development with the preservation of its natural and cultural assets, Albania can carve a niche for itself in the global tourism market, contributing to the country’s economic growth and fostering cross-cultural exchanges.
Now lets take a look at some statistics that emphasise the scale of tourism in Albania:
- International Tourist Arrivals: In 2021, Albania received approximately 4.5 million international tourist arrivals.
- Tourism Revenue: The tourism sector in Albania generated approximately 1.5 billion euros in revenue in 2021.
- Tourism Contribution to GDP: Tourism directly contributed around 9.4% to Albania’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP) in 2021.
- Employment: The tourism sector in Albania employed approximately 200,000 people in 2021, accounting for around 13% of the country’s total employment.
- Top Source Markets: The main source markets for tourism in Albania are Kosovo, North Macedonia, Greece, Montenegro, and Italy.
- Average Length of Stay: On average, tourists visiting Albania stay for around 6-7 days.
- Accommodation: Albania has a diverse range of accommodation options, including hotels, guesthouses, and rental apartments. As of 2021, there were over 1,100 registered hotels in the country.
- Beach Tourism: Albania’s coastline along the Adriatic and Ionian Seas is a major attraction for beach tourism. The country offers approximately 476 kilometers of coastline with numerous beaches and crystal-clear waters.

9. Cultural Tourism: Albania has a rich cultural heritage, including ancient archaeological sites, Ottoman-era architecture, and UNESCO World Heritage Sites like the ancient city of Butrint and the historic center of Gjirokastër.
10. Natural Attractions: Albania boasts beautiful natural landscapes, including the Albanian Alps in the north, stunning lakes like Lake Ohrid and Lake Shkodra, and national parks such as Butrint National Park and Llogara National Park.
Now lets take a look at the premier tourist attractions in Albania, their significance, characteristics, and appeal to visitors:
- Historical and Cultural Attractions:
2.1. The Ancient City of Butrint: Butrint, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, stands as a testament to Albania’s rich history. This archaeological site showcases remnants of ancient civilizations, including Greek, Roman, Byzantine, and Venetian periods. Its well-preserved amphitheater, Roman baths, and Venetian castle enthrall tourists with their architectural grandeur.
2.2. Berat’s Historic Centre: Berat, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, houses a remarkable collection of Ottoman-era buildings, earning it the epithet “The Town of a Thousand Windows.” The Mangalem and Gorica quarters boast picturesque streets, medieval churches, and traditional houses, providing a glimpse into Albania’s past.
- Natural Landscapes:
3.1. Albanian Riviera: The Albanian Riviera, stretching along the country’s southwestern coastline, offers breathtaking vistas of the Ionian Sea. With pristine beaches, secluded coves, and charming coastal towns like Saranda and Himara, this region has become a sought-after destination for beach lovers and nature enthusiasts.
3.2. Valbona Valley National Park: Nestled in the Albanian Alps, Valbona Valley National Park is a haven for outdoor enthusiasts. Its awe-inspiring mountain landscapes, picturesque valleys, and the pristine Valbona River attract hikers, nature lovers, and adventure seekers alike.
- Architectural Marvels:
4.1. Skanderbeg Square: Located in the heart of Tirana, Albania’s capital city, Skanderbeg Square serves as a vibrant hub and a testament to the nation’s resilience and history. Its architectural highlights include the National Historical Museum, the Et’hem Bey Mosque, and the Skanderbeg Statue, paying homage to Albania’s national hero.
4.2. Rozafa Castle: Rozafa Castle, situated near Shkodra, offers panoramic views of Lake Shkodra and the surrounding landscape. This medieval fortress, steeped in legend, captivates visitors with its imposing walls, ancient artifacts, and captivating historical narratives.

Albania’s premier tourist attractions exemplify the country’s multifaceted allure. Whether exploring ancient ruins, basking in the sun along the Albanian Riviera, or immersing oneself in the country’s rich history and culture, visitors are captivated by the unique experiences Albania has to offer. By preserving its heritage and showcasing its natural beauty, Albania has positioned itself as a must-visit destination for travelers seeking a distinctive and enriching experience. Future research could delve deeper into the economic and sociocultural impact of tourism on Albania, further contributing to the understanding and development of the country’s tourism industry.
Tourism plays a pivotal role in Albania’s socio-economic development, offering diverse opportunities for both domestic and international visitors. Now lets summartise the types of tourism in Albania, namely cultural tourism, nature-based tourism, and adventure tourism:
- Cultural Tourism: Cultural tourism in Albania revolves around its remarkable historical sites, archaeological treasures, and traditional heritage. The country boasts a long and captivating history, with influences from Illyrians, Greeks, Romans, Byzantines, and Ottomans, among others. Key cultural attractions include ancient cities like Butrint and Apollonia, UNESCO World Heritage sites such as Berat and Gjirokastër, and Ottoman-style architecture found in cities like Shkodër and Tirana. Additionally, traditional festivals, music, crafts, and gastronomy contribute to the overall allure of cultural tourism in Albania.
- Nature-Based Tourism: Albania’s diverse natural landscapes offer immense potential for nature-based tourism. The country is blessed with stunning mountain ranges, pristine beaches along the Adriatic and Ionian Seas, and a wealth of national parks and protected areas. The Albanian Alps, encompassing the Valbona and Theth valleys, attract hikers and outdoor enthusiasts seeking adventure amidst unspoiled beauty. The Albanian Riviera, with its turquoise waters and picturesque coastal villages, appeals to beach lovers and sun-seekers. The Prespa Lakes, Ohrid Lake, and Butrint National Park present opportunities for birdwatching, wildlife observation, and ecological exploration.
- Adventure Tourism: Adventure tourism in Albania has gained traction due to its untamed landscapes and adrenaline-pumping activities. The country’s mountains, canyons, and rivers serve as playgrounds for activities like hiking, mountain biking, paragliding, rock climbing, canyoning, and whitewater rafting. The Osumi Canyon, the Llogara Pass, and the Via Dinarica trail are particularly renowned adventure destinations. The Albanian coastline offers water sports such as scuba diving, snorkeling, and sailing. These adventurous pursuits attract thrill-seekers looking for unique and off-the-beaten-path experiences.

5. Conclusion: Albania’s tourism industry has flourished due to the popularity of various tourism segments, including cultural tourism, nature-based tourism, and adventure tourism. The country’s rich cultural heritage, awe-inspiring natural landscapes, and diverse range of adventure activities have positioned it as an appealing destination for global travelers seeking authenticity and immersive experiences. As the demand for sustainable and responsible travel continues to grow, Albania’s tourism sector has the potential to foster economic development while preserving its natural and cultural assets. The government and stakeholders should focus on infrastructure development, sustainable practices, and effective marketing strategies to further enhance Albania’s position as a prominent tourism destination.
Next we will explore the multi-dimensional impacts of tourism in Albania, elucidating both the benefits and challenges faced by Albania as a tourist destination.
- Positive Impacts of Tourism in Albania:
2.1 Economic Impacts: The tourism industry in Albania has fostered substantial economic growth, generating employment opportunities, foreign exchange earnings, and infrastructure development. The influx of tourists has led to increased demand for goods and services, stimulating local businesses and fostering entrepreneurship. The revenue generated from tourism has supported the diversification of the economy and encouraged investments in various sectors, contributing to overall economic development.
2.2 Social Impacts: Tourism has brought about numerous positive social impacts in Albania. Interactions between tourists and locals have fostered cultural exchange, promoting understanding and tolerance among different communities. Tourism has also played a pivotal role in the revival and preservation of traditional arts, crafts, and cultural practices, allowing local communities to showcase their heritage. Furthermore, tourism has provided opportunities for the development of hospitality and service-oriented industries, empowering local residents through employment and skill enhancement.
2.3 Environmental Impacts: Tourism in Albania has spurred efforts to conserve and protect its natural resources. The promotion of ecotourism has incentivized the preservation of biodiversity, leading to the establishment of protected areas and national parks. Sustainable tourism practices, such as responsible waste management and eco-friendly infrastructure development, have helped minimize the ecological footprint of the industry. Additionally, environmental preservation has become a priority, as tourists are increasingly attracted to Albania’s pristine landscapes, encouraging the government and local communities to adopt sustainable practices.
- Negative Impacts of Tourism in Albania:
3.1 Economic Impacts: While tourism in Albania has bolstered Albania’s economy, it is not devoid of challenges. The industry’s seasonality can lead to an overreliance on tourism as a primary income source, making local businesses vulnerable to economic downturns during off-peak seasons. Moreover, the influx of tourists can cause price increases in local markets, making it difficult for residents to afford essential goods and services.
3.2 Social Impacts: The rapid growth of tourism in some areas of Albania has led to overcrowding, straining local infrastructure and resources. In popular tourist destinations, there is a risk of cultural commodification and loss of authenticity, as locals may modify their traditions and practices to cater to tourists’ expectations. Additionally, issues such as over tourism and overcrowding can lead to tensions between tourists and locals, potentially resulting in social conflicts.
3.3 Environmental Impacts: Unsustainable tourism practices can pose environmental threats in Albania. Poor waste management and inadequate infrastructure may lead to pollution and degradation of natural resources. The construction of tourist facilities without careful planning and consideration of environmental impact can result in habitat destruction and alteration of ecosystems. Furthermore, increased energy consumption and water usage associated with tourism activities can strain local resources, particularly in ecologically sensitive regions.
The impacts of tourism in Albania are multifaceted, with both positive and negative consequences across social, environmental, and economic dimensions. While tourism has contributed significantly to economic growth, job creation, and cultural exchange, it also presents challenges such as seasonality, overcrowding, and environmental degradation. To maximize the positive impacts and mitigate the negative effects, sustainable tourism practices, including community involvement, environmental conservation, and responsible development, must be prioritized. Such measures will ensure the long-term viability of tourism in Albania while preserving the nation’s natural and cultural heritage for future generations.
Now that we know a bit more about tourism in Albania, lets answer some of the most common questions on this topic:
- Q: Is Albania a safe country for tourists? A: Yes, Albania is generally a safe country for tourists. Like any destination, it’s always important to take common-sense precautions and be aware of your surroundings.
- Q: What are the best places to visit in Albania? A: Albania offers a diverse range of attractions. Some of the top places to visit include the capital city Tirana, the ancient city of Butrint, the Albanian Riviera, Berat’s UNESCO-listed historic center, and Lake Ohrid.
- Q: Do I need a visa to visit Albania? A: The visa requirements vary depending on your nationality. Citizens of many countries, including the United States, European Union member states, and Canada, can enter Albania visa-free for tourism purposes for up to 90 days.
- Q: What is the best time to visit Albania? A: The best time to visit Albania is during the spring (April to June) and autumn (September to October) when the weather is pleasant, and the tourist crowds are relatively smaller. The summer months of July and August are popular but can be quite hot and crowded.
- Q: How is the transportation system in Albania? A: Albania has a developing transportation system. The main cities are well connected by buses and minibuses, and there are domestic flights available. Renting a car is also an option for exploring the country.

- Q: What is the currency used in Albania? A: The official currency of Albania is the Albanian Lek (ALL). Credit cards are accepted in most hotels, restaurants, and larger establishments, but it’s advisable to carry some cash for smaller establishments or rural areas.
- Q: Is English widely spoken in Albania? A: While Albanian is the official language, English is commonly spoken in major tourist areas, hotels, and restaurants. In more remote areas, knowledge of basic Albanian phrases or a phrasebook can be helpful.
- Q: Can I drink tap water in Albania? A: Tap water in Albania is generally safe to drink in larger cities and tourist areas. However, it’s advisable to drink bottled water in remote areas or consult with locals for specific regions.
- Q: Are there any UNESCO World Heritage Sites in Albania? A: Yes, Albania has several UNESCO World Heritage Sites. Some notable examples include the historic centres of Berat and Gjirokastër, Butrint National Park, and the ancient city of Apollonia.
- Q: What are some traditional Albanian dishes I should try? A: Albanian cuisine offers a variety of delicious dishes. Some must-try foods include byrek (savoury pastry), tavë kosi (baked lamb with yoghurt), fërgesë (a meat and pepper stew), and qofte (meatballs). Seafood lovers should try specialties from the coastal regions, such as grilled fish and seafood risotto.
As you can see, tourism Albania is big business! However, it is vital that tourism here is managed effectively to ensure that sustainable tourism principles are adopted.
If you enjoyed this article about tourism in Albania, I am sure you will love these too:
- 20 essential ways to be a sustainable tourist and protect our planet
- 12 fascinating facts about the Dalmatian Coast
- How Many Continents Of The World Are There? + Detailed & Fascinating Facts
- IATA airport codes- list of every airport code in the world!
- 10 fascinating Sheikh Zayed Mosque facts
Liked this article? Click to share!
UN Tourism | Bringing the world closer

share this content
- Share this article on facebook
- Share this article on twitter
- Share this article on linkedin
UN Tourism Launches Tourism Investment Guidelines for Albania
UN Tourism has again placed the focus on tourism investments, bringing together public and private sector leaders in Tirana.
The “Tourism Investments and Economic Development in Europe” conference, jointly organized with Ministry of Tourism and Environment of Albania, was held within the framework of the UN Tourism Regional Commission for Europe. High-level delegates included investors from the hospitality, aviation and real estate industries, alongside private sector stakeholders and various heads of various international organizations.
Participants discussed and explored avenues how to revitalize Europe’s tourism sector through strategic investments, with a focus on long-term resilience and growth in line with the wider Agenda 2030 and Sustainable Development Goals.
“Tourism Doing Business in Albania”
During the conference, UN Tourism launched the latest in its series of “Tourism Doing Business” guidelines, with a new publication focused on Albania. The guidelines provide potential investors with an overview of Albania’s business landscape, its economic resilience and growth potential.
- In 2023 Albania was ranked 4th globally for the largest percentage increase in international tourist arrivals, recording growth of 56% on 2019.
- Albania welcomed 7.5 million international arrivals in 2022, and 10.1 million in 2023.
- The strong robust rebound in tourism contributed to economic growth of nearly 5% growth in 2022. As of 2023, the GDP at current prices reached USD 23 billion compared to USD 12.3 billion in 2012.
- International tourism in Albania constitutes 46% of total exports and 65% of exports in the services sector.
UN Tourism Secretary-General Zurab Pololikashvili says: “Albania presents multifaceted investment opportunities within its tourism sector. With its strategic geographic location, developing infrastructure, and a government dedicated to enhancing foreign direct investment, Albania emerges as an attractive destination for investors. These factors have been instrumental in driving Albania's growth and ongoing development”.
Natalia Bayona, UN Tourism Executive Director says: “The tourism sector in Albania stands as a dynamic and promising landscape, offering a compelling blend of natural beauty, cultural richness, and strategic initiatives shaping its trajectory towards sustainable growth and success. With a surge in greenfield FDI announcements totaling USD 135 million within the tourism cluster, Albania solidifies its position as an attractive investment destination, heralding a promising future ahead”.
Investments and tourism employment growing
The guidelines offer a comprehensive overview of the investment landscape in Albania. Key takeaways include:
- Over the past five years, Albania has consistently attracted foreign direct investment (FDI) at levels surpassing the preceding ten-year average OF EUR 1,004 million. In 2022, the country received EUR 1.372 billion, and between January and September 2023, it received around EUR 1.089 billion.
- As of 2023, Albania registered more than 154 startups in different sectors including financial services, tourism, technology, and innovation.
- The ‘Startup Law’ supports the creation and development of high-growth potential startups in the technology and innovation sector.
Value and Investments strategy
Between 2018 and 2023, four greenfield projects were announced in the tourism cluster for a total of USD 135 million (according to fDi Intelligence Financial Times). Through that Strategic Investment Law, the country has promoted around 21 strategic investment projects related to tourism between 2016 and 2023. These projects, which have either been completed or initiated implementation, represent a total investment of EUR 3.09 billion, generating around 16,900 new jobs.

Tirana, Albania

Related Links:
- Download News Release on PDF
- “Tourism Doing Business: Investing in Albania”
- UN Tourism: 70th Regional Commission for Europe
- “Tourism Investments and Economic Development in Europe” conference
Related Content

UN Tourism and Hotelschool The Hague to Drive Innovatio...

European Committee of the Regions and UN Tourism break ...

UN Tourism and Croatia to Establish Research Centre for...

UN Tourism Members Advance Agenda for Europe as Region ...

IMAGES
COMMENTS
International tourism, number of arrivals - Albania World Tourism Organization, Yearbook of Tourism Statistics, Compendium of Tourism Statistics and data files. License : CC BY-4.0
Tourism in Albania Albania recorded a total of 5.52 million tourists in 2021, ranking 19th in the world in absolute terms. ... By putting the tourist numbers in relation to the population of Albania, the result is much more comparable picture: With 2.0 tourists per resident, Albania ranked 13th in the world. In Southern Europe, it ranked 5th.
Albania had 7.5 million tourists in 2022 but the Institute of Statistics of Albania reports that from January to April, there were 3.54 million visitors, representing a 35 per cent increase.
Tourism covers several activities including tourist services, bars and restaurants, retails trade units, cultural centers, etc. The purpose of the arrivals and departures data for Albanian and foreign citizens, by the means of transport (sea, air, land and border points), is the measurement of some statistical indicators related to tourism.
Albania tourism statistics for 2019 was 2,458,000,000.00, a 6.59% increase from 2018. Albania tourism statistics for 2018 was 2,306,000,000.00, a 12.49% increase from 2017. Albania tourism statistics for 2017 was 2,050,000,000.00, a 12.58% increase from 2016. International tourism receipts are expenditures by international inbound visitors ...
The Institute of Statistics (INSTAT), publishes for the fifth year in a row a special publication on the main indicators on tourism in Albania. Referring to the year 2021, statistics regarding foreign and domestic tourists in Albania, aim to monitor the characteristics and developments of tourism in our country.
Institute of Statistics - Tirana St. Vllazën Huta, Building 35, Entrance 1, Tirana, ZIP Code 1017
Discover data on Tourism Statistics in Albania. Explore expert forecasts and historical data on economic indicators across 195+ countries. ... International Tourism: Number of Arrivals data is updated yearly, averaging 1,273,500.000 Person from Dec 1995 to 2020, with 26 observations. The data reached an all-time high of 6,406,000.000 Person in ...
The UNWTO World Tourism Barometer, a regular tracker of short-term tourism trends providing updated insights into international tourism, has positioned Albania in the third spot globally for the period spanning January to July 2023. ... with 92% of pre-crisis visitor numbers during this seven-month period, while the Americas reached 87%. ...
The value for International tourism, number of arrivals in Albania was 2,658,000 as of 2020. As the graph below shows, over the past 25 years this indicator reached a maximum value of 6,406,000 in 2019 and a minimum value of 119,000 in 1997. Definition: International inbound tourists (overnight visitors) are the number of tourists who travel to ...
This records a decrease from the previous number of 6,406,000.000 Person for 2019. Albania International Tourism: Number of Arrivals data is updated yearly, averaging 1,273,500.000 Person from Dec 1995 to 2020, with 26 observations. The data reached an all-time high of 6,406,000.000 Person in 2019 and a record low of 119,000.000 Person in 1997.
Tourism in Albania has been a key element to the country's economic activity and is constantly developing. ... Lonely Planet ranked Albania as the number 1 destination to be visited in 2011. The New York Times ranked Albania 4th among 52 destinations to be visited in 2014.
December 20, 2022. In the second half of 2022, UNDP in cooperation with the Albanian Tourism Association conducted a study to assess the impact of the war in Ukraine on the tourism sector. The main goal was to collect and analyze data on hospitality and tourism focusing on the main actors from the supply and demand side. In addition to data ...
The number of domestic tourists also increased from 259,835 in January 2022 to 456,239 in 2023. In 2022, some 7.5 million people visited Albania, an increase of over 32% from the year before.
Albania eyes tourist boom. Tim Gosling. 03/15/2023. Albania seeks to scrub stereotypes of poverty, criminality and blood feuds to persuade tourists to visit. But can it exploit its natural and ...
In a striking example, Albania has shown how the tourism sector can drive economic development. Following the country's turbulent economic and political transition in the 1990s, tourism was perched on the sidelines of the Albanian economy. Over the last two decades, however, the contribution of the Albania's tourism and travel sector to the country's (GDP has been increased and reached ...
The number of tourists arriving in Albania for personal purposes increased between 2010 and 2019. In 2021, approximately 2.6 million people visited Albania on vacation or for other recreational ...
Albania Visitor Arrivals data is updated quarterly, available from Mar 2005 to Dec 2023. The data reached an all-time high of 4,661,112 person in Sep 2023 and a record low of 75,438 person in Mar 2005. CEIC calculates quarterly Tourist Arrivals by subtracting Transit Visitors from Total Visitors. The Institute of Statistics provides Total ...
Editor's Picks. Gross domestic product (GDP) per capita in Albania 2028. Total population of Albania 2028. Age structure in Albania 2012-2022. Find the most relevant statistics and facts about ...
The Travel & Tourism market in in Albania is projected to grow by 4.56% (2024-2028) resulting in a market volume of US$90.23m in 2028. ... To estimate the number of users and bookings, we ...
The 9 best places to visit in Albania. Nov 18, 2023 • 7 min read. Albania is slowly becoming the jewel of the Balkans due to its crystal waters, impressive mountains, and affordability for all types of travelers.
Tourist Arrivals in Albania decreased to 1861040 in the fourth quarter of 2023 from 4897668 in the third quarter of 2023. This page provides - Albania Tourist Arrivals- actual values, historical data, forecast, chart, statistics, economic calendar and news.
Now lets take a look at some statistics that emphasise the scale of tourism in Albania: International Tourist Arrivals: In 2021, Albania received approximately 4.5 million international tourist arrivals. Tourism Revenue: The tourism sector in Albania generated approximately 1.5 billion euros in revenue in 2021.
Albania welcomed 7.5 million international arrivals in 2022, and 10.1 million in 2023. The strong robust rebound in tourism contributed to economic growth of nearly 5% growth in 2022. As of 2023, the GDP at current prices reached USD 23 billion compared to USD 12.3 billion in 2012. International tourism in Albania constitutes 46% of total ...