

Family Life

AAP Schedule of Well-Child Care Visits

Parents know who they should go to when their child is sick. But pediatrician visits are just as important for healthy children.
The Bright Futures /American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) developed a set of comprehensive health guidelines for well-child care, known as the " periodicity schedule ." It is a schedule of screenings and assessments recommended at each well-child visit from infancy through adolescence.
Schedule of well-child visits
- The first week visit (3 to 5 days old)
- 1 month old
- 2 months old
- 4 months old
- 6 months old
- 9 months old
- 12 months old
- 15 months old
- 18 months old
- 2 years old (24 months)
- 2 ½ years old (30 months)
- 3 years old
- 4 years old
- 5 years old
- 6 years old
- 7 years old
- 8 years old
- 9 years old
- 10 years old
- 11 years old
- 12 years old
- 13 years old
- 14 years old
- 15 years old
- 16 years old
- 17 years old
- 18 years old
- 19 years old
- 20 years old
- 21 years old
The benefits of well-child visits
Prevention . Your child gets scheduled immunizations to prevent illness. You also can ask your pediatrician about nutrition and safety in the home and at school.
Tracking growth & development . See how much your child has grown in the time since your last visit, and talk with your doctor about your child's development. You can discuss your child's milestones, social behaviors and learning.
Raising any concerns . Make a list of topics you want to talk about with your child's pediatrician such as development, behavior, sleep, eating or getting along with other family members. Bring your top three to five questions or concerns with you to talk with your pediatrician at the start of the visit.
Team approach . Regular visits create strong, trustworthy relationships among pediatrician, parent and child. The AAP recommends well-child visits as a way for pediatricians and parents to serve the needs of children. This team approach helps develop optimal physical, mental and social health of a child.
More information
Back to School, Back to Doctor
Recommended Immunization Schedules
Milestones Matter: 10 to Watch for by Age 5
Your Child's Checkups
- Bright Futures/AAP Recommendations for Preventive Pediatric Health Care (periodicity schedule)
Catch Up on Well-Child Visits and Recommended Vaccinations

Many children missed check-ups and recommended childhood vaccinations over the past few years. CDC and the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) recommend children catch up on routine childhood vaccinations and get back on track for school, childcare, and beyond.

Making sure that your child sees their doctor for well-child visits and recommended vaccines is one of the best things you can do to protect your child and community from serious diseases that are easily spread.
Well-Child Visits and Recommended Vaccinations Are Essential

Well-child visits and recommended vaccinations are essential and help make sure children stay healthy. Children who are not protected by vaccines are more likely to get diseases like measles and whooping cough . These diseases are extremely contagious and can be very serious, especially for babies and young children. In recent years, there have been outbreaks of these diseases, especially in communities with low vaccination rates.
Well-child visits are essential for many reasons , including:
- Tracking growth and developmental milestones
- Discussing any concerns about your child’s health
- Getting scheduled vaccinations to prevent illnesses like measles and whooping cough (pertussis) and other serious diseases

It’s particularly important for parents to work with their child’s doctor or nurse to make sure they get caught up on missed well-child visits and recommended vaccines.
Routinely Recommended Vaccines for Children and Adolescents
Getting children and adolescents caught up with recommended vaccinations is the best way to protect them from a variety of vaccine-preventable diseases . The schedules below outline the vaccines recommended for each age group.
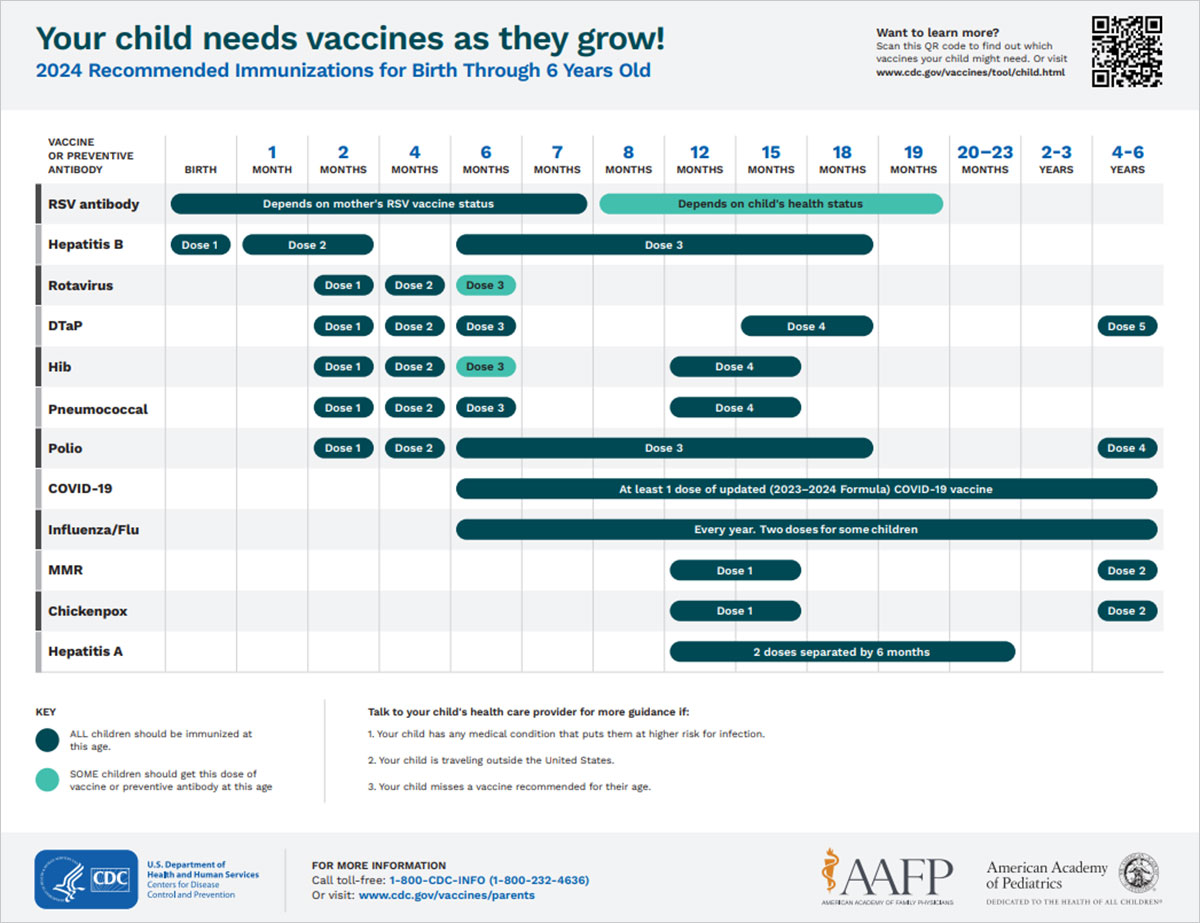
See which vaccines your child needs from birth through age 6 in this easy-to-read immunization schedule.
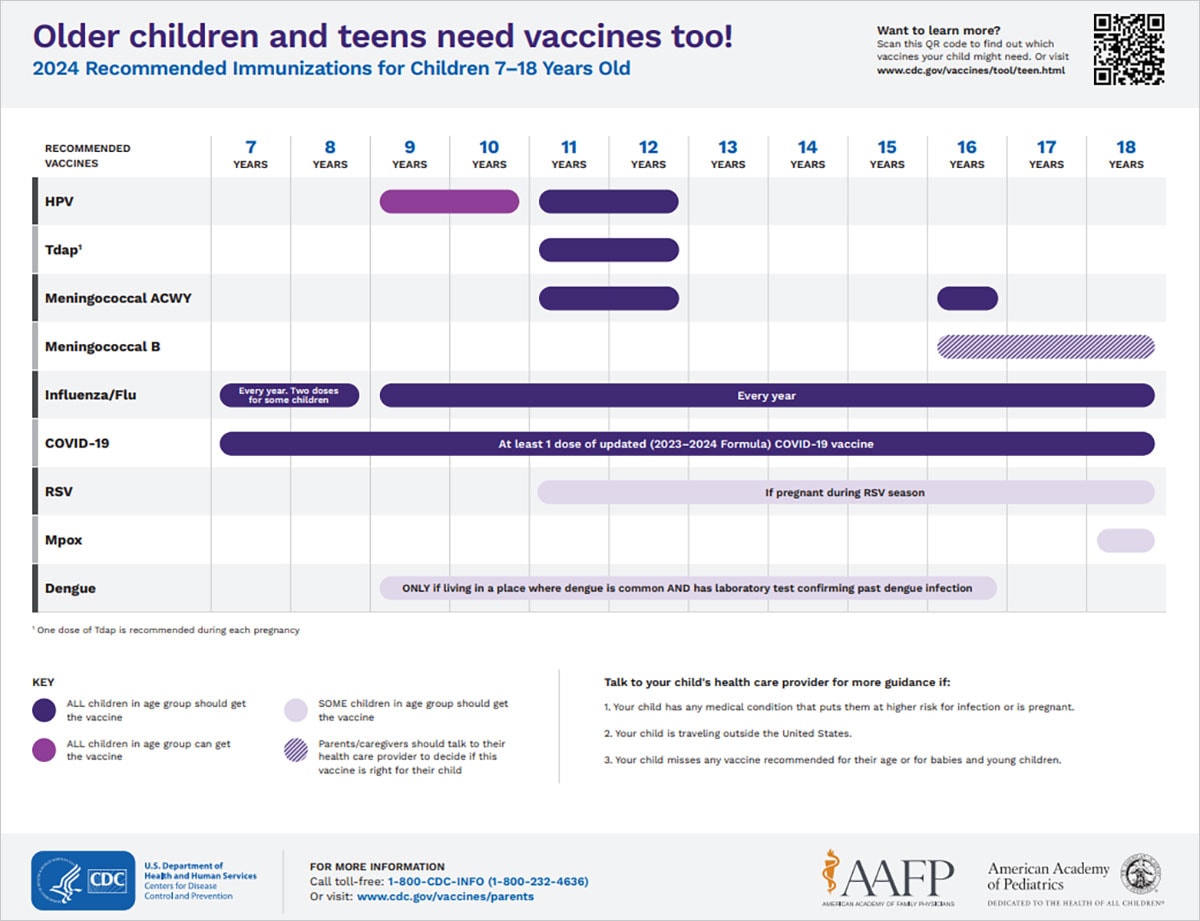
See which vaccines your child needs from ages 7 through 18 in this easy-to-read immunization schedule.
The Vaccines for Children (VFC) program provides vaccines to eligible children at no cost. This program provides free vaccines to children who are Medicaid-eligible, uninsured, underinsured, or American Indian/Alaska Native. Check out the program’s requirements and talk to your child’s doctor or nurse to see if they are a VFC provider. You can also find a VFC provider by calling your state or local health department or seeing if your state has a VFC website.
COVID-19 Vaccines for Children and Teens
Everyone aged 6 months and older can get an updated COVID-19 vaccine to help protect against severe illness, hospitalization and death. Learn more about making sure your child stays up to date with their COVID-19 vaccines .
- Vaccines & Immunizations
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.

KATHERINE TURNER, MD
Am Fam Physician. 2018;98(6):347-353
Related letter: Well-Child Visits Provide Physicians Opportunity to Deliver Interconception Care to Mothers
Author disclosure: No relevant financial affiliations.
The well-child visit allows for comprehensive assessment of a child and the opportunity for further evaluation if abnormalities are detected. A complete history during the well-child visit includes information about birth history; prior screenings; diet; sleep; dental care; and medical, surgical, family, and social histories. A head-to-toe examination should be performed, including a review of growth. Immunizations should be reviewed and updated as appropriate. Screening for postpartum depression in mothers of infants up to six months of age is recommended. Based on expert opinion, the American Academy of Pediatrics recommends developmental surveillance at each visit, with formal developmental screening at nine, 18, and 30 months and autism-specific screening at 18 and 24 months; the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force found insufficient evidence to make a recommendation. Well-child visits provide the opportunity to answer parents' or caregivers' questions and to provide age-appropriate guidance. Car seats should remain rear facing until two years of age or until the height or weight limit for the seat is reached. Fluoride use, limiting or avoiding juice, and weaning to a cup by 12 months of age may improve dental health. A one-time vision screening between three and five years of age is recommended by the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force to detect amblyopia. The American Academy of Pediatrics guideline based on expert opinion recommends that screen time be avoided, with the exception of video chatting, in children younger than 18 months and limited to one hour per day for children two to five years of age. Cessation of breastfeeding before six months and transition to solid foods before six months are associated with childhood obesity. Juice and sugar-sweetened beverages should be avoided before one year of age and provided only in limited quantities for children older than one year.
Well-child visits for infants and young children (up to five years) provide opportunities for physicians to screen for medical problems (including psychosocial concerns), to provide anticipatory guidance, and to promote good health. The visits also allow the family physician to establish a relationship with the parents or caregivers. This article reviews the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) and the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) guidelines for screenings and recommendations for infants and young children. Family physicians should prioritize interventions with the strongest evidence for patient-oriented outcomes, such as immunizations, postpartum depression screening, and vision screening.
Clinical Examination
The history should include a brief review of birth history; prematurity can be associated with complex medical conditions. 1 Evaluate breastfed infants for any feeding problems, 2 and assess formula-fed infants for type and quantity of iron-fortified formula being given. 3 For children eating solid foods, feeding history should include everything the child eats and drinks. Sleep, urination, defecation, nutrition, dental care, and child safety should be reviewed. Medical, surgical, family, and social histories should be reviewed and updated. For newborns, review the results of all newborn screening tests ( Table 1 4 – 7 ) and schedule follow-up visits as necessary. 2
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
A comprehensive head-to-toe examination should be completed at each well-child visit. Interval growth should be reviewed by using appropriate age, sex, and gestational age growth charts for height, weight, head circumference, and body mass index if 24 months or older. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)-recommended growth charts can be found at https://www.cdc.gov/growthcharts/who_charts.htm#The%20WHO%20Growth%20Charts . Percentiles and observations of changes along the chart's curve should be assessed at every visit. Include assessment of parent/caregiver-child interactions and potential signs of abuse such as bruises on uncommonly injured areas, burns, human bite marks, bruises on nonmobile infants, or multiple injuries at different healing stages. 8
The USPSTF and AAP screening recommendations are outlined in Table 2 . 3 , 9 – 27 A summary of AAP recommendations can be found at https://www.aap.org/en-us/Documents/periodicity_schedule.pdf . The American Academy of Family Physicians (AAFP) generally adheres to USPSTF recommendations. 28
MATERNAL DEPRESSION
Prevalence of postpartum depression is around 12%, 22 and its presence can impair infant development. The USPSTF and AAP recommend using the Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale (available at https://www.aafp.org/afp/2010/1015/p926.html#afp20101015p926-f1 ) or the Patient Health Questionnaire-2 (available at https://www.aafp.org/afp/2012/0115/p139.html#afp20120115p139-t3 ) to screen for maternal depression. The USPSTF does not specify a screening schedule; however, based on expert opinion, the AAP recommends screening mothers at the one-, two-, four-, and six-month well-child visits, with further evaluation for positive results. 23 There are no recommendations to screen other caregivers if the mother is not present at the well-child visit.
PSYCHOSOCIAL
With nearly one-half of children in the United States living at or near the poverty level, assessing home safety, food security, and access to safe drinking water can improve awareness of psychosocial problems, with referrals to appropriate agencies for those with positive results. 29 The prevalence of mental health disorders (i.e., primarily anxiety, depression, behavioral disorders, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder) in preschool-aged children is around 6%. 30 Risk factors for these disorders include having a lower socioeconomic status, being a member of an ethnic minority, and having a non–English-speaking parent or primary caregiver. 25 The USPSTF found insufficient evidence regarding screening for depression in children up to 11 years of age. 24 Based on expert opinion, the AAP recommends that physicians consider screening, although screening in young children has not been validated or standardized. 25
DEVELOPMENT AND SURVEILLANCE
Based on expert opinion, the AAP recommends early identification of developmental delays 14 and autism 10 ; however, the USPSTF found insufficient evidence to recommend formal developmental screening 13 or autism-specific screening 9 if the parents/caregivers or physician have no concerns. If physicians choose to screen, developmental surveillance of language, communication, gross and fine movements, social/emotional development, and cognitive/problem-solving skills should occur at each visit by eliciting parental or caregiver concerns, obtaining interval developmental history, and observing the child. Any area of concern should be evaluated with a formal developmental screening tool, such as Ages and Stages Questionnaire, Parents' Evaluation of Developmental Status, Parents' Evaluation of Developmental Status-Developmental Milestones, or Survey of Well-Being of Young Children. These tools can be found at https://www.aap.org/en-us/advocacy-and-policy/aap-health-initiatives/Screening/Pages/Screening-Tools.aspx . If results are abnormal, consider intervention or referral to early intervention services. The AAP recommends completing the previously mentioned formal screening tools at nine-, 18-, and 30-month well-child visits. 14
The AAP also recommends autism-specific screening at 18 and 24 months. 10 The USPSTF recommends using the two-step Modified Checklist for Autism in Toddlers (M-CHAT) screening tool (available at https://m-chat.org/ ) if a physician chooses to screen a patient for autism. 10 The M-CHAT can be incorporated into the electronic medical record, with the possibility of the parent or caregiver completing the questionnaire through the patient portal before the office visit.
IRON DEFICIENCY
Multiple reports have associated iron deficiency with impaired neurodevelopment. Therefore, it is essential to ensure adequate iron intake. Based on expert opinion, the AAP recommends supplements for preterm infants beginning at one month of age and exclusively breastfed term infants at six months of age. 3 The USPSTF found insufficient evidence to recommend screening for iron deficiency in infants. 19 Based on expert opinion, the AAP recommends measuring a child's hemoglobin level at 12 months of age. 3
Lead poisoning and elevated lead blood levels are prevalent in young children. The AAP and CDC recommend a targeted screening approach. The AAP recommends screening for serum lead levels between six months and six years in high-risk children; high-risk children are identified by location-specific risk recommendations, enrollment in Medicaid, being foreign born, or personal screening. 21 The USPSTF does not recommend screening for lead poisoning in children at average risk who are asymptomatic. 20
The USPSTF recommends at least one vision screening to detect amblyopia between three and five years of age. Testing options include visual acuity, ocular alignment test, stereoacuity test, photoscreening, and autorefractors. The USPSTF found insufficient evidence to recommend screening before three years of age. 26 The AAP, American Academy of Ophthalmology, and the American Academy of Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus recommend the use of an instrument-based screening (photoscreening or autorefractors) between 12 months and three years of age and annual visual acuity screening beginning at four years of age. 31
IMMUNIZATIONS
The AAFP recommends that all children be immunized. 32 Recommended vaccination schedules, endorsed by the AAP, the AAFP, and the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices, are found at https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/schedules/hcp/child-adolescent.html . Immunizations are usually administered at the two-, four-, six-, 12-, and 15- to 18-month well-child visits; the four- to six-year well-child visit; and annually during influenza season. Additional vaccinations may be necessary based on medical history. 33 Immunization history should be reviewed at each wellness visit.
Anticipatory Guidance
Injuries remain the leading cause of death among children, 34 and the AAP has made several recommendations to decrease the risk of injuries. 35 – 42 Appropriate use of child restraints minimizes morbidity and mortality associated with motor vehicle collisions. Infants need a rear-facing car safety seat until two years of age or until they reach the height or weight limit for the specific car seat. Children should then switch to a forward-facing car seat for as long as the seat allows, usually 65 to 80 lb (30 to 36 kg). 35 Children should never be unsupervised around cars, driveways, and streets. Young children should wear bicycle helmets while riding tricycles or bicycles. 37
Having functioning smoke detectors and an escape plan decreases the risk of fire- and smoke-related deaths. 36 Water heaters should be set to a maximum of 120°F (49°C) to prevent scald burns. 37 Infants and young children should be watched closely around any body of water, including water in bathtubs and toilets, to prevent drowning. Swimming pools and spas should be completely fenced with a self-closing, self-latching gate. 38
Infants should not be left alone on any high surface, and stairs should be secured by gates. 43 Infant walkers should be discouraged because they provide no benefit and they increase falls down stairs, even if stair gates are installed. 39 Window locks, screens, or limited-opening windows decrease injury and death from falling. 40 Parents or caregivers should also anchor furniture to a wall to prevent heavy pieces from toppling over. Firearms should be kept unloaded and locked. 41
Young children should be closely supervised at all times. Small objects are a choking hazard, especially for children younger than three years. Latex balloons, round objects, and food can cause life-threatening airway obstruction. 42 Long strings and cords can strangle children. 37
DENTAL CARE
Infants should never have a bottle in bed, and babies should be weaned to a cup by 12 months of age. 44 Juices should be avoided in infants younger than 12 months. 45 Fluoride use inhibits tooth demineralization and bacterial enzymes and also enhances remineralization. 11 The AAP and USPSTF recommend fluoride supplementation and the application of fluoride varnish for teeth if the water supply is insufficient. 11 , 12 Begin brushing teeth at tooth eruption with parents or caregivers supervising brushing until mastery. Children should visit a dentist regularly, and an assessment of dental health should occur at well-child visits. 44
SCREEN TIME
Hands-on exploration of their environment is essential to development in children younger than two years. Video chatting is acceptable for children younger than 18 months; otherwise digital media should be avoided. Parents and caregivers may use educational programs and applications with children 18 to 24 months of age. If screen time is used for children two to five years of age, the AAP recommends a maximum of one hour per day that occurs at least one hour before bedtime. Longer usage can cause sleep problems and increases the risk of obesity and social-emotional delays. 46
To decrease the risk of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS), the AAP recommends that infants sleep on their backs on a firm mattress for the first year of life with no blankets or other soft objects in the crib. 45 Breastfeeding, pacifier use, and room sharing without bed sharing protect against SIDS; infant exposure to tobacco, alcohol, drugs, and sleeping in bed with parents or caregivers increases the risk of SIDS. 47
DIET AND ACTIVITY
The USPSTF, AAFP, and AAP all recommend breastfeeding until at least six months of age and ideally for the first 12 months. 48 Vitamin D 400 IU supplementation for the first year of life in exclusively breastfed infants is recommended to prevent vitamin D deficiency and rickets. 49 Based on expert opinion, the AAP recommends the introduction of certain foods at specific ages. Early transition to solid foods before six months is associated with higher consumption of fatty and sugary foods 50 and an increased risk of atopic disease. 51 Delayed transition to cow's milk until 12 months of age decreases the incidence of iron deficiency. 52 Introduction of highly allergenic foods, such as peanut-based foods and eggs, before one year decreases the likelihood that a child will develop food allergies. 53
With approximately 17% of children being obese, many strategies for obesity prevention have been proposed. 54 The USPSTF does not have a recommendation for screening or interventions to prevent obesity in children younger than six years. 54 The AAP has made several recommendations based on expert opinion to prevent obesity. Cessation of breastfeeding before six months and introduction of solid foods before six months are associated with childhood obesity and are not recommended. 55 Drinking juice should be avoided before one year of age, and, if given to older children, only 100% fruit juice should be provided in limited quantities: 4 ounces per day from one to three years of age and 4 to 6 ounces per day from four to six years of age. Intake of other sugar-sweetened beverages should be discouraged to help prevent obesity. 45 The AAFP and AAP recommend that children participate in at least 60 minutes of active free play per day. 55 , 56
Data Sources: Literature search was performed using the USPSTF published recommendations ( https://www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/BrowseRec/Index/browse-recommendations ) and the AAP Periodicity table ( https://www.aap.org/en-us/Documents/periodicity_schedule.pdf ). PubMed searches were completed using the key terms pediatric, obesity prevention, and allergy prevention with search limits of infant less than 23 months or pediatric less than 18 years. The searches included systematic reviews, randomized controlled trials, clinical trials, and position statements. Essential Evidence Plus was also reviewed. Search dates: May through October 2017.
Gauer RL, Burket J, Horowitz E. Common questions about outpatient care of premature infants. Am Fam Physician. 2014;90(4):244-251.
American Academy of Pediatrics; Committee on Fetus and Newborn. Hospital stay for healthy term newborns. Pediatrics. 2010;125(2):405-409.
Baker RD, Greer FR Committee on Nutrition, American Academy of Pediatrics. Diagnosis and prevention of iron deficiency and iron-deficiency anemia in infants and young children (0–3 years of age). Pediatrics. 2010;126(5):1040-1050.
Mahle WT, Martin GR, Beekman RH, Morrow WR Section on Cardiology and Cardiac Surgery Executive Committee. Endorsement of Health and Human Services recommendation for pulse oximetry screening for critical congenital heart disease. Pediatrics. 2012;129(1):190-192.
American Academy of Pediatrics Newborn Screening Authoring Committee. Newborn screening expands: recommendations for pediatricians and medical homes—implications for the system. Pediatrics. 2008;121(1):192-217.
American Academy of Pediatrics, Joint Committee on Infant Hearing. Year 2007 position statement: principles and guidelines for early hearing detection and intervention programs. Pediatrics. 2007;120(4):898-921.
Maisels MJ, Bhutani VK, Bogen D, Newman TB, Stark AR, Watchko JF. Hyperbilirubinemia in the newborn infant > or = 35 weeks' gestation: an update with clarifications. Pediatrics. 2009;124(4):1193-1198.
Christian CW Committee on Child Abuse and Neglect, American Academy of Pediatrics. The evaluation of suspected child physical abuse [published correction appears in Pediatrics . 2015;136(3):583]. Pediatrics. 2015;135(5):e1337-e1354.
Siu AL, Bibbins-Domingo K, Grossman DC, et al. Screening for autism spectrum disorder in young children: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2016;315(7):691-696.
Johnson CP, Myers SM American Academy of Pediatrics Council on Children with Disabilities. Identification and evaluation of children with autism spectrum disorders. Pediatrics. 2007;120(5):1183-1215.
Moyer VA. Prevention of dental caries in children from birth through age 5 years: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Pediatrics. 2014;133(6):1102-1111.
Clark MB, Slayton RL American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Oral Health. Fluoride use in caries prevention in the primary care setting. Pediatrics. 2014;134(3):626-633.
Siu AL. Screening for speech and language delay and disorders in children aged 5 years and younger: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Pediatrics. 2015;136(2):e474-e481.
Council on Children with Disabilities, Section on Developmental Behavioral Pediatrics, Bright Futures Steering Committee, Medical Home Initiatives for Children with Special Needs Project Advisory Committee. Identifying infants and young children with developmental disorders in the medical home: an algorithm for developmental surveillance and screening [published correction appears in Pediatrics . 2006;118(4):1808–1809]. Pediatrics. 2006;118(1):405-420.
Bibbins-Domingo K, Grossman DC, Curry SJ, et al. Screening for lipid disorders in children and adolescents: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2016;316(6):625-633.
National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Expert panel on integrated guidelines for cardiovascular health and risk reduction in children and adolescents. October 2012. https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/sites/default/files/media/docs/peds_guidelines_full.pdf . Accessed May 9, 2018.
Moyer VA. Screening for primary hypertension in children and adolescents: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Ann Intern Med. 2013;159(9):613-619.
Flynn JT, Kaelber DC, Baker-Smith CM, et al. Clinical practice guideline for screening and management of high blood pressure in children and adolescents [published correction appears in Pediatrics . 2017;140(6):e20173035]. Pediatrics. 2017;140(3):e20171904.
Siu AL. Screening for iron deficiency anemia in young children: USPSTF recommendation statement. Pediatrics. 2015;136(4):746-752.
U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for elevated blood lead levels in children and pregnant women. Pediatrics. 2006;118(6):2514-2518.
Screening Young Children for Lead Poisoning: Guidance for State and Local Public Health Officials . Atlanta, Ga.: U.S. Public Health Service; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; National Center for Environmental Health; 1997.
O'Connor E, Rossom RC, Henninger M, Groom HC, Burda BU. Primary care screening for and treatment of depression in pregnant and post-partum women: evidence report and systematic review for the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2016;315(4):388-406.
Earls MF Committee on Psychosocial Aspects of Child and Family Health, American Academy of Pediatrics. Incorporating recognition and management of perinatal and postpartum depression into pediatric practice. Pediatrics. 2010;126(5):1032-1039.
Siu AL. Screening for depression in children and adolescents: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Ann Intern Med. 2016;164(5):360-366.
Weitzman C, Wegner L American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics; Committee on Psychosocial Aspects of Child and Family Health; Council on Early Childhood; Society for Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics; American Academy of Pediatrics. Promoting optimal development: screening for behavioral and emotional problems [published correction appears in Pediatrics . 2015;135(5):946]. Pediatrics. 2015;135(2):384-395.
Grossman DC, Curry SJ, Owens DK, et al. Vision screening in children aged 6 months to 5 years: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2017;318(9):836-844.
Donahue SP, Nixon CN Committee on Practice and Ambulatory Medicine, Section on Ophthalmology, American Academy of Pediatrics; American Association of Certified Orthoptists, American Association for Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus, American Academy of Ophthalmology. Visual system assessment in infants, children, and young adults by pediatricians. Pediatrics. 2016;137(1):28-30.
Lin KW. What to do at well-child visits: the AAFP's perspective. Am Fam Physician. 2015;91(6):362-364.
American Academy of Pediatrics Council on Community Pediatrics. Poverty and child health in the United States. Pediatrics. 2016;137(4):e20160339.
Lavigne JV, Lebailly SA, Hopkins J, Gouze KR, Binns HJ. The prevalence of ADHD, ODD, depression, and anxiety in a community sample of 4-year-olds. J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol. 2009;38(3):315-328.
American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Practice and Ambulatory Medicine, Section on Ophthalmology, American Association of Certified Orthoptists, American Association for Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus, American Academy of Ophthalmology. Visual system assessment of infants, children, and young adults by pediatricians. Pediatrics. 2016;137(1):28-30.
American Academy of Family Physicians. Clinical preventive service recommendation. Immunizations. http://www.aafp.org/patient-care/clinical-recommendations/all/immunizations.html . Accessed October 5, 2017.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Recommended immunization schedule for children and adolescents aged 18 years or younger, United States, 2018. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/schedules/hcp/child-adolescent.html . Accessed May 9, 2018.
National Center for Injury Prevention and Control. 10 leading causes of death by age group, United States—2015. https://www.cdc.gov/injury/images/lc-charts/leading_causes_of_death_age_group_2015_1050w740h.gif . Accessed April 24, 2017.
Durbin DR American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Injury, Violence, and Poison Prevention. Child passenger safety. Pediatrics. 2011;127(4):788-793.
American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Injury and Poison Prevention. Reducing the number of deaths and injuries from residential fires. Pediatrics. 2000;105(6):1355-1357.
Gardner HG American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Injury, Violence, and Poison Prevention. Office-based counseling for unintentional injury prevention. Pediatrics. 2007;119(1):202-206.
American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Injury, Violence, and Poison Prevention. Prevention of drowning in infants, children, and adolescents. Pediatrics. 2003;112(2):437-439.
American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Injury and Poison Prevention. Injuries associated with infant walkers. Pediatrics. 2001;108(3):790-792.
American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Injury and Poison Prevention. Falls from heights: windows, roofs, and balconies. Pediatrics. 2001;107(5):1188-1191.
Dowd MD, Sege RD Council on Injury, Violence, and Poison Prevention Executive Committee; American Academy of Pediatrics. Firearm-related injuries affecting the pediatric population. Pediatrics. 2012;130(5):e1416-e1423.
American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Injury, Violence, and Poison Prevention. Prevention of choking among children. Pediatrics. 2010;125(3):601-607.
Kendrick D, Young B, Mason-Jones AJ, et al. Home safety education and provision of safety equipment for injury prevention (review). Evid Based Child Health. 2013;8(3):761-939.
American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Oral Health. Maintaining and improving the oral health of young children. Pediatrics. 2014;134(6):1224-1229.
Heyman MB, Abrams SA American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition Committee on Nutrition. Fruit juice in infants, children, and adolescents: current recommendations. Pediatrics. 2017;139(6):e20170967.
Council on Communications and Media. Media and young minds. Pediatrics. 2016;138(5):e20162591.
Moon RY Task Force on Sudden Infant Death Syndrome. SIDS and other sleep-related infant deaths: evidence base for 2016 updated recommendations for a safe infant sleeping environment. Pediatrics. 2016;138(5):e20162940.
American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Breastfeeding. Breastfeeding and the use of human milk. Pediatrics. 2012;129(3):e827-e841.
Wagner CL, Greer FR American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Breastfeeding; Committee on Nutrition. Prevention of rickets and vitamin D deficiency in infants, children, and adolescents [published correction appears in Pediatrics . 2009;123(1):197]. Pediatrics. 2008;122(5):1142-1152.
Huh SY, Rifas-Shiman SL, Taveras EM, Oken E, Gillman MW. Timing of solid food introduction and risk of obesity in preschool-aged children. Pediatrics. 2011;127(3):e544-e551.
Greer FR, Sicherer SH, Burks AW American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Nutrition; Section on Allergy and Immunology. Effects of early nutritional interventions on the development of atopic disease in infants and children: the role of maternal dietary restriction, breastfeeding, timing of introduction of complementary foods, and hydrolyzed formulas. Pediatrics. 2008;121(1):183-191.
American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Nutrition. The use of whole cow's milk in infancy. Pediatrics. 1992;89(6 pt 1):1105-1109.
Fleischer DM, Spergel JM, Assa'ad AH, Pongracic JA. Primary prevention of allergic disease through nutritional interventions. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2013;1(1):29-36.
Grossman DC, Bibbins-Domingo K, Curry SJ, et al. Screening for obesity in children and adolescents: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2017;317(23):2417-2426.
Daniels SR, Hassink SG Committee on Nutrition. The role of the pediatrician in primary prevention of obesity. Pediatrics. 2015;136(1):e275-e292.
American Academy of Family Physicians. Physical activity in children. https://www.aafp.org/about/policies/all/physical-activity.html . Accessed January 1, 2018.
Continue Reading

More in AFP
More in pubmed.
Copyright © 2018 by the American Academy of Family Physicians.
This content is owned by the AAFP. A person viewing it online may make one printout of the material and may use that printout only for his or her personal, non-commercial reference. This material may not otherwise be downloaded, copied, printed, stored, transmitted or reproduced in any medium, whether now known or later invented, except as authorized in writing by the AAFP. See permissions for copyright questions and/or permission requests.
Copyright © 2024 American Academy of Family Physicians. All Rights Reserved.
- For Parents
- For Educators
- Sitio para padres
- Parents Home
- General Health
- Growth & Development
- Diseases & Conditions
- Pregnancy & Baby
- Nutrition & Fitness
- Emotions & Behavior
- School & Family Life
- First Aid & Safety
- Doctors & Hospitals
- Expert Answers (Q&A)
- All Categories
- All Wellness Centers

- Sitio para niños
- How the Body Works
- Puberty & Growing Up
- Staying Healthy
- Staying Safe
- Health Problems
- Illnesses & Injuries
- Relax & Unwind
- People, Places & Things That Help

- Sitio para adolescentes
- Sexual Health
- Food & Fitness
- Drugs & Alcohol
- School & Jobs

Well-Child Visit Schedule
- Larger text size Large text size Regular text size
Our well-child visit schedule for checkups lets you know how often kids should see a doctor, even when they're not sick. Read the articles below to find out what to expect at your child's next wellness checkup!
- Well-Child Visit: Newborn
- Well-Child Visit: 3-5 Days
- Well-Child Visit: 1 Month
- Well-Child Visit: 2 Months
- Well-Child Visit: 4 Months
- Well-Child Visit: 6 Months
- Well-Child Visit: 9 Months
- Well-Child Visit: 1 Year (12 Months)
- Well-Child Visit: 15 Months
- Well-Child Visit: 1.5 Years (18 Months)
- Well-Child Visit: 2 Years (24 Months)
- Well-Child Visit: 2.5 Years (30 Months)
- Well-Child Visit: 3 Years
- Well-Child Visit: 4 Years
- Well-Child Visit: 5 Years
- Well-Child Visit: 6 Years
- Well-Child Visit: 7 Years
- Well-Child Visit: 8 Years
- Well-Child Visit: 9 Years
- Well-Child Visit: 10 Years
- Well-Child Visit: 11 Years
- Well-Child Visit: 12 Years
- Well-Child Visit: 13 Years
- Well-Child Visit: 14 Years
- Well-Child Visit: 15 Years
- Well-Child Visit: 16 Years
- Well-Child Visit: 17 Years
- Well-Child Visit: 18 Years
- Well-Child Visit: 19 Years
- Well-Child Visit: 20 Years
- Well-Child Visit: 21 Years
When Is My Child’s Next Well Visit and Why Are These Visits Important?
Jun. 15, 2023 • 5 min read

Summer is just about to get started. Swimming, warmth & sunshine, and making new memories are on everyone’s minds.
Before the new school year begins in September, Rochester Regional Health Pediatric and Family Medicine providers are encouraging families to schedule their well child visits.
Calendars fill up quickly – for families and doctor’s offices alike – so putting that appointment on the schedule early will lessen the stress on children, parents, and providers.
Steven Schulz, MD , is the Rochester Regional Health Primary Care Institute Pediatric Medical Director, and shares about the benefits of well visits for children, and how often to schedule well visits as they grow up.
Why well visits matter for children
As routine check-ups, child well visits play a crucial role in safeguarding the health and well-being of your child.
During a well visit, your child’s healthcare provider is able to assess their overall health and development through physical examinations, growth measurements, and developmental screenings. This helps to identify any potential concerns or issues at an early stage.
Immunizations protect children against potentially harmful diseases, and receiving them at the recommended age helps to keep your child safe – as well as those around them. Well child visits help to keep children on track for those vaccines.
Regular check-ups allow healthcare providers to monitor growth, identify developmental delays, and detect early signs of any underlying health conditions for a child. If a potential intervention can happen earlier for a child, the chances of better outcomes and interventions are higher for the child.
“Every child is different in so many ways,” Dr. Schulz said. “Being able to ask specific questions about your child’s physical, emotional, or social health and development is invaluable for the development and safety of your child.”
Recommended schedule for child visits
From the day a child is born until they become an adult, the number of times they have check-ups with healthcare providers each year varies. It can get confusing trying to remember how many appointments a child might have in a given year, especially with multiple children.
Birth-1 year
Babies usually visit their pediatrician six times before their first birthday, according to the Department of Health and Human Services. The first visit is about 3-5 days old to make sure they are progressing well. After that initial appointment, well visits are scheduled for the following ages:
Since the bodies and minds of young children are developing so rapidly, seeing a pediatrician is important to ensure they are meeting all of the appropriate cognitive, social, emotional, behavioral, and speech development milestones.
The ages for these well visit appointments are:
The CDC lists the most common developmental milestones and the ages at which they are likely to happen.
RELATED: Recognizing Early Signs of Developmental Delays -->
Once a child reaches the age of 5, they are typically seen once a year for a well visit until they reach adulthood. These visits are a good check-in with the child’s pediatrician and a chance to discuss any important health topics and receive guidance from professionals.
Parents can ask about a wide range of issues or concerns, such as nutrition, emotional health and well-being, behavior management, sleep, screen time, and more. Since pediatricians see your child grow and develop over the years, they have a unique perspective about your child's specific age and developmental stages.
“Especially ahead of the upcoming school year, we want to make sure both families and healthcare providers aren’t waiting until the last minute to set up a well visit,” Dr. Schulz said. “Contact your pediatrician’s office and make sure your child’s next visit is already on the calendar.”
At Rochester Regional Health, our providers are constantly keeping your best health in mind. With primary care locations close to you and compassionate doctors who listen to your concerns, we are here to care for your well-being.
Snoring and sleep apnea can be frustrating to live with – for both the patient and their loved ones. CPAP machines are a commonly suggested solution – but what about micro CPAP devices?

The top health systems are evaluated based on workplace culture, employee benefits, professional development opportunities, and overall employee satisfaction.

Dwight Raum, Executive Vice President and Chief Digital Information Officer (CDIO) of Rochester Regional Health, has been named as a ‘Chief Digital Officer to Know’ in an influential national healthcare publication.

Midwives and doulas are integral parts of many families’ birth experiences. Beyond their role in childbirth, these health care professionals provide support and care in many different ways.
- Skip to main content
Child well visits, birth to 15 months
- Child well visit checklist
- Quiz: Child well-being and immunizations
Checking in: Questions to ask at your child's well visits
Welcoming a new child is exciting. But caring for a baby can also leave you with a lot of unanswered questions. Your baby’s care provider can help. From giving immunizations to offering you feeding tips, care providers help your baby grow up healthy. That includes making sure you have the answers and support you need.
A note about immunizations at child well visits
Your child’s care provider will give your baby immunizations during most visits. Immunizations work better and reduce the risk of infection by working with the body's natural defenses to help safely develop immunity to disease. Keeping your baby on schedule is also key, so don’t forget to schedule visits on time.
Learn what to ask at your child's well visits
Preparation is key for a stress-free appointment. Your baby should go to at least 8 child well visits before they are 15 months old. Knowing what will happen at each of these appointments can help you get ready. Knowing what to pack for your visit and questions you might ask when you get there can make your life easier. Watch the videos and view the questions below to get ready for each early child well visit.
Child Well Visits: Newborn
Video transcript.
Screen 1: What to expect at your baby’s appointment – Newborn
Screen 2: Your newborn will need a checkup before going home.
Screen 3: What to expect before you leave the hospital:
- Physical checkup (measurements, vitals).
- Screenings: Critical congenital heart defect, vision, hearing, newborn bilirubin, blood (check for disorders).
- Developmental and behavioral assessment.
- Immunizations: HepB.
Screen 4: Before you leave:
- Make sure your contact information is current.
- Schedule your next appointment.
Screen 5: In light of COVID-19, remember to practice social distancing at your well-child visits. Wash your hands often and wear a mask. Contact your care provider with questions about your visit.
Screen 6: UnitedHealthcare Logo
Your newborn will need a checkup before going home from the hospital. Watch the video to learn what screenings and immunizations you can expect at your child’s first appointment.
3 to 5-day visit
Child well visits: 3 to 5-day visit.
Screen 1: What to expect at your baby’s appointment – 3-5 Days
Screen 2: Early well-child visits and immunizations set your baby up for a healthy future.
Screen 3: What to expect at your child’s appointment:
- Physical checkup: Measurements, vitals.
- Umbilical cord examination.
- Screenings: Vision, hearing, blood (check for disorders).
- Review screenings done at birth.
Screen 4: You’ll also talk about if baby can:
- Suck to eat
- Grasp your finger
- React when startled
Screen 5: Before you leave:
Screen 6: In light of COVID-19, remember to practice social distancing at your well-child visits. Wash your hands often and wear a mask. Contact your care provider with questions about your visit.
UnitedHealthcare Logo
Watch the video to get an idea of what to expect at your appointment
In addition, here are some questions you may want to ask:
- How can I keep my baby comfortable and safe from seasonal weather?
- What can I do to make breastfeeding more comfortable for me and baby?
- When will my baby gain more weight?
- Should I always put my baby to sleep on their back?
- How do I care for my baby’s umbilical cord?
- How often should my baby get a bath?
- How do I calm and soothe my baby?
1-month visit
Child well visits: 1 month appointment.
Screen 1: What to expect at your baby’s appointment – 1 Month
- Immunizations: HepB.
- Postpartum depression screening (for mothers).
- Raise hands
- Focus on your face
Screen 7: UnitedHealthcare Logo
- When will my baby sleep through the night?
- What should I do for the peeling skin on my baby’s head?
- How do I care for my infant's skin?
- What is a normal number of wet or soiled diapers I should change every day?
- Are there programs to help me buy formula or breast pumps?
2-month visit
Child well visits: 2 month appointment.
Screen 1: What to expect at your baby’s appointment – 2 Months
- Physical checkup: (measurements, vitals).
- Screenings: Vision, hearing.
- Immunizations: DTaP, Hib, IPV, RV, HepB, PCV13.
- Developmental assessment.
- Turn and lift head
- Kick while laying on back
- Notice hands
- Follow objects with eyes
- How often should my baby be eating?
- Should I be using formula in addition to breastfeeding?
- How can I keep my baby comfortable after immunizations?
- How can I find childcare I can trust?
- When should I stop swaddling my baby?
- I’ve been feeling sad and anxious since delivering my baby. What should I do?
- What is “tummy time”?
4-month visit
Child well visits: 4 month appointment.
Screen 1: What to expect at your baby’s appointment – 4 Months
- Roll onto tummy
- Reach for objects
- Watch an object move
- Laugh and giggle
Screen 7: UnitedHealthcare Logo
- Is Tylenol safe to give my baby for a fever?
- How can I help my baby have healthy teeth?
- How can I soothe my baby during teething?
- How can we begin to create a sleeping routine?
- How long should my baby spend doing “tummy time” each day?
- How long should my baby nap each day?
6-month visit
Child well visits: 6 month appointment.
Screen 1: What to expect at your baby’s appointment – 6 Months
- Screenings: Vision, hearing, oral health.
- Immunizations: DTaP, Hib, IPV, RV, HepB, PCV13, IIV.
- Roll in both directions
- Play with toes
- Hold a bottle
- Sit with good head control
- When and how should I introduce foods other than breastmilk or formula?
- How can I wean my baby off night feedings?
- How long should my baby use a pacifier?
- Can my baby sleep with a favorite blanket or toy?
- When can my baby start drinking from a sippy cup?
9-month visit
Child well visits: 9 month appointment.
Screen 1: What to expect at your baby’s appointment – 9 Months
- Screenings: Vision, hearing, anemia, lead, oral health.
- Immunizations: IIV.
- Sit unassisted
- Crawl and pull up to stand
- Work to get toys that are out of reach
- I think my baby is behind in development (e.g., crawling). What can I do to help?
- What do I need to babyproof in my home once my baby can crawl?
- Should I be brushing my baby’s new teeth?
- How long should my baby be sleeping at night?
- How long should I let my baby cry at night?
12-month visit
Child well visits: 12 month appointment.
Screen 1: What to expect at your baby’s appointment – 12 Months
- Screenings: Vision, hearing, lead, oral health.
- Immunizations: MMR, HepA, Varicella, PCV13, IIV.
- Walk while holding onto something
- Use gestures to get things
- Eat solid foods with fingers
- Say more than one word
- Respond to name
- What should I do when baby pulls my hair or bites?
- Are my baby’s sleep patterns normal?
- How can I treat diaper rash?
- What can I do about sore arms and back from holding my baby?
- Should my baby nap at the same time each day?
- How do I keep my child safe as they learn to walk and explore?
15-month visit
Child well visits: 15 month appointment.
Screen 1: What to expect at your baby’s appointment – 15 Months
- Immunizations: DTaP, Hib, IIV.
- Walk and run
- Squat and stand back up
- Throw or kick a ball
- Point for things
- When should my baby switch from a crib to a bed?
- How much juice or milk should my baby be drinking?
- Should my baby have screen time?
- When should my baby go to the dentist?
- When should I switch to a front-facing car seat?
Wellness visits are also important for your child after 15 months
As your child grows, it’s important to continue to have regular checkups with your health care provider. You can view checklists for preventive care visits at every age, from 1 month to adulthood.
Looking for resources to help support you and your child?
- Most health insurance plans cover early child well visits or provide assistance. Call the number on your insurance card for more details.
- If you are a UnitedHealthcare Community Plan member, you may have access to our Healthy First Steps program , which can help you find a care provider, schedule well-child visits, connect with educational and community resources and more. To get started, call 1-800-599-5985 , TTY 711, Monday through Friday, from 8 a.m. to 5 p.m. 1
- If you need help getting to an appointment, or getting formula or healthy food, call the number on your insurance card.
- If you are having a hard time getting food or are experiencing unemployment, your care provider may be able to connect you with resources that can help.
Related content
- Preventive care
More like this:
- What’s preventive care and what’s covered?
- Children's health
A Comprehensive Guide to Well-child Visits
Schedule online or call to make an appointment.
- Norton Children’s Pediatricians
- FAQs: Back-to-School Physicals and Sports Physicals
- Pediatrician Offices
- Flu in Children
- Child Development Milestones From Birth Through Age 18
- Recommended Children’s Vaccination Schedule
- Parent & Baby Care Resources
- New Parents: Frequently Asked Questions
- New Parent Classes
The Importance of Well-child Visits at Every Age
Norton children’s medical group.
Keep on top of your child’s health by scheduling a well-child visit today. Our pediatrician offices are conveniently located across Kentucky and Southern Indiana.
Book your appointment directly by choosing a location or provider.
Every parent wants to know that their child is growing and healthy. A well-child visit is a crucial part of every child’s health care journey, from the time they are born until they reach adulthood.
A well-child visit is a regularly scheduled health check up with your child’s pediatrician . These appointments serve many important purposes. They focus on your child’s overall health, preventive care, growth and developmental milestones, immunizations, plus serve as a time for parents to discuss any questions or concerns they may have about their child’s health or parenting. These visits also can help catch any potential health issues early and connect your child with additional support if needed for specific physical or mental health concerns. Building a strong relationship with a pediatrician is an important part of your child’s health care journey. Pediatricians are specially trained to focus on children’s health. They will conduct physical and mental health screenings, along with a full physical health assessment, and offer medical guidance to your child and family. The benefit of your child seeing a pediatrician is the continuity it provides of your child seeing the same doctor(s) as they grow up.
Well-child visits may seem like a routine part of your child’s growth, but they play an important role in their overall health care, including their physical, mental, social and emotional well-being. How often you need to schedule your child’s well-child visits will vary based on their age and developmental needs.
During a baby’s first year, they grow rapidly and will require more frequent visits with the pediatrician to ensure they are reaching their developmental milestones on time. Toddlers will continue to see their pediatrician at regular intervals throughout the year, and young children will need to check in with their pediatrician at least once a year. The full well-child visit schedule recommended by the American Academy of Pediatrics, is listed below:
By becoming a part of your family’s medical home, the pediatricians with Norton Children’s Medical Group , can get to know your family on an individual basis, become familiar with your child’s health care needs and unique personality, plus offer the best tools, information and guidance to empower every child and parent to live a healthy lifestyle.
Although well-child visits, on their own, are not legally mandated, health physicals often are required for entry into school or day care and for participation in sports. Many state laws require these types of health check ups and immunizations for school children, and the well-child visit can serve as a great time to complete these requirements with a health care professional. Regularly scheduled check ups with your child’s pediatrician are strongly recommended by medical professionals to make sure your child receives the proper care at every stage of their growth.
During your child’s visit, you can expect your pediatrician to do the following:
- The pediatrician will perform a thorough physical exam to assess your child’s general health, growth and any potential physical concerns. This includes regular screenings for physical and mental health issues.
- Observing your child’s developmental progress and behavior helps identify any developmental delays or behavioral issues.
- The pediatrician provides guidance on proper nutrition and feeding practices tailored to your child’s age and needs.
- Updating your child’s medical history and sharing any family health history helps the pediatrician make informed decisions about your child’s care.
- Well-child visits include getting recommended vaccinations to protect your child from various diseases. Keeping vaccinations up to date is crucial for their health and safety.
- Well-child visits provide a place for you to ask questions, share concerns and seek guidance on parenting, health and development.
- Having a record of your child’s medical history and vaccinations helps ensure accurate and effective care.
- If your child is a patient at one of our pediatrician offices, parents or guardians have proxy access to the child’s Norton MyChart account to review medical history and immunization records.
- Inform the pediatrician about any medications your child takes. It helps to bring the specific prescription bottles to confirm the name and dosage of the medications.
- Sharing recent health changes or concerns (both physical and mental) ensures that the pediatrician has the most up-to-date information to provide appropriate care.
- Mention any developmental milestones your child has reached since the last visit or if they have experienced any backslides.
- Bringing a notebook and pen or device (such as the Notes app or voice recorder on your phone) to take notes on the pediatrician’s recommendations and advice helps you remember and put their guidance into practice.
- Many insurance plans cover well-child visits as preventive care. At Norton Children’s Medical Group, we accept Medicaid and most commercial insurance plans.
- Understanding your coverage helps you plan financially. Confirming your insurance coverage before the visit helps you avoid unexpected expenses. Staying within your insurance network can help minimize out-of-pocket costs for well-child visits.
Well-child check ups are more than just routine appointments. They are a cornerstone for monitoring and supporting your child’s overall health and development. It is important to follow the recommended well-child visit schedule to ensure your child’s pediatrician can screen them for any health issues, provide necessary preventive care and immunizations, and give them the physical and mental support they need to achieve optimal health. It’s also a time for parents to receive support and helpful information from the pediatrician. Prioritizing your child’s health can help set them up for a brighter, healthier and happier future. Building a strong relationship with a pediatrician can help encourage more positive health care experiences and better long-term health later in life.
Benefits of Norton Children’s Medical Group
- Convenient locations with more than 25 pediatrician offices in Louisville and surrounding areas in Kentucky and Southern Indiana
- New patients can be seen within 24 hours
- Same-day sick appointments are available
- Schedule appointments online, get appointment reminders, communicate with your child’s medical provider, view and request immunization records, refill prescriptions and more through your free Norton MyChart account
- Night and weekend hours are available
- Access to Norton Children’s After Hours Care and the after-hours nurse care line
- Medicaid and most major commercial insurance plans accepted

Related Stories

Norton Healthcare, Norton Children’s expand services in Westport Plaza

Genetic tests provided as part of study for kids referred for possible autism
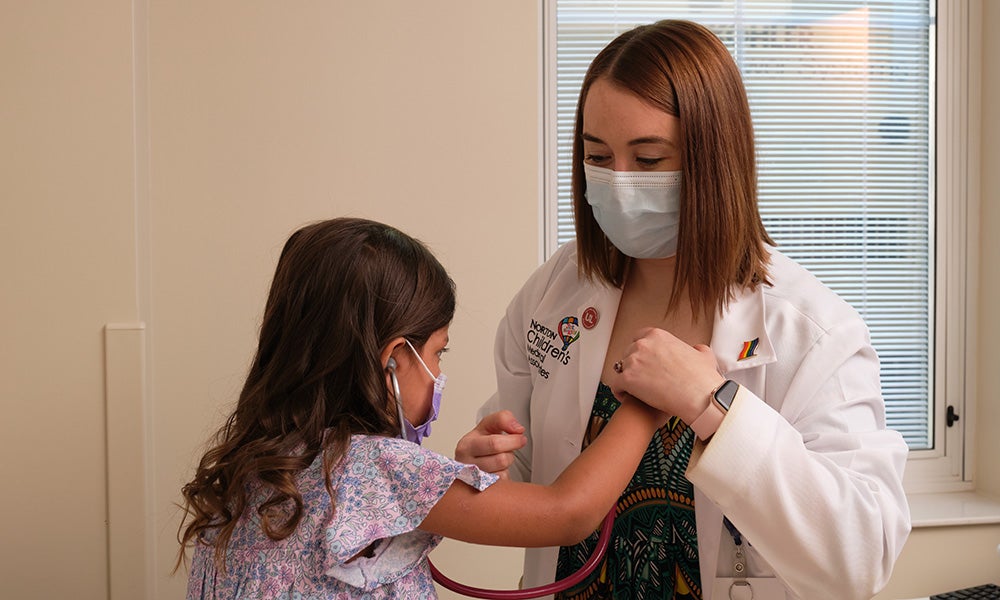
Discuss hyperactivity or inattention in a preschooler at your next well-child visit

Checklist: What to bring to your baby’s first pediatrician appointment
Doctor Visits
Make the Most of Your Teen’s Visit to the Doctor (Ages 15 to 17 Years)

Take Action
Teens ages 15 to 17 years need to go to the doctor or nurse for a “well-child visit” once a year.
A well-child visit is when you take your teen to the doctor to make sure they’re healthy and developing normally. This is different from other visits for sickness or injury.
At a well-child visit, the doctor or nurse can help catch any problems early, when they may be easier to treat.
Learn what to expect so you can make the most of each visit.
Child Development
How do i know if my teen is growing and developing on schedule.
Your teen’s doctor or nurse can help you identify “developmental milestones,” or signs to look for that show your teen is developing normally. This is an important part of the well-child visit.
Some developmental milestones are related to your teen’s behavior and learning, and others are about physical changes in your teen’s body.
See a complete list of developmental milestones for your teen .
Behavior Changes
What are some changes i might see in my teen’s behavior.
Developmental milestones for teens ages 15 to 17 years include:
- Spending less time with family and more time with friends
- Worrying more about the future (like going to college or finding a job)
- Thinking more about romantic relationships and sex
- Trying new things like new sports or hobbies — or possibly experimenting with tobacco, alcohol, or drugs
This is also a time when some teens may start showing signs of depression, anxiety, or eating disorders. That’s why it’s important to:
- Make sure the doctor screens your teen for depression
- Have your teen screened for anxiety
Physical Changes
What are some physical changes my teen is going through.
Teens ages 15 to 17 years may be nearing the end of puberty. Puberty is when a child’s body develops into an adult’s body.
- Get more information about puberty to share with your daughter
- Get more information about puberty to share with your son
Teens might not ask you questions about sex, their bodies, or relationships. That’s why it’s a good idea for you to start the conversation. You can also encourage your teen to ask the doctor or nurse any questions they have about body changes or other health concerns.
Learn how to talk with your teen about sex .
Take these steps to help you and your teen get the most out of well-child visits.
Gather important information.
Take any medical records you have to the appointment, including a record of vaccines (shots) your teen has received.
Make a list of any important changes in your teen’s life since the last visit, like a:
- New brother or sister
- Separation or divorce — or a parent spending time in jail or prison
- New school or a move to a new neighborhood
- Serious illness or death of a friend or family member
Use this tool to keep track of your teen’s family health history .
Help your teen get more involved in visits to the doctor.
The doctor will probably ask you to leave the room during part of the visit, usually the physical exam. This lets your teen develop a relationship with the doctor or nurse and ask questions in private. It’s an important step in teaching your teen to take control of their health care.
Your teen can also:
- Call to schedule appointments
- Help you fill out medical forms
- Write down questions for the doctor or nurse
For more ideas, check out these tips to help teens take charge of their health care . You can also share this list of questions for the doctor with your teen .
What about cost?
Under the Affordable Care Act, insurance plans must cover well-child visits. Depending on your insurance plan, you may be able to get well-child visits at no cost to you. Check with your insurance company to find out more.
Your teen may also qualify for free or low-cost health insurance through Medicaid or the Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP). Learn about coverage options for your family.
If you don’t have insurance, you may still be able to get free or low-cost well-child visits. Find a health center near you and ask about well-child visits.
To learn more, check out these resources:
- Free preventive care for children covered by the Affordable Care Act
- How the Affordable Care Act protects you and your family
- Understanding your health insurance and how to use it [PDF - 698 KB]
Ask Questions
Make a list of questions you want to ask the doctor..
Before the well-child visit, write down 3 to 5 questions you have. This visit is a great time to ask the doctor or nurse any questions about:
- A health condition your teen has (like acne or asthma)
- Changes in your teen’s behavior or mood
- Loss of interest in favorite activities
- Tobacco, alcohol, or drug use
- Problems at school (like learning challenges or not wanting to go to school)
Here are some questions you may want to ask:
- Is my teen up to date on vaccines?
- How can I make sure my teen is getting enough physical activity?
- How can I help my family eat healthy?
- How can I help my teen succeed at school?
- How can our family set rules more effectively?
- How can I help my teen become a safe driver?
- How can I talk with my teen about tobacco, alcohol, and drugs?
Take a notepad, smartphone, or tablet and write down the answers so you can remember them later.
Ask what to do if your teen gets sick.
Make sure you know how to get in touch with a doctor or nurse when the office is closed. Ask how to get hold of the doctor on call, or if there's a nurse information service you can call at night or on the weekend.
What to Expect
Know what to expect..
During each well-child visit, the doctor or nurse will ask you questions, do a physical exam, and update your teen’s medical history. You and your teen will also be able to ask your questions and discuss any problems.
The doctor or nurse will ask your teen questions.
The doctor or nurse may ask about:
- Behavior — Do you have trouble following directions at home or at school?
- Health — Do you often get headaches or have other kinds of pain?
- Safety — Do you always wear a seatbelt in the car? Do you and your friends use tobacco, alcohol, or drugs?
- School and activities — Do you look forward to going to school? What do you like to do after school?
- Family and friends — Have there been any changes in your family recently? Do you have close friends?
- Emotions — Do you often feel sad or bored? Do you often feel scared or very worried? Is there someone you trust who you can talk to about problems?
- Sexuality — Do you have any questions about your body? Have you talked with your parents about dating and sex? Are you dating anyone now?
- The future — Have you started to think about what you want to do after high school?
The answers to questions like these will help the doctor or nurse make sure your teen is healthy, safe, and developing normally.
Physical Exam
The doctor or nurse will also check your teen’s body..
To check your teen’s body, the doctor or nurse will:
- Measure height and weight and figure out your teen's body mass index (BMI)
- Check your teen’s blood pressure
- Check your teen's vision and hearing
- Check your teen’s body parts (called a physical exam)
- Decide if your teen needs any lab tests, like a blood test
- Give your teen vaccines they need
Behavior and Emotions
The doctor or nurse will pay special attention to signs of certain issues. .
The doctor or nurse will offer additional help if your teen may:
- Be depressed
- Have anxiety
- Struggle with an eating disorder
- Use tobacco, alcohol, or other drugs
- Experience any kind of violence
And if your teen may be having sex, the doctor or nurse will talk about preventing STIs (sexually transmitted infections) — also called STDs (sexually transmitted diseases) — and pregnancy. Learn how to talk with your teen about preventing STIs .
The doctor or nurse will make sure you and your teen have the resources you need.
This may include telling you and your teen about:
- Websites or apps that have helpful health information
- Organizations in your community where you can go for help
If needed, the doctor or nurse may also refer your teen to a specialist.
Content last updated February 16, 2024
Reviewer Information
This information on well-child visits was adapted from materials from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the National Institutes of Health.
Reviewed by: Sara B. Kinsman, M.D., Ph.D. Director, Division of Child, Adolescent and Family Health Maternal and Child Health Bureau Health Resources and Services Administration
You may also be interested in:

Talk to Your Kids About Tobacco, Alcohol, and Drugs

Talk to Your Kids About Sex and Healthy Relationships

Get Your Teen Screened for Depression
The office of disease prevention and health promotion (odphp) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website..
Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by ODPHP or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.

An official website of the United States government Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
Well-Child Care
Improving infant well-child visits.
High-quality well-child visits can improve children’s health, support caregivers’ behaviors to promote their children’s health, and prevent injury and harm. The American Academy of Pediatrics and Bright Futures recommend nine well-care visits by the time children turn 15 months of age. These visits should include a family-centered health history, physical examination, immunizations, vision and hearing screening, developmental and behavioral assessment, an oral health risk assessment, a social assessment, maternal depression screening, parenting education on a wide range of topics, and care coordination as needed. i When children receive the recommended number of high-quality visits, they are more likely to be up-to-date on immunizations, have developmental concerns recognized early, and are less likely to visit the emergency department. ii , iii , iv , v , vi , vii However, many infants do not receive the recommended number of infant well-child visits.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) offers quality improvement (QI) technical assistance (TA) to help states increase the attendance and quality of well-child visits for Medicaid and Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP) beneficiaries ages 0 to 15 months.
QI TA resources , to help state Medicaid and CHIP staff and their QI partners get started improving the use of infant well-child visits for their beneficiaries
Improving Infant Well-Child Visit learning collaborative resources , to share different approaches to improving well-child visit care and state examples
For more information on these materials and other QI TA, please email [email protected] .
QI TA Resources
These resources can help states get started in developing their own infant well-child QI projects:
Getting Started on Quality Improvement Video . This video provides an overview of how Medicaid and CHIP agencies can start a QI project to improve the use of infant well-child visits. The Model for Improvement begins with small tests of change, enabling state teams to “learn their way” toward strong programs and policies.
Driver Diagram and Change Idea Table . A driver diagram is a visual display of what “drives” or contributes to improvements in infant well-child visits. This example of a driver diagram shows the relationship between the primary drivers (the high-level elements, processes, structures, or norms in the system that must change to use and quality of infant well-child visits) and the secondary drivers (the places, steps in a process, time-bound moments, or norms in which changes are made to spur improvement). The document also includes change idea tables, which contain examples of evidence-based or evidence-informed QI interventions to improve the use of infant well-child care. The change ideas were tailored for Medicaid and CHIP.
Measurement Strategy . This document provides examples of measures that can be used to monitor infant well-child care QI projects.
Improving Infant Well-Child Visits: Learning Collaborative Resources
Beginning in 2021, CMS facilitated the two year Infant Well-Child Visit learning collaborative to support state Medicaid and CHIP agencies’ efforts to improve the use of infant well-child visits from 0-15 months of age. The learning collaborative included a webinar series and an affinity group to support state Medicaid and agencies’ quality improvement efforts. The webinars, listed and linked to below, described approaches that states can use to improve attendance and quality of infant well-child visits.
California, Missouri, North Carolina, South Carolina, Texas and Virginia participated in the action-oriented affinity group where teams designed and implemented an infant well-child quality improvement (QI) project in their state with tailored TA from CMS. Learnings from participating states can be found in the state highlights brief.
Learning Collaborative Webinar Series
State Spotlights Webinar on Improving Infant-Well Child Care ( Video ) ( Transcript ). This 2024 webinar spotlighted several state QI projects from the affinity group, highlighting their strategies, partnerships, and lessons learned.
Using Payment, Policy and Partnerships to Improve Infant Well-Child Care ( Audio )( Transcript ). This August 2021 webinar focused on Medicaid and CHIP payment incentives, managed care contracts, and other strategies that can increase the use and quality of infant well-child visits and advance equity. Speakers from the CMS and Mathematica introduced CMS’ Maternal and Infant Health Initiative and shared the importance of high-quality well-child visits and the opportunities within Medicaid and CHIP to impact infant health. Speakers from Pennsylvania and Texas’ Medicaid and CHIP agencies described their efforts to expand and incentivize participation in infant well-child visits, such as through value-based purchasing, performance improvement projects, CHIP Health Services Initiatives (HSIs), and partnerships with aligned service providers like the Special Supplemental Nutrition Program for Women, Infants, and Children (WIC). State presenters offered insights into ways to incentivize efforts to close gaps in care, engage families, and improve performance on quality measures. During the Q&A session, presenters discussed the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on well-child care, the potential of using telehealth or hybrid visits to increase access, and incentives for managed care entities, and addressing the social determinants of health in value-based payment strategies.
Improving Quality and Utilization of Infant Well-Child Visits ( Audio )( Transcript ). This September 2021 webinar focused on the characteristics of a high-performing system of well-child health care. CMS and Mathematica presenters shared the Maternal and Infant Health Initiative’s Theory of Change. Speakers from Washington and Arkansas Medicaid and CHIP agencies discussed how their states have achieved high rates of participation in infant well-child visits and how they use data to monitor performance and disparities and ensure access to services. Washington shared insights on leveraging collaborative performance improvement projects to identify and address barriers to care. Arkansas discussed the state’s per member per month incentives for performance and minimum performance measures for infant well-child visit rates. During the Q&A session, presenters highlighted efforts to improve health equity, engage parents and providers, and leverage performance measures and quality tools to improve attendance at infant well-child visits.
Models of Care that Drive Improvement in Infant Well-Child Visits ( Audio )( Transcript ). In this September 2021 webinar, three states—Oregon, Michigan, and North Carolina—shared approaches to designing and implementing models of care associated with improved infant well-child visit participation, including patient-centered medical homes (PCMHs) and home visiting. States offered insights on the importance of strategic alignment of policies, processes, and partnerships. Oregon discussed its home visiting program and quality incentive strategy for its coordinated care organizations. The state incentivizes progress on the HEDIS measures and other measures designed by the state’s Pediatric Improvement Partnership, including a measure of social-emotional health service capacity and access for infants and children. Michigan discussed how they requires MCOs to identify and publish disparities in well-child visit rates and how they encourage plans to reduce disparities. The state also uses an algorithm that automatically assigns members to MCOs based on MCOs’ performance and reimburses for maternal-infant health home visiting. North Carolina shared its Keeping Kids Well program, which aims to increase well-child visit and immunization rates and reduce disparities in those rates. The program offers coaches to practices to support their improvements, established an advisory board of key interested parties, and provides customized vaccination notices for practices to distribute to beneficiaries, in partnership with health systems and pharmaceutical companies. The state also used the Healthy Opportunities payment to incentivize the identification and redress of health-related social needs and provided the Health Equity Payment to providers serving areas with high poverty rates.
i 3 Hagan, J.F., J.S. Shaw, and P.M. Duncan (eds.). Bright Futures: Guidelines for Health Supervision of Infants, Children, and Adolescents. 4th ed. Elk Grove Village, IL: American Academy of Pediatrics, 2017.
ii Gill, J.M., A. Saldarriaga, A.G. Mainous, and D. Unger. “Does Continuity Between Prenatal and Well-Child Care Improve Childhood Immunizations?” Family Medicine, vol. 34, no. 4, April 2002, pp. 274–280.
iii Buchholz, M., and A. Talmi. “What We Talked About at the Pediatrician’s Office: Exploring Differences Between Healthy Steps and Traditional Pediatric Primary Care Visits.” Infant Mental Health Journal, vol. 33, no. 4, 2012, pp. 430–436.
iv DeVoe, J.E., M. Hoopes, C.A. Nelson, et al. “Electronic Health Record Tools to Assist with Children’s Insurance Coverage: A Mixed Methods Study.” BMC Health Services Research, vol.18, no. 1, May 2018, p. 354–360.
v Coker, T.R., S. Chacon, M.N. Elliott, et al. “A Parent Coach Model for Well-Child Care Among Low-Income Children: A Randomized Controlled Trial.” Pediatrics, vol. 137, no. 3, March 2016, p. e20153013.
vi Flores, G., H. Lin, C. Walker, M. Lee, J. Currie, R. Allgeyer, M. Fierro, M. Henry, A. Portillo, and K. Massey. “Parent Mentoring Program Increases Coverage Rates for Uninsured Latino Children.” Health Affairs, vol. 37, no. 3, 2018, pp. 403–412.
vii Hakim, R.B., and D.S. Ronsaville. “Effect of Compliance with Health Supervision Guidelines Among US Infants on Emergency Department Visits.” Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine, vol. 156, no. 10, October 2002, pp. 1015–1020.
Shop for Plans
Shop for your own coverage, plans through your employer.
Learn about the medical, dental, pharmacy, behavioral, and voluntary benefits your employer may offer.
Looking for Medicare coverage?
Well-child visits.
It's important for your child to have regularly scheduled checkups, often called well-child visits, beginning shortly after birth and lasting through the teen years.
These appointments allow your doctor to keep a close eye on your child's general health and development. Finding possible problems early gives your child the best chance for proper and successful treatment. Also, any concerns you have about your child can be discussed during these visits.
During these visits, the doctor examines your child and asks you questions about your child's development and behavior. Immunizations also are either given or scheduled at this time.
Your child's doctor will recommend a schedule for well-child visits. One example is for visits at ages: footnote 1
- 3 to 5 days old.
- By 1 month.
After age 3, well-child visits are usually scheduled yearly through the teen years.
Citations Bright Futures/American Academy of Pediatrics (2020). Recommendations for preventive pediatric health care. American Academy of Pediatrics . https://downloads.aap.org/AAP/PDF/periodicity_schedule.pdf. Accessed February 27, 2020.
Current as of: October 24, 2023
Author: Healthwise Staff
Clinical Review Board All Healthwise education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Healthwise, Incorporated, disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use . Learn how we develop our content .
To learn more about Healthwise, visit Healthwise.org .
© 1995-2024 Healthwise, Incorporated. Healthwise, Healthwise for every health decision, and the Healthwise logo are trademarks of Healthwise, Incorporated.
Related Links
Page footer, i want to..., secure member sites, the cigna group information.
Cigna. All rights reserved.
Individual and family medical and dental insurance plans are insured by Cigna Health and Life Insurance Company (CHLIC), Cigna HealthCare of Arizona, Inc., Cigna HealthCare of Illinois, Inc., Cigna HealthCare of Georgia, Inc., Cigna HealthCare of North Carolina, Inc., Cigna HealthCare of South Carolina, Inc., and Cigna HealthCare of Texas, Inc. Group health insurance and health benefit plans are insured or administered by CHLIC, Connecticut General Life Insurance Company (CGLIC), or their affiliates (see a listing of the legal entities that insure or administer group HMO, dental HMO, and other products or services in your state). Accidental Injury, Critical Illness, and Hospital Care plans or insurance policies are distributed exclusively by or through operating subsidiaries of Cigna Corporation, are administered by Cigna Health and Life Insurance Company, and are insured by either (i) Cigna Health and Life Insurance Company (Bloomfield, CT); (ii) Life Insurance Company of North America (“LINA”) (Philadelphia, PA); or (iii) New York Life Group Insurance Company of NY (“NYLGICNY”) (New York, NY), formerly known as Cigna Life Insurance Company of New York. The Cigna name, logo, and other Cigna marks are owned by Cigna Intellectual Property, Inc. LINA and NYLGICNY are not affiliates of Cigna.
All insurance policies and group benefit plans contain exclusions and limitations. For availability, costs and complete details of coverage, contact a licensed agent or Cigna sales representative. This website is not intended for residents of New Mexico.
Selecting these links will take you away from Cigna.com to another website, which may be a non-Cigna website. Cigna may not control the content or links of non-Cigna websites. Details
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
- Education, training and skills
- Pupil wellbeing, behaviour and attendance
- Alternative provision and pupil referral units
New visits to understand how well children with SEND are prepared for adulthood
New guidance from Ofsted and the Care Quality Commission (CQC) for visits looking at how children and young people with special educational needs and/or disabilities (SEND) are being prepared for adulthood.

Ofsted and the CQC have today published guidance for the next series of thematic visits looking at how children and young people with special educational needs and/or disabilities ( SEND ) are being prepared for adulthood.
As part of the area SEND inspection arrangements, Ofsted and the CQC will carry out a series of in-depth reviews to explore a particular aspect of the SEND system between spring and summer 2024.
Read the ‘Thematic reviews of preparation for adulthood arrangements in local areas’ guidance.
The visits will consider all phases of a child with SEND ’s transition to adulthood, from early years settings through to post-16 education, to get an in-depth picture of how preparation for adulthood ( PFA ) arrangements are working. These arrangements include any support delivered by local area partners across education, health and social care that focuses on the 4 key pathways for preparation for adulthood based on the ‘ SEND code of practice’ – employment, independent living, community inclusion and health.
Ofsted and the CQC will explore how local area partners work together to make sure their decisions are focused on young people’s interests and aspirations. Evidence will be gathered from key stakeholders, including children and young people with SEND and their families. Inspectors will consider a range of topics including:
- how young people with SEND are being supported to achieve their full potential. For example, through further education or supported internships
- how young people with SEND are empowered to make decisions for themselves and live as independently as possible
- how children and young people with SEND are supported to participate in society
- how children and young people with SEND are supported to be as healthy as possible in adulthood
- how local area partners work together to develop and implement strategies for PFA
- the enablers and barriers to effectively preparing young people with SEND for adulthood
Lee Owston, Ofsted’s National Director for Education:
The current SEND system is not meeting the needs of too many children and their families. It is vital that every child is provided with the support and guidance they need to thrive and live as independently as possible throughout their adult lives. I hope that these visits provide valuable insight into how we can improve the experiences of children with SEND as the government develops its SEND and alternative provision improvement plan.
Nigel Thompson, Deputy Director of Multiagency Operations at the Care Quality Commission:
When children, young people and their families face times of transition it is not only vital that services understand their needs, but also that those children, young people and their families are involved in and prepared for the change. Looking at people’s experiences alongside Ofsted, we will be able to explore how agencies and health care providers are working together – where improvements can be made and share good practice.
Notes to editors
- Findings from the visits will be shared in a single national report in autumn 2024. This report will list all the areas visited but won’t attribute findings to individual areas unless the area agrees to be identified.
- The visits will not result in judgements about local areas. The overarching report will highlight examples of good practice and identify any systemic concerns. Where good practice is identified, this will be shared with the Department for Education and the Department for Health and Social Care to support their development of policy for the SEND and alternative provision improvement plan.
Press office
8.30am to 6pm Monday to Friday 0300 013 0415
Share this page
The following links open in a new tab
- Share on Facebook (opens in new tab)
- Share on Twitter (opens in new tab)
Is this page useful?
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. We’ll send you a link to a feedback form. It will take only 2 minutes to fill in. Don’t worry we won’t send you spam or share your email address with anyone.
Trump may miss his son Barron's high school graduation because he'll be on trial over hush money payments to a porn star
- Donald Trump's criminal trial may prevent him from attending son Barron's high school graduation.
- The historic trial began with jury selection in a Manhattan courtroom on Monday.
- The judge has not yet decided on Trump's request to skip trial for the graduation event.

Donald Trump may have to miss out on his son Barron's high school graduation ceremony next month due to the timing of the former president's first historic criminal trial .
Trump's hush-money trial kicked off with jury selection on Monday in a Manhattan courtroom.
As the court prepared for the first day of voir dire, New York Supreme Court Justice Juan Merchan said he received requests from Trump's attorneys for the former president to skip out on the trial on May 17 so that he could attend Barron Trump's high school graduation in Florida.
Related stories
Merchan said that he would not yet rule on Donald Trump's request to not have the trial held that day.
"It really depends on if we are on time and where we are in the trial," Merchan explained.
Jury selection is expected to last up to two weeks.
After court adjourned Monday afternoon, Trump complained to reporters.
" As you know, my son is graduating from high school and it looks like the judge will not let me go to the graduation of my son, who has worked very, very hard," Trump told reporters Monday afternoon. "He was looking forward, for years, to that graduation with his mother and father there, and it looks like the judge isn't going to allow me to escape this scam."
Trump is charged with 34 felony counts of falsifying business records, alleging that he lied on documents to disguise payments to adult film actress Stormy Daniels.
Prosecutors allege Donald Trump's ex-personal attorney and former fixer Michael Cohen facilitated $130,000 in payments to Daniels just days before the 2016 presidential election to buy her silence over a 2006 sexual encounter with Donald Trump.
Trump has denied the charges.
Merchan didn't outright deny Trump's request to attend the ceremony, but did shoot down his second ask — to be able to attend April 25 arguments at the Supreme Court, where his lawyers will try to convince the justices he has presidential immunity as a defense against the election interference charges against him.
Watch: Donald Trump was indicted in New York. Here's what we know so far.
- Main content
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
Diverse Cultures and Shared Experiences Shape Asian American Identities
About six-in-ten feel connected to other asians in the u.s., table of contents.
- The making of Asian American identity and knowledge of Asian history in the U.S.
- Immigrant ties shape Asian Americans' identities and their life in the U.S.
- Asians in the U.S. share similar views among themselves and with the U.S. public on what it means to be American
- How Asians in the U.S. describe their identity
- Asian adults and the general public agree: U.S. Asians have many different cultures
- Whom do U.S. Asians consider Asian?
- A majority of Asian adults say others would describe them as Asian when walking past them on the street
- For many Asian adults, where they were born shapes friendships formed in the U.S.
- Most Asian adults are comfortable with intermarriage
- Some Asians say they have hidden their heritage
- Connections with other Asian Americans, politics and political parties
- Need for a national leader advancing the concerns of Asian Americans
- Asian American registered voters and political party
- About one-quarter of Asian adults say they are informed about U.S. Asian history
- What being ‘truly American’ means to U.S. Asians
- Fewer than half of U.S. Asians consider themselves typical Americans
- What do Asian Americans view as important for the American dream?
- Most Asian adults say the American dream is within reach, but about a quarter say they will never achieve it
- Acknowledgments
- Sample design
- Data collection
- Weighting and variance estimation
- Largest origin groups
- Educational attainment
- Immigration status
- Length of time living in the U.S. among immigrants
- Citizenship status among immigrants
Pew Research Center conducted this analysis to understand the rich diversity of people of Asian origin or ancestry living in the United States and their views of identity. The study is part of the Center’s multiyear, comprehensive, in-depth quantitative and qualitative research effort focused on the nation’s Asian population. Its centerpiece is this nationally representative survey of 7,006 Asian adults exploring the experiences, attitudes and views of Asians living in the U.S. The survey sampled U.S. adults who self-identify as Asian, either alone or in combination with other races or Hispanic ethnicity. It was offered in six languages: Chinese (Simplified and Traditional), English, Hindi, Korean, Tagalog and Vietnamese. Responses were collected from July 5, 2022, to Jan. 27, 2023, by Westat on behalf of Pew Research Center.
The Center recruited a large sample to examine the diversity of the U.S. Asian population, with oversamples of the Chinese, Filipino, Indian, Korean and Vietnamese populations. These are the five largest origin groups among Asian Americans. The survey also includes a large enough sample of self-identified Japanese adults, making findings about them reportable. In this report, the six largest ethnic groups include those who identify with one Asian ethnicity only, either alone or in combination with a non-Asian race or ethnicity. Together, these six groups constitute 81% of all U.S. Asian adults, according to a Pew Research Center analysis of the Census Bureau’s 2021 American Community Survey (ACS), and are the six groups whose attitudes and opinions are highlighted throughout the report. Survey respondents were drawn from a national sample of residential mailing addresses, which included addresses from all 50 states and the District of Columbia. Specialized surnames list frames maintained by the Marketing Systems Group were used to supplement the sample. Those eligible to complete the survey were offered the opportunity to do so online or by mail with a paper questionnaire. For more details, see the Methodology . For questions used in this analysis, see the Topline Questionnaire .
The survey research plan and questionnaire were reviewed and approved by Westat’s institutional review board (IRB), which is an external and independent committee of experts specializing in protecting the rights of research participants.
Even though the U.S. Asian population was the fastest growing racial and ethnic group in the country from 2000 to 2019 , it is still a relatively small population. According to the 2021 American Community Survey, the country’s Asian population constitutes 7% of the U.S. population (of all ages) and 7% of adults (those ages 18 and older).
Pew Research Center designed this study with these details in mind to be as inclusive as possible of the diversity of Asian American experiences. Even so, survey research is limited when it comes to documenting the views and attitudes of the less populous Asian origin groups in the U.S. To address this, the survey was complemented by 66 pre-survey focus groups of Asian adults , conducted from Aug. 4 to Oct. 14, 2021, with 264 recruited participants from 18 Asian origin groups. Focus group discussions were conducted in 18 different languages and moderated by members of their origin groups.
Findings for less populous Asian origin groups in the U.S., those who are not among the six largest Asian origin groups, are grouped under the category “Other” in this report and are included in the overall Asian adult findings in the report. These ethnic origin groups each make up about 2% or less of the Asian population in the U.S., making it challenging to recruit nationally representative samples for each origin group. The group “Other” includes those who identify with one Asian ethnicity only, either alone or in combination with a non-Asian race or Hispanic ethnicity. Findings for those who identify with two or more Asian ethnicities are not presented by themselves in this report but are included in the overall Asian adult findings.
To learn more about how members of less populous Asian origin groups in the U.S. identify, see the quote sorter based on our focus group discussions. There, you can read how participants describe their identity in their own words.
For this analysis, an additional national survey of 5,132 U.S. adults was conducted from Dec. 5 to 11, 2022, using Pew Research Center’s American Trends Panel . The survey of U.S. adults was conducted in English and Spanish. Respondents are recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses.
Pew Research Center has conducted multiple studies that focus on Asian Americans. Previous demographic studies examined the diversity of origins , key facts , and rising income inequality among Asians living in the U.S. and key findings about U.S. immigrants. Qualitative studies have focused on what it means to be Asian in America as well as barriers to English language learning among Asian immigrants. Previous surveys have focused on concerns over discrimination and violence against Asian Americans, as well as studies about their religious beliefs . Find these publications and more on the Center’s Asian Americans topic page .
Pew Research Center is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts, its primary funder. The Center’s Asian American portfolio was funded by The Pew Charitable Trusts, with generous support from The Asian American Foundation; Chan Zuckerberg Initiative DAF, an advised fund of the Silicon Valley Community Foundation; the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation; the Henry Luce Foundation; the Doris Duke Foundation; The Wallace H. Coulter Foundation; The Dirk and Charlene Kabcenell Foundation; The Long Family Foundation; Lu-Hebert Fund; Gee Family Foundation; Joseph Cotchett; the Julian Abdey and Sabrina Moyle Charitable Fund; and Nanci Nishimura.
We would also like to thank the Leaders Forum for its thought leadership and valuable assistance in helping make this survey possible.
The strategic communications campaign used to promote the research was made possible with generous support from the Doris Duke Foundation.
The terms Asian, Asians living in the United States , U.S. Asian population and Asian Americans are used interchangeably throughout this report to refer to U.S. adults who self-identify as Asian, either alone or in combination with other races or Hispanic identity.
Ethnicity and ethnic origin labels, such as Chinese and Chinese origin, are used interchangeably in this report for findings for ethnic origin groups, such as Chinese, Filipino, Indian, Japanese, Korean or Vietnamese. For this report, ethnicity is not nationality. For example, Chinese in this report are those self-identifying as of Chinese ethnicity, rather than necessarily being a current or former citizen of the People’s Republic of China. Ethnic origin groups in this report include those who self-identify as one Asian ethnicity only, either alone or in combination with a non-Asian race or ethnicity.
Less populous Asian origin groups in this report are those who self-identify with ethnic origin groups that are not among the six largest Asian origin groups. The term includes those who identify with only one Asian ethnicity. These ethnic origin groups each represent about 2% or less of the overall Asian population in the U.S. For example, those who identify as Burmese, Hmong or Pakistani are included in this category. These groups are unreportable on their own due to small sample sizes, but collectively they are reportable under this category.
The terms Asian origins and Asian origin groups are used interchangeably throughout this report to describe ethnic origin groups.
Immigrants in this report are people who were not U.S. citizens at birth – in other words, those born outside the U.S., Puerto Rico or other U.S. territories to parents who are not U.S. citizens. I mmigrant , first generation and foreign born are used interchangeably to refer to this group.
Naturalized citizens are immigrants who are lawful permanent residents who have fulfilled the length of stay and other requirements to become U.S. citizens and who have taken the oath of citizenship.
U.S. born refers to people born in the 50 U.S. states or the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico or other U.S. territories.
Second generation refers to people born in the 50 states or the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico or other U.S. territories with at least one first-generation (immigrant) parent.
Third or higher generation refers to people born in the 50 states or the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico or other U.S. territories with both parents born in the 50 states, D.C., Puerto Rico or other U.S. territories.
The nation’s Asian population is fast growing and diverse. Numbering more than 23 million, the population has ancestral roots across the vast, ethnically and culturally rich Asian continent. For Asians living in the United States, this diversity is reflected in how they describe their own identity. According to a new, nationwide, comprehensive survey of Asian adults living in the U.S., 52% say they most often use ethnic labels that reflect their heritage and family roots, either alone or together with “American,” to describe themselves. Chinese or Chinese American, Filipino or Filipino American, and Indian or Indian American are examples of these variations.
There are other ways in which Asians living in the U.S. describe their identity. About half (51%) of Asian adults say they use American on its own (10%), together with their ethnicity (25%) or together with “Asian” as Asian American (16%) when describing their identity, highlighting their links to the U.S.
And while pan-ethnic labels such as Asian and Asian American are commonly used to describe this diverse population broadly, the new survey shows that when describing themselves, just 28% use the label Asian (12%) on its own or the label Asian American (16%).
The survey also finds that other labels are used by Asian Americans. Some 6% say they most often prefer regional terms such as South Asian and Southeast Asian when describing themselves.
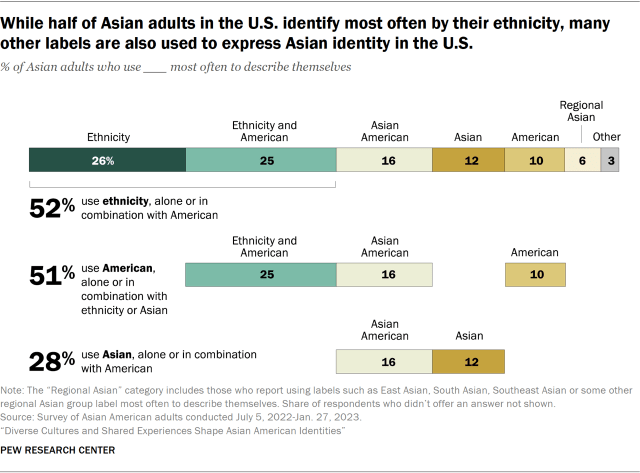
Asian adults see more cultural differences than commonalities across their group as well. When asked to choose between two statements – that Asians in the U.S. share a common culture, or that Asians in the U.S. have many different cultures – nearly all (90%) say U.S. Asians have many different cultures. Just 9% say Asians living in the U.S. share a common culture. This view is widely held across many demographic groups among Asian Americans, according to the survey.
The view that Asian Americans have many different cultures is also one held by the general public, according to another Pew Research Center survey of U.S. adults, conducted in December 2022. Among all U.S. adults, 80% say Asians in the U.S. have many different cultures, while 18% say they share a common culture. 1
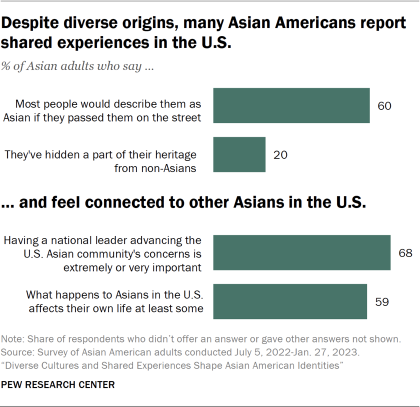
Though Asian Americans’ identities reflect their diverse cultures and origins, Asian adults also report certain shared experiences. A majority (60%) say most people would describe them as “Asian” while walking past them on the street, indicating most Asian adults feel they are seen by others as a single group, despite the population’s diversity. One-in-five say they have hidden a part of their heritage (their ethnic food, cultural practices, ethnic clothing or religious practices) from others who are not Asian, in some cases out of fear of embarrassment or discrimination. Notably, Asian adults ages 18 to 29 are more likely to say they have done this than Asians 65 and older (39% vs. 5%).
Asian adults in the U.S. also feel connected with other Asian Americans. About six-in-ten (59%) say that what happens to Asians in the U.S. affects their own lives, at least to some extent. 2 And about two-thirds (68%) of Asian Americans say it is extremely or very important to have a national leader advocating for the concerns and needs of the Asian population in the U.S.
The new survey also shows that large majorities of Asian adults share similar views on what it takes to be considered truly American. And they consider many of the same factors to be important in their views of the American dream.
These are among the key findings from Pew Research Center’s new survey of Asian American adults, conducted by mail and online from July 5, 2022, to Jan. 27, 2023. This is the largest nationally representative survey of its kind to date that focused on Asian Americans. The survey was conducted in English and five Asian languages, among a representative sample of 7,006 Asian adults living in the United States.
Asian Americans are 7% of the U.S. population, according to a Pew Research Center analysis of the 2021 American Community Survey. Their population is diverse, with roots in more than 20 countries in East Asia, Southeast Asia and the Indian subcontinent. About 54% of the national Asian population are immigrants. The six largest origin groups (Chinese, Filipino, Indian, Japanese, Korean and Vietnamese), a focus of this survey and report, together account for 79% of all Asian Americans.
Overall, about 34% of Asian Americans are the U.S.-born children of immigrant parents, and another 14% are of third or higher generation (meaning their parents were born in the U.S. as well), according to a Pew Research Center analysis of the 2022 Current Population Survey, March Annual Social and Economic Supplement.
This survey and report focus on Asian adults in the U.S. The six largest origin groups together account for 81% of Asian adults. And 68% of Asian American adults are immigrants, according to Center analysis of the 2021 American Community Survey. Additionally, 25% are the U.S.-born children of immigrant parents and 10% are of third or higher generation, according to Center analysis of government data.
The pan-ethnic term “Asian American” emerged in Berkeley, California, in the 1960s as part of a political movement to organize the diverse U.S. Asian population. The creation of an Asian American identity was in reaction to a long history of exclusion of Asians in the country, including the 1882 Chinese Exclusion Act and a pair of Supreme Court cases in the 1920s clarifying that Asians, including South Asians, are not “free White persons” and therefore were excluded from becoming naturalized U.S. citizens. 3 Subsequently, the term was adopted by the federal government and today is the principal identity label used by media, academics, researchers and others to describe today’s diverse Asian American population.
In most cases today, someone is considered Asian or Asian American if they self-identify as such. But Asian Americans do not necessarily agree on which regional or ethnic groups from the Asian continent they consider to be Asian, according to the new survey. The vast majority of Asian adults say they consider those from East Asia, such as Chinese or Koreans (89%); Southeast Asia, such as Vietnamese or Filipinos (88%); and to a lesser extent South Asia such as Indians or Pakistanis (67%) to be Asian.
But Asian adults are split on whether they consider Central Asians such as Afghans or Kazakhs to be Asian (43% of Asian adults say they are). While about half of Indian adults (56%) say they would include Central Asians in the category Asian, fewer than half of Filipino (40%), Chinese (39%), Japanese (34%), Korean (32%) and Vietnamese (30%) adults consider them Asian.
Few Asians say they are knowledgeable about U.S. Asian history
Asian Americans have a long history in the United States. From Chinese laborers who helped build the first transcontinental railroad, to Japanese immigrants who arrived as plantation workers in what is now the state of Hawaii, to the incarceration of Japanese Americans during World War II, to Filipinos being treated as U.S. nationals while the Philippines was a U.S. territory, the Asian American experience has been a part of U.S. history.
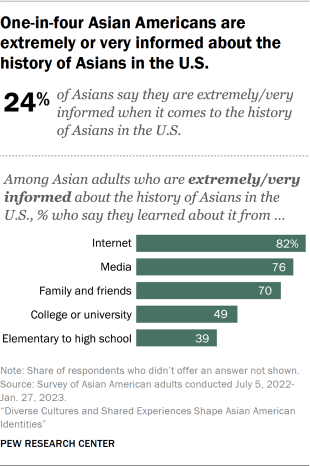
With the passage of the landmark Immigration and Nationality Act of 1965, a new wave of immigrants from Asia began arriving in the United States, creating a new, contemporary U.S. Asian history. The Vietnam War and other conflicts in Southeast Asia brought Vietnamese and other Southeast Asian refugees to the U.S. , first with the passage of the 1975 Indochina Migration and Refugee Assistance Act and then with the Refugee Act of 1980. The 1990 Immigration Act raised immigration ceilings and set in place processes that allowed the flows of Asian immigrants, particularly of high-skilled immigrants, to continue and expand. The U.S. technology boom of the 1990s and 2000s attracted many high-skilled immigrants, particularly from India and China, to tech centers around the country.
This rich history, however, is little-known to Asian adults, according to the new survey. One-in-four (24%) say they are very or extremely informed about history of Asians in the United States, while an equal share (24%) say they are little or not at all informed.
The majority of those very or extremely informed about the history of Asians in the U.S. say they learned about this history through informal channels: internet (82%), media (76%) and family and friends (70%). In contrast, 49% learned about it from college or university courses and 39% from elementary through high school.
Immigrant ties shape Asian Americans’ identities and their life in the U.S.
Immigration experiences, connections with home countries, and how long someone has lived in the U.S. shape many Asian Americans’ identities. Among Asian adults in the U.S., immigrants are more likely than those who are U.S. born to describe their identity most often with their ethnic labels, either alone or together with the label American (56% vs. 41%).
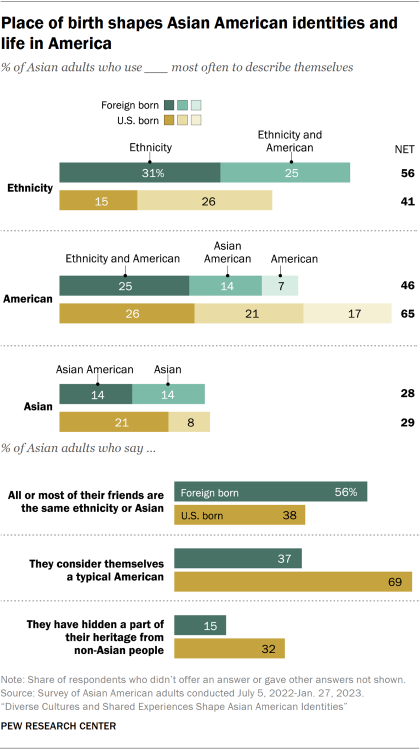
Meanwhile, Asian immigrants are less likely than U.S.-born Asians (46% vs. 65%) to say they most often describe themselves as American in some way – whether by their ethnic label combined with American, as Asian American, or simply as American. Still, nearly half of Asian immigrants describe themselves in one of these three ways.
When it comes to identifying with the label Asian – either alone or as Asian American – immigrant and U.S.-born Asians are about equally likely to say they do so (28% and 29% respectively). Immigrant Asians are less likely than U.S.-born Asians to identify most often as Asian American (14% vs. 21%).
On the question of seeing themselves more as a “typical American” or “very different from a typical American,” Asian immigrant adults are far less likely than those born in the U.S. to think of themselves as a typical American (37% vs. 69%).
Nativity is also tied to how Asians in the U.S. develop their friendships. Those who immigrated to the U.S. are more likely to have friends who are Asian or of the same ethnicity as them than are U.S.-born Asians (56% vs. 38%).
Asian immigrants (15%) are also less likely than U.S.-born Asians (32%) to have ever hidden a part of their heritage from people who are not Asian. When asked in an open-ended question to explain why they hide aspects of their culture, some U.S.-born respondents mentioned phrases such as “fear of discrimination,” “being teased” and “embarrassing.”
Views of identity among Asian American immigrants are often tied to time spent in the U.S.
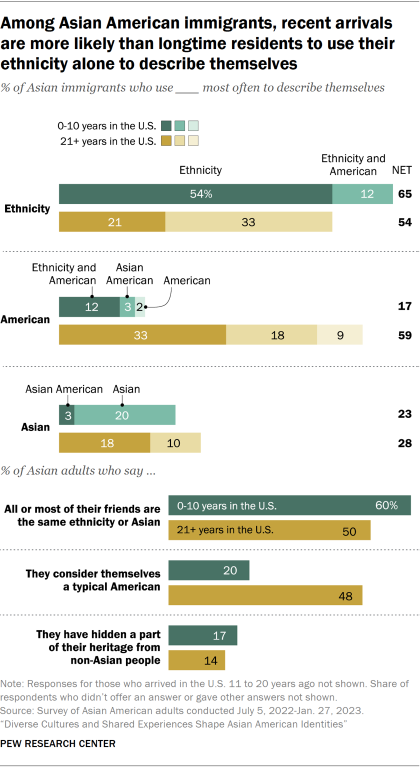
How long Asian immigrants have lived in the U.S. also shapes their identity and experiences. Those who arrived in the U.S. in the past 10 years are more likely than those who arrived more than 20 years ago to say they most often use their ethnicity, such as Filipino or Vietnamese, to describe themselves. And about two-thirds (65%) of those who arrived in the U.S. in the past decade describe their identity most often with their ethnicity’s name, either alone or combined with American, compared with 54% among those who have been in the country for more than two decades.
Roughly half (54%) of those who have arrived in the past 10 years say they most often use only their ethnicity to describe themselves, compared with just 21% of those who arrived more than two decades ago who say the same.
On the other hand, just 17% of Asian immigrants who arrived in the country in the past 10 years describe themselves most often as American, by their ethnic label combined with American, or as Asian American, while 59% of those who arrived more than 20 years ago do so.
When it comes to their circle of friends, 60% of Asian immigrants who arrived in the past 10 years say most or all of their friends are also Asian Americans, while 50% of those who arrived more than 20 years ago say the same.
And when asked if they think of themselves as typical Americans or not, Asian immigrants who arrived in the U.S. in the past decade are substantially less likely than those who arrived more than two decades ago to say they are typical Americans (20% vs. 48%).
The new survey also explored the views Asian Americans have about traits that make one “truly American.” Overall, Asian Americans and the general U.S. population share similar views of what it means to be American. Nearly all Asian adults and U.S. adults say that accepting people of diverse racial and religious backgrounds (94% and 91%), believing in individual freedoms (92% and 94%) and respecting U.S. political institutions and laws (89% and 87%) are important for being truly American.
Similarly, Asian Americans and the U.S. general population share in their views about the American dream. They say having freedom of choice in how to live one’s life (96% and 97% respectively), having a good family life (96% and 94%), retiring comfortably (96% and 94%) and owning a home (both 86%) are important to their view of the American dream. Smaller shares of Asian and U.S. adults (30% and 27%) say owning a business is important to their view of the American dream.
Here are other survey findings highlighting the diverse views and attitudes of Asian adults living in the U.S.:
- Indian adults are the most likely of the six largest Asian origin groups to say they most often use their ethnicity, without the addition of “American,” to describe themselves. About four-in-ten Indian adults (41%) say they do this. By comparison, smaller shares of Korean (30%), Filipino (29%), Chinese (26%) and Vietnamese (23%) adults do the same. Japanese adults (14%) are the least likely among the largest groups to use their ethnic identity term alone.
- Japanese adults are the least likely among the largest Asian origin groups to say they have friendships with other Asians. About one-in-three Japanese adults (34%) say most or all their friends share their own ethnicity or are otherwise Asian. By contrast, about half of all Indian (55%), Vietnamese (55%), Chinese (51%), Korean (50%) and Filipino (48%) respondents say the same.
- One-in-four Korean adults (25%) say they have hidden part of their heritage from people who are not Asian. Some 20% of Indian, 19% of Chinese, 18% of Vietnamese, 16% of Filipino and 14% of Japanese adults say they have done the same.
- Across the largest ethnic groups, about half or more say that what happens to Asians in the U.S. affects what happens in their own lives. About two-thirds of Korean (67%) and Chinese (65%) adults say this. By comparison, 61% of Japanese, 54% of Filipino, 55% of Indian and 52% of Vietnamese adults say they are impacted by what happens to Asians nationally.
- Most Asian adults among the largest ethnic origin groups say a national leader advancing the U.S. Asian community’s concerns is important. Roughly three-in-four Filipino (74%) and Chinese (73%) adults say it is very or extremely important to for the U.S. Asian community to have a national leader advancing its concerns. A majority of Vietnamese (69%), Korean (66%), Japanese (63%) and Indian adults (62%) says the same.
- About half of Vietnamese registered voters (51%) identify with or lean to the Republican Party. In contrast, about two-thirds of Indian (68%), Filipino (68%) and Korean (67%) registered voters identify with or lean toward the Democratic Party. And 56% of Chinese registered voters also associate with the Democratic Party.
- This finding is from a nationally representative survey of 5,132 U.S. adults conducted by Pew Research Center from Dec. 5 to 11, 2022, using the Center’s American Trends Panel . ↩
- In recent years, a major source of concern and fear among many Asian adults in the U.S. has been the rise in reported violence against Asian Americans . ↩
- For more on the history of the creation of an Asian American identity, see Lee, Jennifer and Karthick Ramakrishnan. 2019. “ Who counts as Asian .” Ethnic and Racial Studies. ↩
Sign up for The Briefing
Weekly updates on the world of news & information
- Asian Americans
- Immigrant Populations
- Integration & Identity
- Racial & Ethnic Identity
- Racial Bias & Discrimination
Key facts about Asian Americans living in poverty
Methodology: 2023 focus groups of asian americans, 1 in 10: redefining the asian american dream (short film), the hardships and dreams of asian americans living in poverty, key facts about asian american eligible voters in 2024, most popular, report materials.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Bright Futures/American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) developed a set of comprehensive health guidelines for well-child care, known as the "periodicity schedule." It is a schedule of screenings and assessments recommended at each well-child visit from infancy through adolescence. Schedule of well-child visits. The first week visit (3 to 5 ...
Take blood pressure. Measure oxygen levels. Listen to your child's lungs. Look at your child's eyes, ears, and throat. Press on your child's tummy to feel organs. Move your child's hips ...
The Vaccines for Children (VFC) program provides vaccines to eligible children at no cost. This program provides free vaccines to children who are Medicaid-eligible, uninsured, underinsured, or American Indian/Alaska Native. Check out the program's requirements and talk to your child's doctor or nurse to see if they are a VFC provider.
Immunizations are usually administered at the two-, four-, six-, 12-, and 15- to 18-month well-child visits; the four- to six-year well-child visit; and annually during influenza season ...
Our well-child visit schedule for checkups lets you know how often kids should see a doctor, even when they're not sick. Read the articles below to find out what to expect at your child's next wellness checkup! Your Child's Checkup: Newborn. Your Child's Checkup: 3-5 Days. Your Child's Checkup: 1 Month.
Of course, visiting the pediatrician's office often early in your child's life gives you more opportunities to learn what to expect, ask questions, and help build your parenting skills. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends the following well-check schedule for the first year of your child's life. 3 to 5 days.
7-10 years: Annual well-child check. Vision/hearing and TB screenings; any immunizations previously missed. 11-12 years: Annual well-child check. Depression and TB screenings; DTaP, HPV and ...
Your child's doctor will recommend a schedule for well-child visits. One example is for visits at ages: footnote 1. 3 to 5 days old. By 1 month. 2 months. 4 months. 6 months. 9 months. 1 year. 15 months. 18 months. 2 years. 30 months. 3 years. After age 3, well-child visits are usually scheduled yearly through the teen years.
How often should I schedule well-child visits? When you should come in for a well-child visit depends on your child's age. We follow guidelines set by the American Academy of Pediatrics. Well-child visits are recommended at the following ages for infants and toddlers: First-week visit (3-5 days old)
How often do I need to take my child for well-child visits? Young children grow quickly, so they need to visit the doctor or nurse regularly to make sure they're healthy and developing normally. Children ages 1 to 4 need to see the doctor or nurse when they're: 12 months old; 15 months old (1 year and 3 months) 18 months old (1 year and 6 ...
Regular well-child visits can keep your kid and family healthy and prevent serious illness. It's normal to have questions as they quickly grow from birth to adulthood. Make sure you have plenty of time before and after their checkup to avoid any stress. Write down questions or concerns as soon as they come to mind before your kid's well ...
1-4 years. Since the bodies and minds of young children are developing so rapidly, seeing a pediatrician is important to ensure they are meeting all of the appropriate cognitive, social, emotional, behavioral, and speech development milestones. The ages for these well visit appointments are: 12 months. 15 months. 18 months.
Well-child visit: 13 years: Well-child visit. Varicella blood test, if vaccine not given and no history of chickenpox. 14 & 15 years: Well-child visit. HPV for ages 15 through 26 and immunocompromised persons, 3-dose series given at 0, 1-2 months, 6 months. 16 years: Well-child visit. MCV booster. 17 years: Well-child visit
If you are a UnitedHealthcare Community Plan member, you may have access to our Healthy First Steps program, which can help you find a care provider, schedule well-child visits, connect with educational and community resources and more. To get started, call 1-800-599-5985, TTY 711, Monday through Friday, from 8 a.m. to 5 p.m.
Find a pediatrician. Call (502) 629-5437 (KIDS), option 3. Every parent wants to know that their child is growing and healthy. A well-child visit is a crucial part of every child's health care journey, from the time they are born until they reach adulthood. A well-child visit is a regularly scheduled health check up with your child's ...
The Well-Child Visit: Why Go and What to Expect Depending on your child's age, you may have well-child visits every few weeks, months, or yearly (see the AAP Schedule of Well-Child Care Visits link below). To help you create a plan for when you get home, write a "to do" list during the visit. List tasks that you can easily fit into your
Overview. Kids ages 11 to 14 years need to go to the doctor or nurse for a "well-child visit" once a year. A well-child visit is when you take your child to the doctor to make sure they're healthy and developing normally. This is different from other visits for sickness or injury. At a well-child visit, the doctor or nurse can help catch ...
Regularly scheduled checkups, often referred to as well-child visits, begin shortly after birth and last through the teenage years. All CHKD pediatric practices follow the American Academy of Pediatric (AAP) Guidelines on well-child visits. Typically, we see newborns within one to three days after hospital discharge.
Overview. Teens ages 15 to 17 years need to go to the doctor or nurse for a "well-child visit" once a year. A well-child visit is when you take your teen to the doctor to make sure they're healthy and developing normally. This is different from other visits for sickness or injury. At a well-child visit, the doctor or nurse can help catch ...
Improving Infant Well-Child VisitsHigh-quality well-child visits can improve children's health, support caregivers' behaviors to promote their children's health, and prevent injury and harm. The American Academy of Pediatrics and Bright Futures recommend nine well-care visits by the time children turn 15 months of age.
410-955-5000 Maryland. 855-695-4872 Outside of Maryland. +1-410-502-7683 International. In addition to taking your child to the healthcare provider when your child is ill, or needs an exam to participate in a particular activity, routine well-care visits for your child are recommended.
Your child's doctor will recommend a schedule for well-child visits. One example is for visits at ages: footnote 1. 3 to 5 days old. By 1 month. 2 months. 4 months. 6 months. 9 months. 1 year. 15 months. 18 months. 2 years. 30 months. 3 years. After age 3, well-child visits are usually scheduled yearly through the teen years.
The CDC says that in 2021, there were 11.6 abortions in the U.S. per 1,000 women ages 15 to 44. (That figure excludes data from California, the District of Columbia, Maryland, New Hampshire and New Jersey.) Like Guttmacher's data, the CDC's figures also suggest a general decline in the abortion rate over time.
Press office. 8.30am to 6pm Monday to Friday 0300 013 0415. The following links open in a new tab. Published 8 February 2024. New guidance from Ofsted and the Care Quality Commission (CQC) for ...
Donald Trump may have to miss out on his son Barron's high school graduation ceremony next month due to the timing of the former president's first historic criminal trial. Trump's hush-money trial ...
Overall, about 34% of Asian Americans are the U.S.-born children of immigrant parents, and another 14% are of third or higher generation (meaning their parents were born in the U.S. as well), according to a Pew Research Center analysis of the 2022 Current Population Survey, March Annual Social and Economic Supplement.