NASA has solved the mystery of Voyager 1's strange data transmissions

As NASA wrestles with Artemis 1's engine woes that are delaying the return to human exploration of the moon, the agency has solved another mystery, one causing its 45-year-old spacecraft, Voyager 1, to transmit garbled data.
NASA engineers have found the bug that was causing critical instruments on the four-decade-old spacecraft to send "garbled" health information to mission controllers on Earth.
- Apple Vision Pro review: Fascinating, flawed, and needs to fix 5 things
- Apple builds a slimmed-down AI model using Stanford, Google innovations
- I tested the AI gadget that got the internet buzzing and it left me wanting more
- 9 biggest announcements at Google I/O 2024: Gemini, Search, Project Astra, and more
Voyager 1's attitude articulation and control system (AACS), which keeps its antenna directed at Earth, earlier this year started to send back information that didn't reflect what was actually happening onboard . The AACS appeared to be functioning normally, but the data it was sending back was deemed invalid because it didn't match any possible state the system could be in.
SEE: What is Artemis? Everything you need to know about NASA's new moon mission
Also, the rest of the probe appeared healthy, since it continued to gather and return science data.
The agency today said it has found the source of the garbled information: a zombie computer that should not have been used to relay telemetry data.
"The AACS had started sending the telemetry data through an onboard computer known to have stopped working years ago, and the computer corrupted the information," NASA said in a press release .
While NASA engineers have solved the problem, they still don't know why the AACS started routing information through the non-functioning computer. However, they guess that the AACS probably received a faulty command from another onboard computer.
NASA notes that if that other onboard computer generated a bad command, there could be an issue somewhere else on the spacecraft. The search continues for what the underlying issue is, but engineers believe it won't drastically harm its future.
SEE: NASA's new tiny, high-powered laser could find water on the Moon
"We're happy to have the telemetry back," said Suzanne Dodd, Voyager's project manager.
"We'll do a full memory readout of the AACS and look at everything it's been doing. That will help us try to diagnose the problem that caused the telemetry issue in the first place. So we're cautiously optimistic, but we still have more investigating to do."
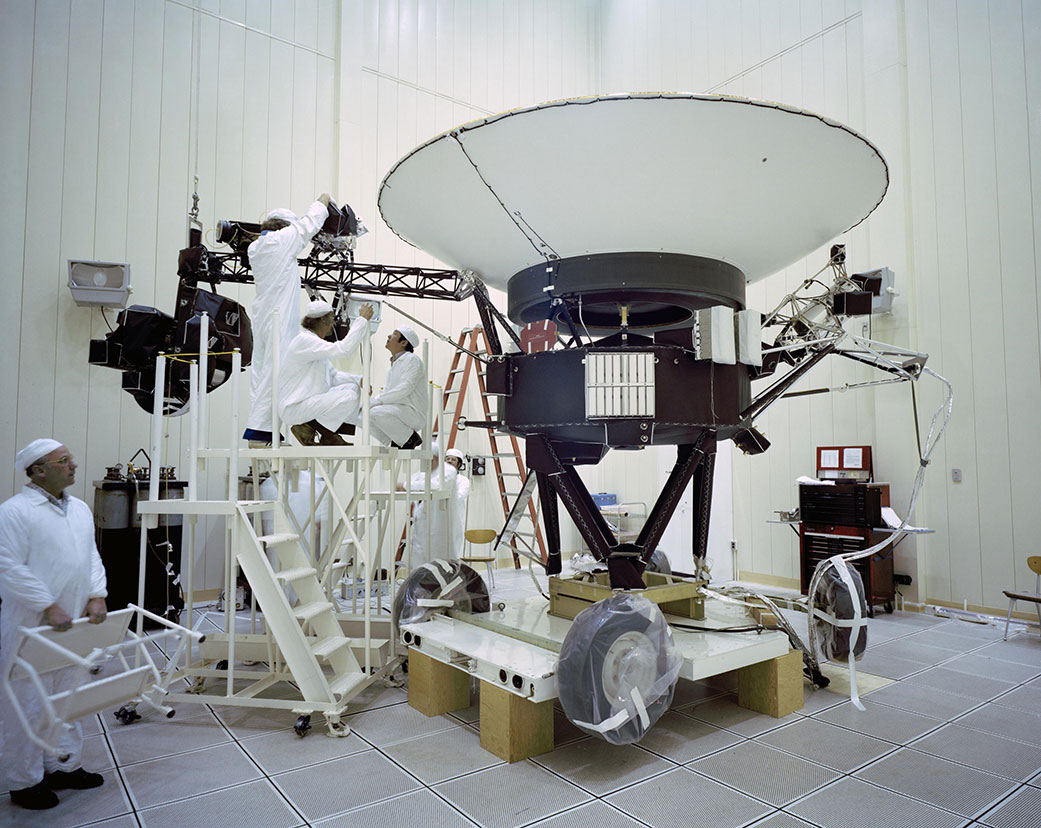
Voyager 1 launched from Cape Canaveral in September 1977 and is now the farthest spacecraft from Earth, traveling in space at about 14.5 billion miles (23.3 billion kilometers) away. It would take light about 20 hours to travel from the spacecraft.
The Voyager 1 was the first human-made object to reach into interstellar space and in 1998 overtook NASA's Pioneer 10 to become the most distant human-made object.
It reached interstellar space in August 2012 and, among other things, takes measurements of the density of material in interstellar space . It will eventually exit the solar system but not for a long, long time.

The best robot vacuums you can buy in 2024: Expert tested
The flagship roborock s7 mav ultra robot vacuum mop is still $500 off after prime day, crowdstrike caused windows outage chaos for airports, banks, and more. here's what happened.

Suggested Searches
- Climate Change
- Expedition 64
- Mars perseverance
- SpaceX Crew-2
- International Space Station
- View All Topics A-Z
Humans in Space
Earth & climate, the solar system, the universe, aeronautics, learning resources, news & events.

NASA-Funded Studies Explain How Climate Is Changing Earth’s Rotation

55 Years Ago: Apollo 11’s One Small Step, One Giant Leap

Hubble Studies a Potential Galactic Merger
- Search All NASA Missions
- A to Z List of Missions
- Upcoming Launches and Landings
- Spaceships and Rockets
- Communicating with Missions
- James Webb Space Telescope
- Hubble Space Telescope
- Why Go to Space
- Commercial Space
- Destinations
- Living in Space
- Explore Earth Science
- Earth, Our Planet
- Earth Science in Action
- Earth Multimedia
- Earth Science Researchers
- Pluto & Dwarf Planets
- Asteroids, Comets & Meteors
- The Kuiper Belt
- The Oort Cloud
- Skywatching
- The Search for Life in the Universe
- Black Holes
- The Big Bang
- Dark Energy & Dark Matter
- Earth Science
- Planetary Science
- Astrophysics & Space Science
- The Sun & Heliophysics
- Biological & Physical Sciences
- Lunar Science
- Citizen Science
- Astromaterials
- Aeronautics Research
- Human Space Travel Research
- Science in the Air
- NASA Aircraft
- Flight Innovation
- Supersonic Flight
- Air Traffic Solutions
- Green Aviation Tech
- Drones & You
- Technology Transfer & Spinoffs
- Space Travel Technology
- Technology Living in Space
- Manufacturing and Materials
- Science Instruments
- For Kids and Students
- For Educators
- For Colleges and Universities
- For Professionals
- Science for Everyone
- Requests for Exhibits, Artifacts, or Speakers
- STEM Engagement at NASA
- NASA's Impacts
- Centers and Facilities
- Directorates
- Organizations
- People of NASA
- Internships
- Our History
- Doing Business with NASA
- Get Involved
NASA en Español
- Aeronáutica
- Ciencias Terrestres
- Sistema Solar
- All NASA News
- Video Series on NASA+
- Newsletters
- Social Media
- Media Resources
- Upcoming Launches & Landings
- Virtual Events
- Sounds and Ringtones
- Interactives
- STEM Multimedia

Ground Antenna Trio to Give NASA’s Artemis Campaign ‘LEGS’ to Stand On

Eileen Collins Broke Barriers as America’s First Female Space Shuttle Commander

NASA Research Volunteers to Begin Next Simulated Mission to Mars

Remembering Joe Engle: Astronaut, Test Pilot, Legend

Registration Opens for the 2024 NASA International Space Apps Challenge

NASA Celebrates 20 Years of Earth-Observing Aura Satellite
Ice Giant Resources
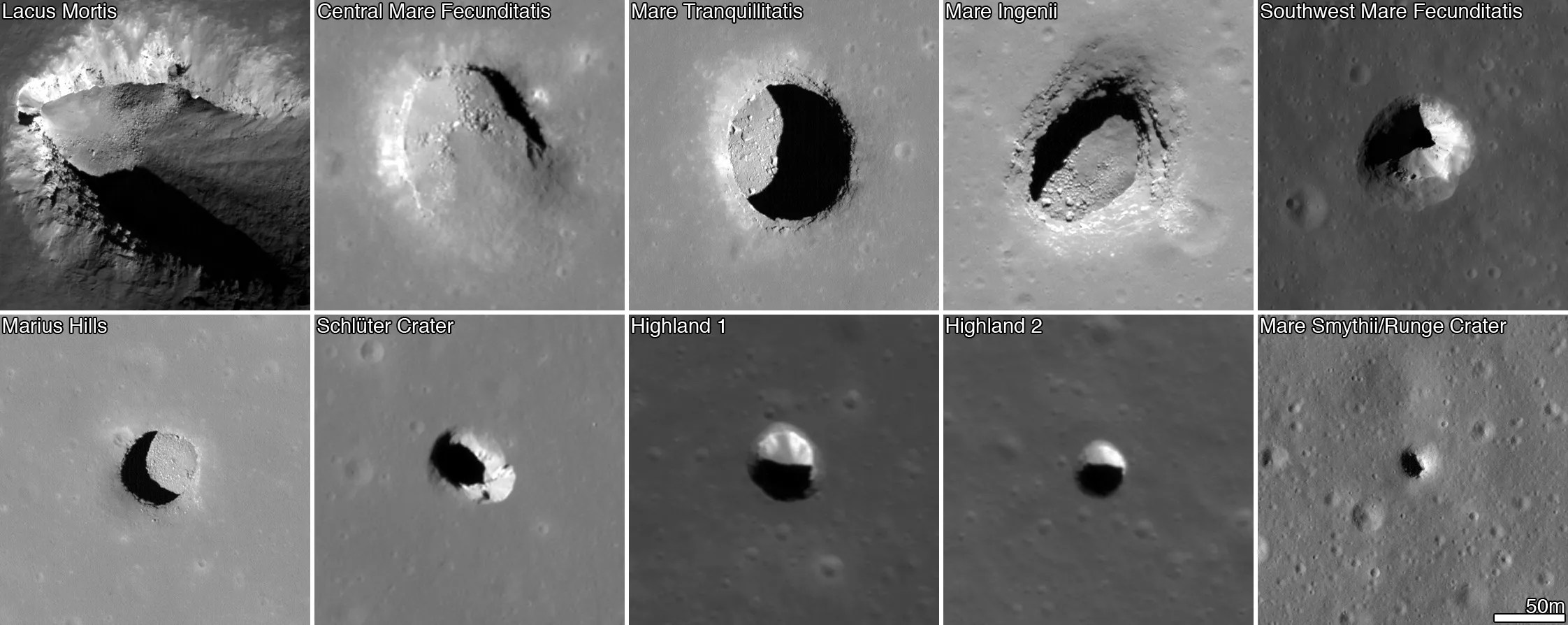

New Evidence Adds to Findings Hinting at Network of Caves on Moon
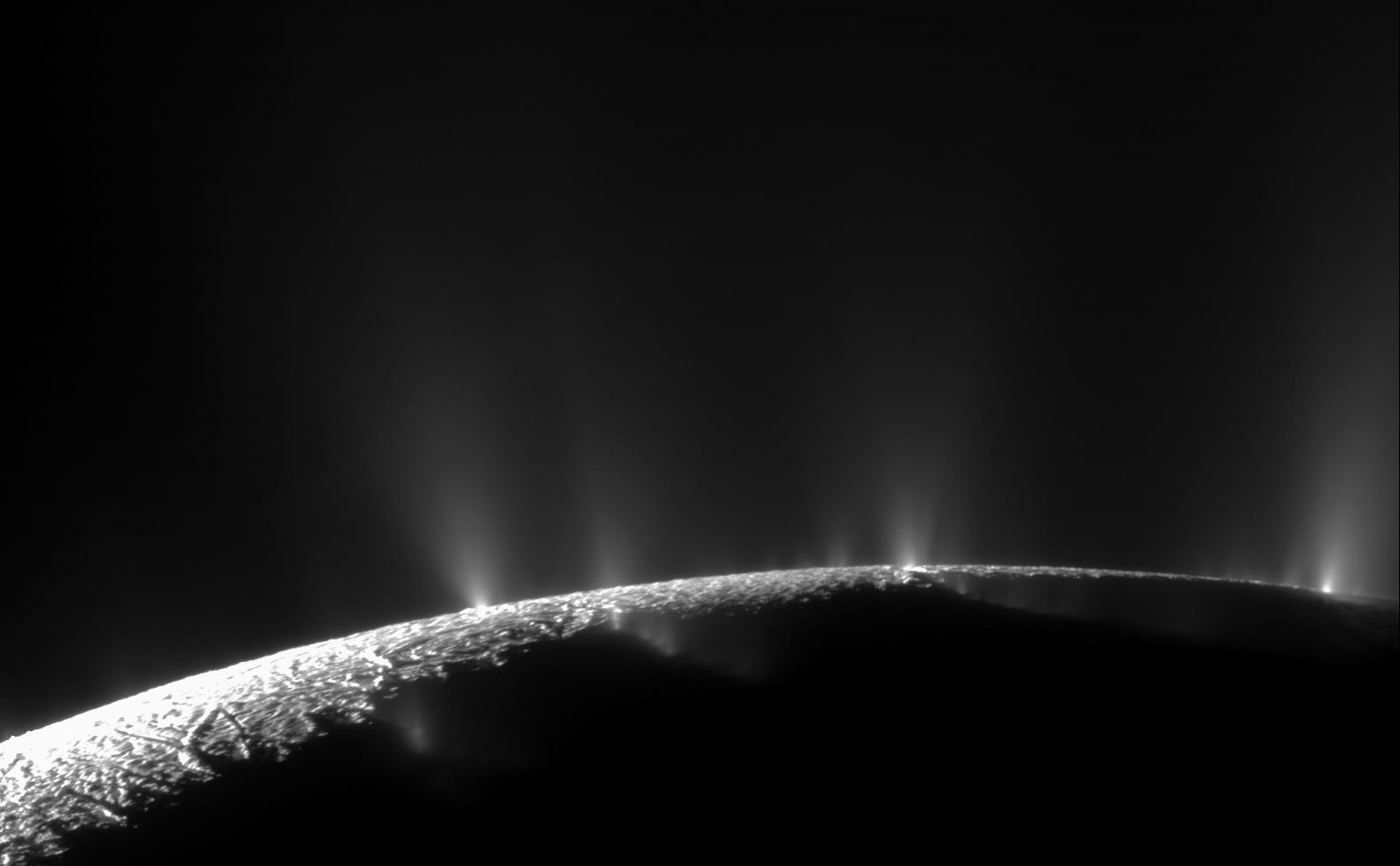

NASA: Life Signs Could Survive Near Surfaces of Enceladus and Europa

Discovery Alert: With Six New Worlds, 5,500 Discovery Milestone Passed!

Amendment 35: C.20 Interdisciplinary Consortia for Astrobiology Research Final Text and Due Dates.

Amendment 34: A.14 Integrated Water Field Campaign Final Text and Due Dates

LIVE: NASA is with you from Oshkosh
Nasa to host panels, forums, and more at oshkosh 2024.

Here’s How AI Is Changing NASA’s Mars Rover Science

Tech Today: NASA’s Moonshot Launched Commercial Fuel Cell Industry
Slow Your Student’s ‘Summer Slide’ and Beat Boredom With NASA STEM

Experience the Launch of NASA’s SpaceX Crew-9 Mission

NASA Awards Launch Excitement for STEM Learning Nationwide

Astronauta de la NASA Frank Rubio

Diez maneras en que los estudiantes pueden prepararse para ser astronautas

Astronauta de la NASA Marcos Berríos
Engineers investigating nasa’s voyager 1 telemetry data, jet propulsion laboratory.
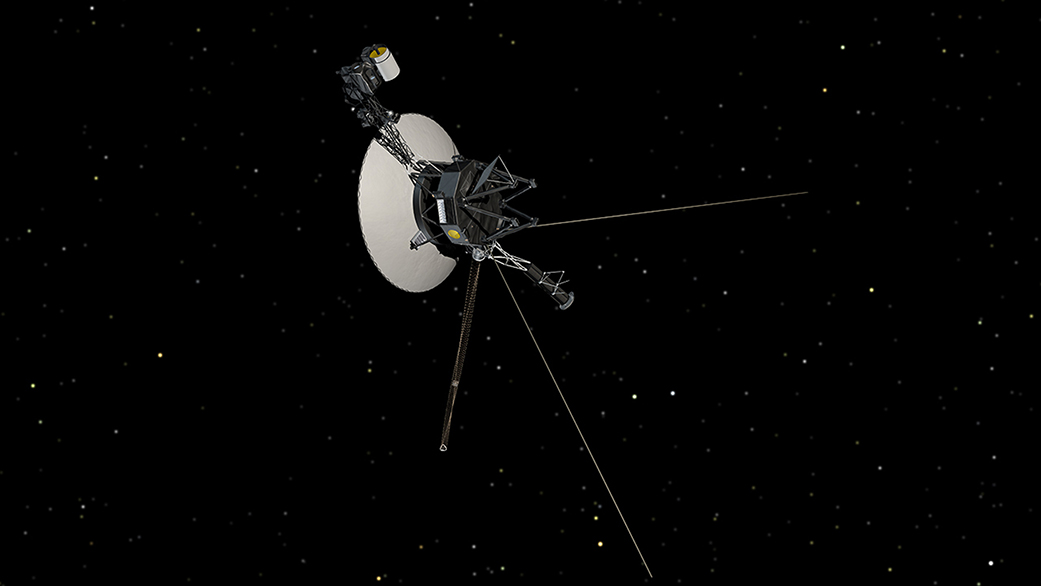

While the spacecraft continues to return science data and otherwise operate as normal, the mission team is searching for the source of a system data issue.
The engineering team with NASA’s Voyager 1 spacecraft is trying to solve a mystery: The interstellar explorer is operating normally, receiving and executing commands from Earth, along with gathering and returning science data. But readouts from the probe’s attitude articulation and control system (AACS) don’t reflect what’s actually happening onboard.
The AACS controls the 45-year-old spacecraft’s orientation. Among other tasks, it keeps Voyager 1’s high-gain antenna pointed precisely at Earth, enabling it to send data home. All signs suggest the AACS is still working, but the telemetry data it’s returning is invalid. For instance, the data may appear to be randomly generated, or does not reflect any possible state the AACS could be in.
The issue hasn’t triggered any onboard fault protection systems, which are designed to put the spacecraft into “safe mode” – a state where only essential operations are carried out, giving engineers time to diagnose an issue. Voyager 1’s signal hasn’t weakened, either, which suggests the high-gain antenna remains in its prescribed orientation with Earth.
The team will continue to monitor the signal closely as they continue to determine whether the invalid data is coming directly from the AACS or another system involved in producing and sending telemetry data. Until the nature of the issue is better understood, the team cannot anticipate whether this might affect how long the spacecraft can collect and transmit science data.
Voyager 1 is currently 14.5 billion miles (23.3 billion kilometers) from Earth, and it takes light 20 hours and 33 minutes to travel that difference. That means it takes roughly two days to send a message to Voyager 1 and get a response – a delay the mission team is well accustomed to.
“A mystery like this is sort of par for the course at this stage of the Voyager mission,” said Suzanne Dodd, project manager for Voyager 1 and 2 at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. “The spacecraft are both almost 45 years old, which is far beyond what the mission planners anticipated. We’re also in interstellar space – a high-radiation environment that no spacecraft have flown in before. So there are some big challenges for the engineering team. But I think if there’s a way to solve this issue with the AACS, our team will find it.”
It’s possible the team may not find the source of the anomaly and will instead adapt to it, Dodd said. If they do find the source, they may be able to solve the issue through software changes or potentially by using one of the spacecraft’s redundant hardware systems.
It wouldn’t be the first time the Voyager team has relied on backup hardware: In 2017, Voyager 1’s primary thrusters showed signs of degradation, so engineers switched to another set of thrusters that had originally been used during the spacecraft’s planetary encounters . Those thrusters worked, despite having been unused for 37 years.
Voyager 1’s twin, Voyager 2 (currently 12.1 billion miles, or 19.5 billion kilometers, from Earth), continues to operate normally.
Launched in 1977, both Voyagers have operated far longer than mission planners expected, and are the only spacecraft to collect data in interstellar space. The information they provide from this region has helped drive a deeper understanding of the heliosphere, the diffuse barrier the Sun creates around the planets in our solar system.
Each spacecraft produces about 4 fewer watts of electrical power a year, limiting the number of systems the craft can run. The mission engineering team has switched off various subsystems and heaters in order to reserve power for science instruments and critical systems. No science instruments have been turned off yet as a result of the diminishing power, and the Voyager team is working to keep the two spacecraft operating and returning unique science beyond 2025.
While the engineers continue to work at solving the mystery that Voyager 1 has presented them, the mission’s scientists will continue to make the most of the data coming down from the spacecraft’s unique vantage point.
More About the Mission
The Voyager spacecraft were built by JPL, which continues to operate both. JPL is a division of Caltech in Pasadena. The Voyager missions are a part of the NASA Heliophysics System Observatory, sponsored by the Heliophysics Division of the Science Mission Directorate in Washington.
For more information about the Voyager spacecraft, visit:
https://www.nasa.gov/voyager
Calla Cofield Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif. 626-808-2469 [email protected] 2022-073
NASA finds clue while solving Voyager 1's communication breakdown case
An outlier signal has brought ground control closer to decoding the troubling problem.

NASA engineers are a step closer to solving the communication problem that left the Voyager 1 spacecraft, which presently sits outside the solar system, unable to send usable data back to Earth.
In 2012, Voyager 1 became the first human-made object to leave the solar system and enter interstellar space . For 11 years following this achievement, the spacecraft dutifully sent data to ground control. This was data that detailed how space works beyond the influence of the sun. In Nov. 2023, however, Voyager 1's communications with ground operators stopped making sense.
To be clear, however, Voyager 2 , which followed its spacecraft sibling out of the solar system in 2018, is still operational and communicating with Earth.
"Effectively, the call between the spacecraft and the Earth was still connected, but Voyager's 'voice' was replaced with a monotonous dial tone," Voyager 1's engineering team previously told Space.com .
The source of the issue appears to be one of Voyager 1's three onboard computers: The flight data subsystem (FDS). This computer, NASA says , is responsible for packaging science and engineering data before it's sent to Earth by the spacecraft's telemetry modulation unit.
Related: NASA's Voyager 1 glitch has scientists sad yet hopeful: 'Voyager 2 is still going strong'
The positive step towards solving communications issues between ground control and Voyager 1 came on March 3 when the Voyager mission team detected activity from one section of the FDS that was different from the rest of the computer’s garbled data stream.
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!
Voyager 1's messaging to Earth comes in the form of 1s and 0s, a computer language called binary code — but since the end of last year, this code has carried no meaning. Even the newly detected signal is still not in the correct format Voyager 1 should be using when FDS is functioning as designed, meaning the operating team was initially not quite sure what to make of it.
This changed, however, when an engineer at NASA's Deep Space Network , which is tasked with operating radio antennas that communicate with Voyager 1 and its interstellar sibling Voyager 2, as well as other NASA spacecraft closer to home, got a look at the code. The unnamed engineer was able to decode the outlier signal, discovering that it contained a readout of the FDS' entire memory.

Encoded with the FDS memory are performance instructions and code values that can change either if the spacecraft's status changes or if commanded to do so. Science and engineering data to be sent back to Earth are also locked up in the memory.
The team will now compare this new signal, which occurred because of a prompt, or "poke," from mission control, to data that was sent back to Earth just before Voyager 1 started spouting binary nonsense. Finding discrepancies between regular Voyager 1 data and this poke-prompted signal will help the crew hunt for the source of the issue. The idea of the poke was to prompt FDS to try using different sequences in its software package and determine if the communication issue could be resolved by navigating around a corrupted or damaged section.
— Voyager 2: An iconic spacecraft that's still exploring 45 years on
— NASA's interstellar Voyager probes get software updates beamed from 12 billion miles away
— NASA Voyager 2 spacecraft extends its interstellar science mission for 3 more years
Voyager 1 is currently around 15 billion miles (24 billion kilometers) from Earth, meaning that solving communication issues can be a painstaking process. It takes 22.5 hours to receive a radio signal from Voyager 1, then another 22.5 hours to receive a response via the Deep Space Network's antennas.
That means the results of NASA's poke were received on March 3, and on March 7 engineers started working to decode this signal. Three days later they determined the signal contains an FDS memory readout.
NASA scientists and engineers will continue to analyze this readout to restore communication with the pioneering space mission that extended humanity's reach beyond the solar system.
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: [email protected].
Robert Lea is a science journalist in the U.K. whose articles have been published in Physics World, New Scientist, Astronomy Magazine, All About Space, Newsweek and ZME Science. He also writes about science communication for Elsevier and the European Journal of Physics. Rob holds a bachelor of science degree in physics and astronomy from the U.K.’s Open University. Follow him on Twitter @sciencef1rst.
All about rockets
Where will we be in space in 2049? A look at spaceflight over the next 25 years
United Nations marks Apollo 11 55th with international moon missions stamps
Most Popular
- 2 This Week In Space podcast: Episode 120 — Remembering Apollo 11 & Looking Ahead
- 3 What became of the flags Apollo astronauts left on the moon?
- 4 Is there a 'true' story behind the fake Apollo moon landing in 'Fly Me to the Moon?'
- 5 NASA marks moon landing anniversary by dedicating building to 'women of Apollo'
DATA INTERFACES
Through the Rate, Flux and Spectra User Interfaces you may generate figures and download CRS data for the lifetime of the Voyager mission. These interfaces have been tested with Microsoft Edge, Chrome and Firefox browsers.
Note: Voyager-1 and Voyager-2 flux data are not available after 04/28/2022. The Voyager-1 data requires recalibration as a result of the V1 CRS Heater Turn Off.
Warning: the voyager crs team is working on correcting early misssion data (voyager 1 and voyager 2) which contain a ground communication facility error flag. recent reprocessing of data for the entire mission has resulted in incorrect fluxes occasionally appearing in our public database when these flags are present. data for 1984, 1985 and 1993 are particularly affected. please use caution if you are working with data from these years., notice: the data interface portions of this website are unavailable pending software updates., documentation.
NASA’s Voyager 1 Resumes Sending Engineering Updates to Earth

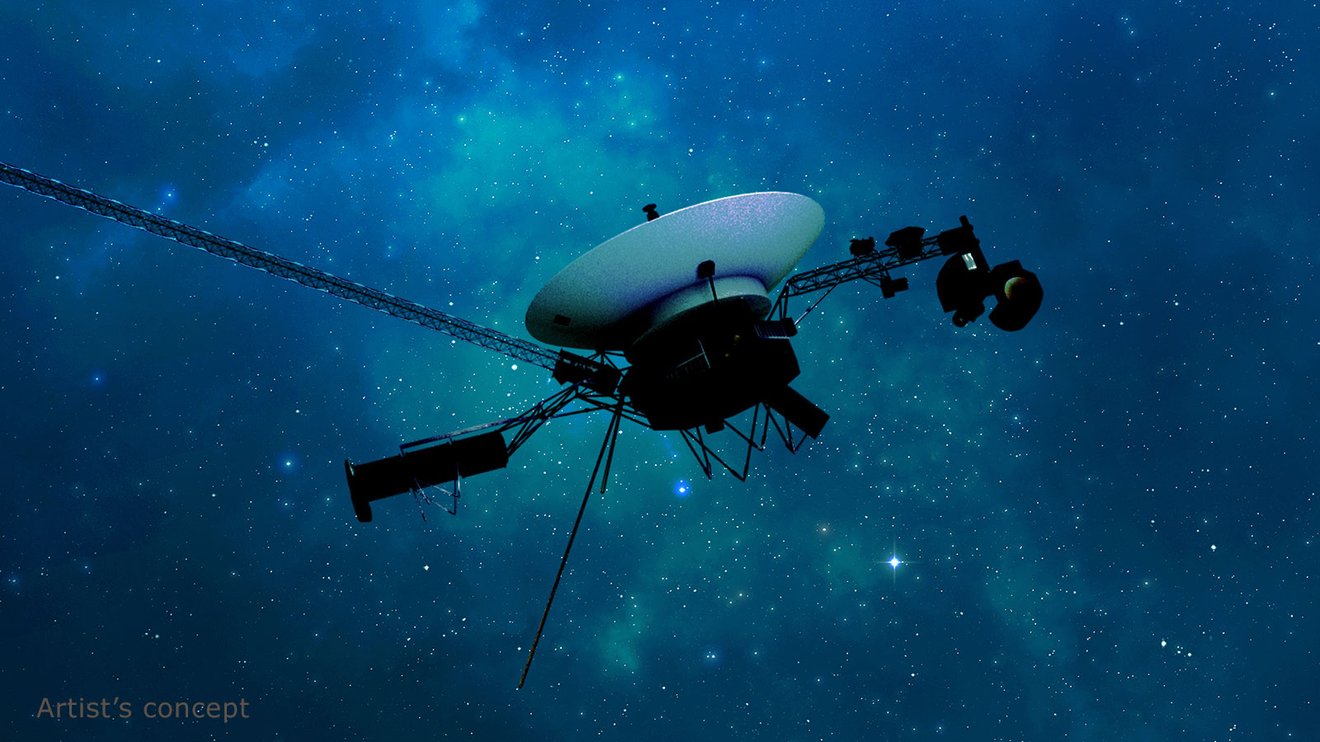
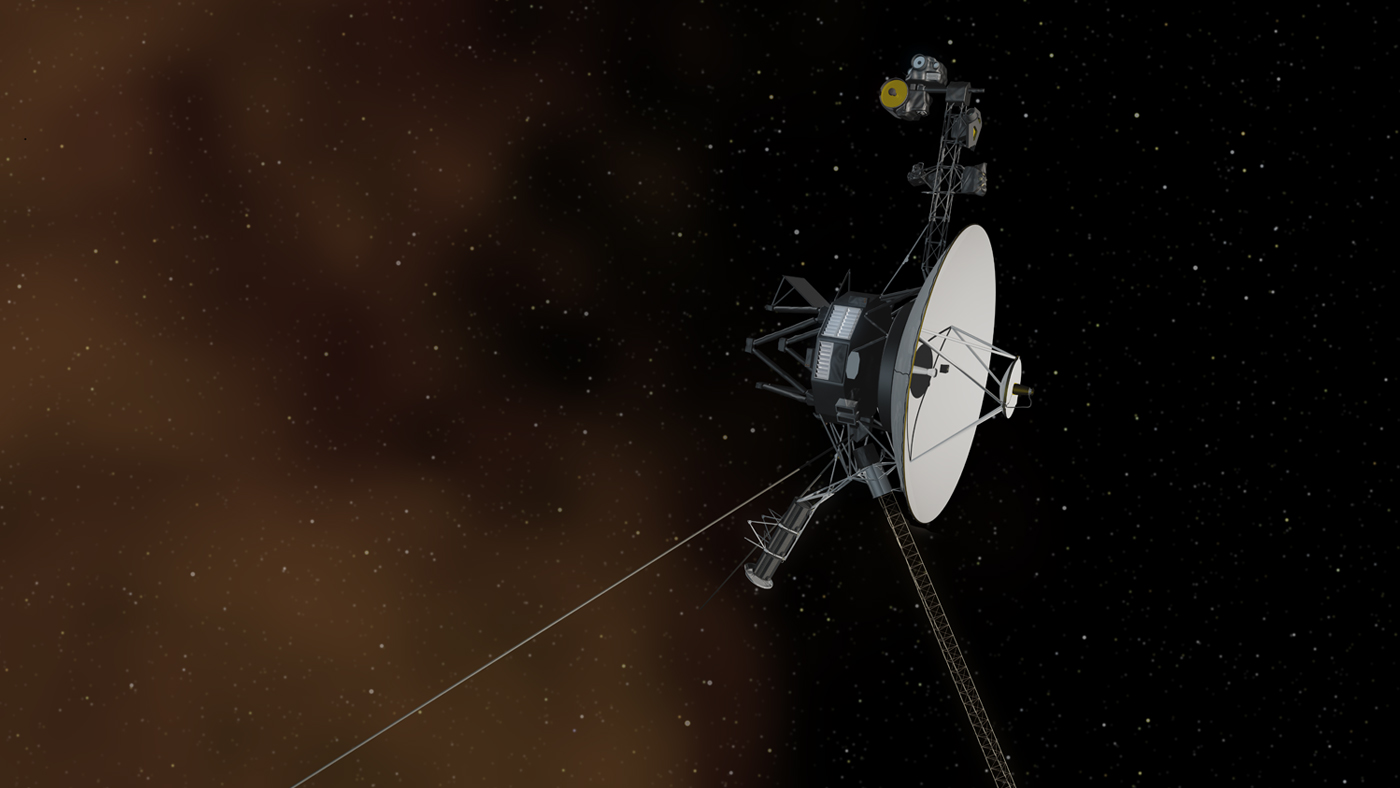
NASA’s Voyager 1 spacecraft is depicted in this artist’s concept traveling through interstellar space, or the space between stars, which it entered in 2012.
After some inventive sleuthing, the mission team can — for the first time in five months — check the health and status of the most distant human-made object in existence.
For the first time since November , NASA’s Voyager 1 spacecraft is returning usable data about the health and status of its onboard engineering systems. The next step is to enable the spacecraft to begin returning science data again. The probe and its twin, Voyager 2, are the only spacecraft to ever fly in interstellar space (the space between stars).
Voyager 1 stopped sending readable science and engineering data back to Earth on Nov. 14, 2023, even though mission controllers could tell the spacecraft was still receiving their commands and otherwise operating normally. In March, the Voyager engineering team at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California confirmed that the issue was tied to one of the spacecraft’s three onboard computers, called the flight data subsystem (FDS). The FDS is responsible for packaging the science and engineering data before it’s sent to Earth.

After receiving data about the health and status of Voyager 1 for the first time in five months, members of the Voyager flight team celebrate in a conference room at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory on April 20.
The team discovered that a single chip responsible for storing a portion of the FDS memory — including some of the FDS computer’s software code — isn’t working. The loss of that code rendered the science and engineering data unusable. Unable to repair the chip, the team decided to place the affected code elsewhere in the FDS memory. But no single location is large enough to hold the section of code in its entirety.
So they devised a plan to divide the affected code into sections and store those sections in different places in the FDS. To make this plan work, they also needed to adjust those code sections to ensure, for example, that they all still function as a whole. Any references to the location of that code in other parts of the FDS memory needed to be updated as well.
The team started by singling out the code responsible for packaging the spacecraft’s engineering data. They sent it to its new location in the FDS memory on April 18. A radio signal takes about 22 ½ hours to reach Voyager 1, which is over 15 billion miles (24 billion kilometers) from Earth, and another 22 ½ hours for a signal to come back to Earth. When the mission flight team heard back from the spacecraft on April 20, they saw that the modification worked: For the first time in five months, they have been able to check the health and status of the spacecraft.
Get the Latest News from the Final Frontier
During the coming weeks, the team will relocate and adjust the other affected portions of the FDS software. These include the portions that will start returning science data.
Voyager 2 continues to operate normally. Launched over 46 years ago , the twin Voyager spacecraft are the longest-running and most distant spacecraft in history. Before the start of their interstellar exploration, both probes flew by Saturn and Jupiter, and Voyager 2 flew by Uranus and Neptune.
Caltech in Pasadena, California, manages JPL for NASA.
News Media Contact
Calla Cofield
Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif.
626-808-2469

Voyager 1 Sends Clear Data to NASA for the First Time in Five Months
The farthest spacecraft from Earth had been transmitting nonsense since November, but after an engineering tweak, it finally beamed back a report on its health and status
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/accounts/headshot/Will-Sullivan-photo.png)
Will Sullivan
Daily Correspondent
:focal(2016x1133:2017x1134)/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/filer_public/32/30/3230d19e-cc50-4905-840c-7f3afeb2a0c3/e1-pia26275-voyager-copy-16.jpg)
For the first time in five months, NASA has received usable data from Voyager 1, the farthest spacecraft from Earth.
The aging probe, which has traveled more than 15 billion miles into space, stopped transmitting science and engineering data on November 14. Instead, it sent NASA a nonsensical stream of repetitive binary code . For months, the agency’s engineers undertook a slow process of trial and error, giving the spacecraft various commands and waiting to see how it responded. Thanks to some creative thinking, the team identified a broken chip on the spacecraft and relocated some of the code that was stored there, according to the agency .
NASA is now receiving data about the health and status of Voyager 1’s engineering systems. The next step is to get the spacecraft to start sending science data again.
“Today was a great day for Voyager 1,” Linda Spilker , a Voyager project scientist at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), said in a statement over the weekend, per CNN ’s Ashley Strickland. “We’re back in communication with the spacecraft. And we look forward to getting science data back.”
Hi, it's me. - V1 https://t.co/jgGFBfxIOe — NASA Voyager (@NASAVoyager) April 22, 2024
Voyager 1 and its companion, Voyager 2, separately launched from Earth in 1977. Between the two of them, the probes have studied all four giant planets in the outer solar system—Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune—along with 48 of their moons and the planets’ magnetic fields. The spacecraft observed Saturn’s rings in detail and discovered active volcanoes on Jupiter’s moon Io .
Originally designed for a five-year mission within our solar system, both probes are still operational and chugging along through space, far beyond Pluto’s orbit. In 2012, Voyager 1 became the first human-made object to reach interstellar space, the area between stars. The probe is now about eight times farther from the sun than Uranus is on average.
Over the decades, the Voyager spacecraft have transmitted data collected on their travels back to NASA scientists. But in November, Voyager 1 started sending gibberish .
Engineers determined Voyager 1’s issue was with one of three onboard computers, called the flight data system (FDS), NASA said in a December blog post . While the spacecraft was still receiving and executing commands from Earth, the FDS was not communicating properly with a subsystem called the telemetry modulation unit (TMU). The FDS collects science and engineering data and combines it into a package that the TMU transmits back to Earth.
Since Voyager 1 is so far away, testing solutions to its technical issues requires time—it takes 22.5 hours for commands to reach the probe and another 22.5 hours for Voyager 1’s response to come back.
On March 1, engineers sent a command that coaxed Voyager 1 into sending a readout of the FDS memory, NASA said in a March 13 blog post . From that readout, the team confirmed a small part—about 3 percent—of the system’s memory had been corrupted, NASA said in an April 4 update .
The core of the problem turned out to be a faulty chip hosting some software code and part of the FDS memory. NASA doesn’t know what caused the chip to stop working—it could be that a high-energy particle from space collided with it, or the chip might have just run out of steam after almost 50 years spent hurtling through the cosmos.
“It’s the most serious issue we’ve had since I’ve been the project manager, and it’s scary because you lose communication with the spacecraft,” Suzanne Dodd , Voyager project manager at JPL, told Scientific American ’s Nadia Drake in March.
To receive usable data again, the engineers needed to move the affected code somewhere else that wasn’t broken. But no single location in the FDS memory was large enough to hold all of the code, so the engineers divided it into chunks and stored it in multiple places, per NASA .
The team started with moving the code responsible for sending Voyager’s status reports, sending it to its new location in the FDS memory on April 18. They received confirmation that the strategy worked on April 20, when the first data on the spacecraft’s health since November arrived on Earth.
In the next several weeks, the team will relocate the parts of the FDS software that can start returning science data.
Get the latest stories in your inbox every weekday.
/https://tf-cmsv2-smithsonianmag-media.s3.amazonaws.com/accounts/headshot/Will-Sullivan-photo.png)
Will Sullivan | | READ MORE
Will Sullivan is a science writer based in Washington, D.C. His work has appeared in Inside Science and NOVA Next .

What Voyager 1's near-death experience says about the future of space exploration
F rom more than 15 billion miles away, NASA engineers last April began repairing a space probe that is headed to the constellation of Ophiucus, though it won't arrive for some 38,000 years. NASA launched Voyager 1 in 1977 and it has already outlived expectations, but the space agency hopes to continue receiving data from the probe until at least 2030. Yet after Voyager 1 experienced a computer glitch in November, it began transmitting incomprehensible data (which isn't entirely unusual for it), prompting NASA to initiate those long-distance fixes.
After some uncertainty if any of it would work, the repairs succeeded . Even better, when Salon spoke with NASA about the problem of fixing distance spacecraft, the experts were optimistic about its future and what it says about space exploration in general.
To understand why, it is first necessary to break down what happened to Voyager 1 in the first place. In November, the space probe sent a signal that did not include any data. Engineers figured out that the issue was either with the flight data subsystem (FDS) or the telemetry modulation unit (TMU). By the last week of February, NASA sent a "poke" to Voyager 1 to prompt the FDS to send a memory readout with data; not only did this succeed, but NASA soon uploaded a separate command that caused Voyager 1 to reply with a full memory readout that helped them identify the specific issue with the FDS.
"The team confirmed that the issue is with the FDS," NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory media relations specialist Calla Cofield told Salon. "A chip responsible for storing 256 words of the FDS memory has a stuck bit (the code is stuck at a 0 or a 1), indicating the part failed, either due to age or due to external particle damage. This section represents about 3% of the FDS memory. The team would need to relocate the portion of the software code stored on the damaged chip."
During the April mission, NASA transmitted a command to the Voyager 1 to both relocate the portion of the impacted FDS software code and redirect references to that code to other places in the spacecraft software.
"On April 20, the team received engineering data from the spacecraft, indicating that the command was a success," Cofield said. "All indications suggest the spacecraft is fine after five months of no contact."
The team began once again receiving scientific data from Voyager 1 on May 19, and by June all of the science instruments on Voyager 1 had resumed sending usable data. Even so, Cofield added that "housekeeping [is] still ongoing with the spacecraft."
Of course, this is not the end of the issue; Voyager 1 is not the only space probe out there that may some day require repairs. Currently there are two other space probes that have left the Solar System and remain operational, Voyager 2 and New Horizons. Additionally NASA has sent out two other probes that are now defunct, Pioneer 10 and Pioneer 11. Can the lessons which allowed NASA to repair Voyager 1 be applied to these and other distant space craft?
Want more health and science stories in your inbox? Subscribe to Salon's weekly newsletter Lab Notes .
"The future is less about repairs than about finding ways to work around problems," Bob Rasmussen, a member of the Voyager flight team, said. "We know several life-limiting factors and have strategies for preserving capability as long as possible. We can’t predict outright failures though, so we need to deal with them as they arise."
This is not to say that Rasmussen is entirely hopeful about NASA's ability to salvage malfunctioning probes. In 2019, the agency had to turn off a heater for the cosmic ray subsystem instrument in Voyager 2 to conserve the probe's power. In April NASA further kept Voyager 2 chugging along by tapping into a small reservoir of backup power that is used to fuel the onboard safety mechanism. By doing this, NASA believes it can keep the craft powered with enough juice that they will not need to shut down a scientific instrument until 2026.
Voyager 1 and 2, meanwhile, are always on the verge of a more lasting breakdown . Even if all of their systems perform optimally going forward, the spacecrafts are still not expected to survive past the 2030s. If anything, the fact that they lasted this long is a testament to the skill and dedication of the 1970s engineers who built them. Unfortunately, there could be a day when more than one of their vital systems simply ceases to properly function.
"Worst case is that both can fail at any time," Rasmussen said. "Not all failures are recoverable. For many, we would never be able to tell what happened, because contact would simply cease."
Rasmussen added that the best case scenario is that Voyager 1 continues to function for another five to 10 years. "We have a long-term strategy for gradually reducing activities as power wanes and for using degraded modes of operation," Rasmussen said. "But we also know what happens to best laid plans."
On a tragic note , June was also the month in which Ed Stone, the man who pioneered the Voyager missions and led their missions for half a century, died. In their obituary for former Jet Propulsion Laboratory director, NASA wrote that Stone was "a trailblazer who dared mighty things in space" and "took humanity on a planetary tour of our solar system and beyond, sending NASA where no spacecraft had gone before."

- svg]:fill-accent-900 [&>svg]:stroke-accent-900">
How the most distant object ever made by humans is spending its dying days
By Rahul Rao
Posted on Apr 28, 2021 4:00 PM EDT
4 minute read
The eyes of the world might be fixed upon Mars, where last week alone, the Ingenuity helicopter took flight and the Perseverance rover made oxygen . But farther—much farther—Voyager 1, one of the oldest space probes and the most distant human-made object from Earth, is still doing science.
The probe is well into the fourth decade of its mission, and it hasn’t come near a planet since it flew past Saturn in 1980. But even as it drifts farther and farther from a dimming sun, it’s still sending information back to Earth, as scientists recently reported in The Astrophysical Journal.
For decades, Voyager has been sailing away at around 11 miles (17 kilometers) every second. Each year, it travels another 3.5 AU (the distance between Earth and the sun) away from us. Now, it’s sending messages home even as it prepares to leave this solar system behind.
There are multiple ways to think about the “edge of the solar system.” One is a boundary region called the heliopause. That’s the frontier where the solar wind (the soup of charged particles continually thrown off by the sun) is too weak to hold off the interstellar medium—the plasma, dust, and radiation that fill the bulk of space.
When Voyager 1 left Earth in 1977, nobody was certain where the heliopause was, according to Bill Kurth , an astrophysicist at the University of Iowa who has been working with Voyager 1 since before it launched. Some scientists then even thought the heliopause was as close as 10 or even 5 AU—around the orbits of Jupiter, which Voyager 1 passed in 1979, or Saturn.
In reality, the heliopause is around 120 AU away. We know this partly because Voyager 1 crossed the heliopause in August 2012, a whole three and a half decades after it departed Earth. That puts the probe well and truly in interstellar space.
[Related: Voyager 2 can finally probe the rarified plasma surrounding our solar system ]
Out here, space is filled with interstellar medium—but you’ll not see very much of it. A cube of air at sea level on Earth contains more than a trillion times as many molecules as an equal-sized cube of even the interstellar medium’s densest parts. The region that Voyager 1 is traversing is sparser still. And for the most part, it’s quiet.
But every few years, as Voyager 1 records more data about the plasma and dust out here, it finds something . For instance, in 2012 and again in 2014, Voyager 1 felt a shock. According to Kurth, what Voyager 1 recorded was a magnetic spike, accompanied by a burst of energetic electrons that caused intense, oscillating electric fields. These shocks are the most distant effects of the sun, rippling outwards even past the heliopause.
What Voyager 1 encountered in 2020 was another jump in magnetic field strength, but without those intense electrical oscillations. Scientists instead think it’s a pressure front, a much more subtle disturbance moving out into the interstellar medium. Voyager 1 previously encountered something like it in 2017.
According to Jon Richardson , an astrophysicist at MIT who wasn’t an author on the paper, this latest finding shows that Voyager 1 is still capable of surprising scientists. Normally, he says, the probe would need to experience a shock in the surrounding plasma to measure its density. But with observations like this one, scientists have found a way to use Voyager 1 to continually monitor that density—over 13 billion miles away from us.
Richardson also says the findings show that Voyager 1 continues to feel the sun’s tendrils, billions of miles past the heliopause. “The sun is still having a major effect,” he says, “far outside the heliosphere.”
Meanwhile, Voyager 1 is still within the sun’s gravitational influence. In about 300 years, scientists expect, Voyager 1 will start to enter the inner edge of the Oort cloud, that shroud of comets which stretches as far as several light-years away.
We’ve never actually seen evidence of the Oort cloud, but sadly, Voyager 1 likely won’t be the one to reveal it. The probe is quite literally living on borrowed time. Plutonium-238, the radioisotope that powers the probe’s generator, has a half-life of about 88 years.
[Related: Ask Us Anything: What happens to your body when you die in space? ]
As a result, Voyager 1 is starting to lose fuel. Scientists are already having to make choices about which parts of the probe they should keep functional. By the mid-2020s, it’s likely that the probe won’t be able to power even a single instrument.
Still, scientists like Kurth hope they can eke the probe’s life out to 2027, the 50th anniversary of its launch. That, Kurth says, is a milestone that none of Voyager 1’s designers could ever have foreseen.
Latest in NASA
Nasa’s viper rover won’t be going to the moon after all nasa’s viper rover won’t be going to the moon after all.
By Tom Hawking
What it was like to spend a year in NASA’s Mars base simulation What it was like to spend a year in NASA’s Mars base simulation
By Andrew Paul
Plasma data measured by Voyager 2 up through 27 June 2024 (2024/179)
The outer atmosphere of the sun expands outward to form the solar wind, with average speeds of 400 km/sec (roughly one million miles per hour). the plasma science experiment on voyager 2 measures that speed every 192 seconds, and that information is returned to earth over the deep space net., voyager 2 currents (near and beyond the heliopause), the currents in the lowest l-mode channel of the pls d cup. the d cup points nearest to the interstellar plasma flow direction. the d1 cup covers the energy range 10-30 ev. at 2018.86 voyager 2 crossed the heliopause. v2 is making the first measurements of the interstellar plasma. we removed noisy and otherwise contaminated data from this plot., voyager 2 solar wind speed plots (up thru the heliopause), - click on figure to see larger version of each plot, these plots show hourly averages of the solar wind speeds measured by voyager 2 over the last 3800 and 100 days, prior to the heliopause, respectively., acquiring the voyager 1 and 2 data, voyager plasma data are available from mit through the links below (but note that updated versions of some browsers no longer support ftp links) or directly through anonymous ftp to space.mit.edu. (cd pub/plasma/vgr). please look at the readme files in each directory before using these data., voyager 1: hourly averages and fine resolution data are available by year for 1977-1980., voyager 2: daily averages , hourly averages and fine resolution data are available by year for 1977-heliopause (november, 2018). in addition, currents (l-modes) and (m-modes) are available (2018-present)., show recent events., voyager 2 solar wind dynamic pressure (up thru the heliopause), these plots show hourly averages of the solar wind dynamic pressure observed by voyager 2 over the entire mission (100-day averages) and over the last ten years (25-day averages), respectively. these pressures are normalized to 1 au by multiplying by the square of the spacecraft's distance., voyager data overview (up thru the heliopause), these plots show 50-day averages of the solar wind speed, density, and temperature over the life of the voyager mission (from 1977 to the heliopause), and 1-day averages over the last three years prior to the heliopause, respectively. the density shown is normalized to earth by multiplying by the distance to voyager in au squared., nasa jpl voyager project home page, for more information contact john richardson at mit (e-mail: [email protected])..

- The Contents
- The Making of
- Where Are They Now
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Q & A with Ed Stone
golden record
Where are they now.
- frequently asked questions
- Q&A with Ed Stone
News | May 18, 2022
Engineers investigating nasa's voyager 1 telemetry data.
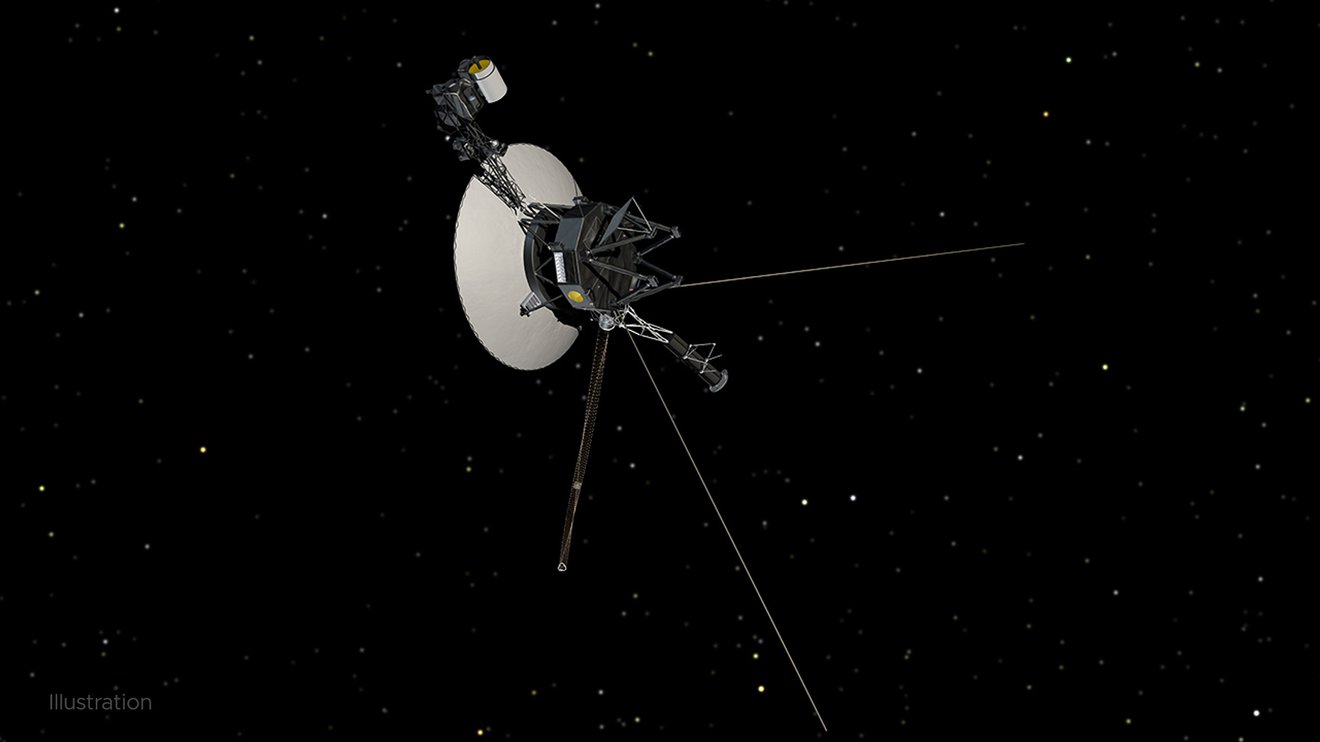

While the spacecraft continues to return science data and otherwise operate as normal, the mission team is searching for the source of a system data issue.
The AACS controls the 45-year-old spacecraft's orientation. Among other tasks, it keeps Voyager 1's high-gain antenna pointed precisely at Earth, enabling it to send data home. All signs suggest the AACS is still working, but the telemetry data it's returning is invalid. For instance, the data may appear to be randomly generated, or does not reflect any possible state the AACS could be in.
The issue hasn't triggered any onboard fault protection systems, which are designed to put the spacecraft into "safe mode" – a state where only essential operations are carried out, giving engineers time to diagnose an issue. Voyager 1's signal hasn't weakened, either, which suggests the high-gain antenna remains in its prescribed orientation with Earth.
The team will continue to monitor the signal closely as they continue to determine whether the invalid data is coming directly from the AACS or another system involved in producing and sending telemetry data. Until the nature of the issue is better understood, the team cannot anticipate whether this might affect how long the spacecraft can collect and transmit science data.
Voyager 1 is currently 14.5 billion miles (23.3 billion kilometers) from Earth, and it takes light 20 hours and 33 minutes to travel that difference. That means it takes roughly two days to send a message to Voyager 1 and get a response – a delay the mission team is well accustomed to.
"A mystery like this is sort of par for the course at this stage of the Voyager mission," said Suzanne Dodd, project manager for Voyager 1 and 2 at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. "The spacecraft are both almost 45 years old, which is far beyond what the mission planners anticipated. We're also in interstellar space – a high-radiation environment that no spacecraft have flown in before. So there are some big challenges for the engineering team. But I think if there's a way to solve this issue with the AACS, our team will find it."
It's possible the team may not find the source of the anomaly and will instead adapt to it, Dodd said. If they do find the source, they may be able to solve the issue through software changes or potentially by using one of the spacecraft's redundant hardware systems.
It wouldn't be the first time the Voyager team has relied on backup hardware: In 2017, Voyager 1's primary thrusters showed signs of degradation, so engineers switched to another set of thrusters that had originally been used during the spacecraft's planetary encounters . Those thrusters worked, despite having been unused for 37 years.
Voyager 1's twin, Voyager 2 (currently 12.1 billion miles, or 19.5 billion kilometers, from Earth), continues to operate normally.
Launched in 1977, both Voyagers have operated far longer than mission planners expected, and are the only spacecraft to collect data in interstellar space. The information they provide from this region has helped drive a deeper understanding of the heliosphere, the diffuse barrier the Sun creates around the planets in our solar system.
Each spacecraft produces about 4 fewer watts of electrical power a year, limiting the number of systems the craft can run. The mission engineering team has switched off various subsystems and heaters in order to reserve power for science instruments and critical systems. No science instruments have been turned off yet as a result of the diminishing power, and the Voyager team is working to keep the two spacecraft operating and returning unique science beyond 2025.
While the engineers continue to work at solving the mystery that Voyager 1 has presented them, the mission's scientists will continue to make the most of the data coming down from the spacecraft's unique vantage point.
More About the Mission
The Voyager spacecraft were built by JPL, which continues to operate both. JPL is a division of Caltech in Pasadena. The Voyager missions are a part of the NASA Heliophysics System Observatory, sponsored by the Heliophysics Division of the Science Mission Directorate in Washington.
For more information about the Voyager spacecraft, visit:
https://voyager.jpl.nasa.gov
News Media Contact
Calla Cofield Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif. 626-808-2469 [email protected] 2022-073

Way out in interstellar space, Voyager 1 is roaming where no human has ever been, revealing secrets of our universe more than 15 billion miles away. Today, the story of its nearly 50-year journey through space and the scientists trying to keep it with us.

Voyager 1 launched on Sept. 5, 1977, during the height of the space age. In the decades since, this unmanned spacecraft has ventured to the outer edges of our universe, sending back one-of-a-kind images and exploring realms that humans will probably never reach.
Voyager 1 is now more than 15 billion miles away in interstellar space, still collecting data and sending it back to Earth. But late last year, Voyager 1 faced its biggest crisis yet. It went silent and stopped communicating. In the months that followed, scientists at NASA launched an all-hands-on-deck effort to find a solution.
Today on “Post Reports,” science reporter Joel Achenbach on Voyager’s journey through space, its fragile future and the desperate effort to keep it with us. We hear from Linda Spilker, project scientist for Voyager 1, and David Cummings, a member of a “tiger team” at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory.
Today’s show was produced by Elana Gordon. It was edited by Peter Bresnan and mixed by Sean Carter. Thanks to Stephen Smith.
Subscribe to The Washington Post here .
Enable the Flash Briefing in the Amazon Skill store or search for "The Washington Post" in the Skill section of your Alexa app. Then ask, "Alexa, what's my Flash Briefing?" or "Alexa, what's the news?"
Send Post Reports to your Google Assistant device or say, "Okay Google, play the news from Post Reports."

What the Secret Service got wrong
Today, a deep dive into the Secret Service and their response to the attempted assassination of former president Donald Trump.

How the 1984 Olympics saved the Games
With only days before the Opening Ceremonies kick off the 2024 Summer Olympics in Paris, we go back to 1984 – when the Games faced international ruin and were reinvented in Los Angeles.
More podcasts

Luna Life Assistant 17+
Advice for daily horoscope, voyager oyun yazilim sanayi̇ ti̇caret anoni̇m şi̇rketi̇, designed for ipad.
- 5.0 • 1 Rating
- Offers In-App Purchases
Screenshots
Description.
Introducing Luna, your ultimate companion for life and astrological advice, powered by advanced AI technology. This innovative iOS app combines the wisdom of astrology with the intelligence of artificial intelligence to provide you with personalized guidance, helping you navigate life's challenges and make informed decisions. Key Features: Personalized Astrological Insights: Luna delves into the cosmic patterns influencing your life by generating detailed astrological profiles. By analyzing your birth chart, the app provides daily, weekly, and monthly horoscopes tailored to your unique astrological sign. Whether you're a fiery Aries, a practical Taurus, or a dreamy Pisces, you'll receive insights that resonate with your personality and current life situations. Life Advice Tailored to You: Our AI-driven life coach offers practical advice on various aspects of your life, including career, relationships, health, and personal growth. By learning from your preferences, behaviors, and goals, the app delivers actionable suggestions and motivational tips to help you achieve your aspirations. Compatibility Analysis: Curious about your compatibility with a partner, friend, or colleague? Luna provides in-depth compatibility reports based on astrological principles. Understand the dynamics of your relationships, discover potential challenges, and find ways to strengthen your bonds with those around you. Daily Affirmations and Mindfulness: Start your day with positive affirmations and mindfulness exercises designed to boost your confidence and well-being. The app offers a curated selection of daily affirmations that align with your astrological profile, helping you maintain a positive mindset and stay focused on your goals. Moon Phases and Lunar Calendar: Stay in tune with the lunar cycles and harness the energy of the moon to enhance your life. Luna features a comprehensive lunar calendar that tracks moon phases, eclipses, and important astrological events. Learn how to align your activities with the moon's energy for optimal results. AI-Powered Chatbot: Our AI-powered chatbot is available 24/7 to answer your questions and provide instant advice. Whether you need quick guidance on a decision or detailed insights into a complex situation, the chatbot is equipped with a vast knowledge base to assist you at any time. Why Choose Luna? Holistic Approach: Luna takes a holistic approach to self-improvement by integrating astrological wisdom with practical life advice. This unique combination ensures that you receive well-rounded guidance that addresses both your inner and outer worlds. User-Friendly Interface: The app is designed with simplicity and ease of use in mind. The intuitive interface allows you to access all features effortlessly, making your journey towards self-discovery and personal growth a seamless experience. Regular Updates: We are committed to providing you with the best possible experience. Luna is regularly updated with new features, improved functionalities, and fresh content to keep you engaged and inspired. Privacy and Security: Your privacy is our top priority. All your personal data and astrological information are securely stored and protected. We adhere to strict privacy policies to ensure that your information remains confidential. Conclusion Luna is more than just an app; it's a trusted companion on your journey through life. By blending the ancient wisdom of astrology with the cutting-edge capabilities of AI, we offer a unique and enriching experience that empowers you to live your best life. Download Luna today and embark on a path of self-discovery, personal growth, and cosmic harmony Terms of Service: https://voyagerapplication.com/terms-of-service/ Privacy Policy: https://voyagerapplication.com/privacy-policy/
Version 1.0.1
Thank you for using Luna. This update includes bug fixes.
Ratings and Reviews
App privacy.
The developer, VOYAGER OYUN YAZILIM SANAYİ TİCARET ANONİM ŞİRKETİ , indicated that the app’s privacy practices may include handling of data as described below. For more information, see the developer’s privacy policy .
Data Used to Track You
The following data may be used to track you across apps and websites owned by other companies:
Data Not Linked to You
The following data may be collected but it is not linked to your identity:
- Diagnostics
Privacy practices may vary, for example, based on the features you use or your age. Learn More
Information
- Monthly Premium $24.99
- Annual $59.99
- Weekly Premium $6.99
- Developer Website
- App Support
- Privacy Policy
More By This Developer
My Gentlemen's Club
Ticket Empire : Transport Idle
Difference Master - Find them!
Find 4th Object
Spot Differences: Find All!
Gold Miner: Drill Empire
Navigation Menu
Search code, repositories, users, issues, pull requests..., provide feedback.
We read every piece of feedback, and take your input very seriously.
Saved searches
Use saved searches to filter your results more quickly.
To see all available qualifiers, see our documentation .
- Notifications You must be signed in to change notification settings
The memory layer for Personalized AI
mem0ai/mem0
Folders and files, repository files navigation.

Mem0: The Memory Layer for Personalized AI
Mem0 provides a smart, self-improving memory layer for Large Language Models, enabling personalized AI experiences across applications.
Note: The Mem0 repository now also includes the Embedchain project. We continue to maintain and support Embedchain ❤️. You can find the Embedchain codebase in the embedchain directory.
🚀 Quick Start
Installation, basic usage, 🔑 core features.
- Multi-Level Memory : User, Session, and AI Agent memory retention
- Adaptive Personalization : Continuous improvement based on interactions
- Developer-Friendly API : Simple integration into various applications
- Cross-Platform Consistency : Uniform behavior across devices
- Managed Service : Hassle-free hosted solution
📖 Documentation
For detailed usage instructions and API reference, visit our documentation at docs.mem0.ai .
🔧 Advanced Usage
For production environments, you can use Qdrant as a vector store:
- Integration with various LLM providers
- Support for LLM frameworks
- Integration with AI Agents frameworks
- Customizable memory creation/update rules
- Hosted platform support
🙋♂️ Support
Join our Slack or Discord community for support and discussions. If you have any questions, feel free to reach out to us using one of the following methods:
- Join our Discord
- Join our Slack
- Follow us on Twitter
Releases 187
Used by 1.2k.
Contributors 112
- Python 69.7%
- Jupyter Notebook 6.7%
- JavaScript 2.3%
- Dockerfile 0.2%
- Makefile 0.2%

Interstellar Messengers

Voyager 1 and its twin Voyager 2 are the only spacecraft ever to operate outside the heliosphere, the protective bubble of particles and magnetic fields generated by the Sun. Voyager 1 reached the interstellar boundary in 2012, while Voyager 2 (traveling slower and in a different direction than its twin) reached it in 2018.
Mission Type
Science Targets
Featured News
Ed Stone, Former Director of JPL, Voyager Project Scientist, Dies

Voyager 1 Returning Science Data From All Four Instruments

NASA’s Voyager Will Do More Science With New Power Strategy

NASA’s Voyager Team Focuses on Software Patch, Thrusters

Voyager, NASA’s Longest-Lived Mission, Logs 45 Years in Space
Voyager Blog

Mission Updates
Voyager 1 Resumes Sending Science Data from Two Instruments
The Interstellar Mission
After completing the first in-depth reconnaissance of the outer planets, the twin Voyagers are on a new mission to chart the edge of interstellar space.
The Golden Record
The contents of the golden record were selected for NASA by a committee led by Carl Sagan of Cornell University.
The Spacecraft
The twin Voyagers are escaping our solar system in different directions at more than 3 astronomical units (AU) a year.

The Pale Blue Dot
The behind-the-scenes story of the making of Voyager 1's iconic image of Earth as "a mote of dust suspended in a sunbeam."

Discover More Topics From NASA


COMMENTS
Note: Because Earth moves around the Sun faster than Voyager 1 or Voyager 2 is traveling from Earth, the one-way light time between Earth and each spacecraft actually decreases at certain times of the year. Cosmic Ray Data: This meter depicts the dramatic changes in readings by Voyager's cosmic ray instrument.
The Voyager 1 spacecraft is sending back a steady stream of scientific data from uncharted territory for the first time since a computer glitch sidelined the historic NASA mission seven months ago ...
Voyager's 30-Year Plan. The Voyager Interstellar Mission has the potential for obtaining useful interplanetary, and possibly interstellar, fields, particles, and waves science data until around the year 2020 when the spacecraft's ability to generate adequate electrical power for continued science instrument operation will come to an end.
NASA 's Voyager 1 spacecraft is fully operational once more, with all four science instruments returning usable data to Earth. The problems began in November 2023, when Voyager 1 lost its ability ...
Voyager 1 has resumed returning science data from two of its four instruments for the first time since a computer issue arose with the spacecraft in November 2023. NEWS | March 15, 2024 Since November 2023, NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft has been sending a steady radio signal to Earth, but the signal does not contain usable data.
Voyager 1 launched from Cape Canaveral in September 1977 and is now the farthest spacecraft from Earth, traveling in space at about 14.5 billion miles (23.3 billion kilometers) away.
The engineering team with NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft is trying to solve a mystery: The interstellar explorer is operating normally, receiving and executing commands from Earth, along with gathering and returning science data. But readouts from the probe's attitude articulation and control system (AACS) don't reflect what's actually happening onboard.
Two other instruments required some additional work, but now, all four are returning usable science data. The four instruments study plasma waves, magnetic fields, and particles. Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 are the only spacecraft to directly sample interstellar space, which is the region outside the heliosphere — the protective bubble of ...
The spacecraft has resumed gathering information about interstellar space. NASA's Voyager 1 spacecraft is conducting normal science operations for the first time following a technical issue that arose in November 2023. The team partially resolved the issue in April when they prompted the spacecraft to begin returning engineering data, which includes information about the health […]
Rockets aren't the only thing we launch. Welcome to our improved NASA website! If you don't find what you are looking for, please try searching above, give us feedback , or return to the main site . Voyager science data are available on-line at the National Space Science Data Center (NSSDC) and at the investigators' institutions.
They mystery of its junk data has been solved, NASA says.(Image credit: NASA) NASA 's Voyager 1 probe is finally making sense again in interstellar space. After months of sending junk data about ...
Voyager 1's twin, Voyager 2 (currently 12.1 billion miles, or 19.5 billion kilometers, from Earth), continues to operate normally. Launched in 1977, both Voyagers have operated far longer than mission planners expected, and are the only spacecraft to collect data in interstellar space.
In 2023, humanity's pioneering space mission, Voyager 1, stopped sending understandable data back to Earth. Now, NASA engineers may be closer to discovering the source of the issue.
The PGH rate consists of greater than 70 MeV/nuc nuclei, primarily protons, and is a good indicator of the level of modulation of galactic cosmic rays. It can also respond to large solar flares. The Voyager 1 heater was turned off in May, 2022. Corrections to the Voyager 1 flux data are pending. The Voyager 2 heater was turned off in June 2019.
The probe and its twin, Voyager 2, are the only spacecraft to ever fly in interstellar space (the space between stars). Voyager 1 stopped sending readable science and engineering data back to Earth on Nov. 14, 2023, even though mission controllers could tell the spacecraft was still receiving their commands and otherwise operating normally.
NASA / JPL-Caltech. For the first time in five months, NASA has received usable data from Voyager 1, the farthest spacecraft from Earth. The aging probe, which has traveled more than 15 billion ...
Voyager 1 has been exploring our solar system since 1977. The probe is now in interstellar space, the region outside the heliopause, or the bubble of energetic particles and magnetic fields from the Sun. Voyager 1 was launched after Voyager 2, but because of a faster route it exited the asteroid belt earlier than its twin, and it overtook Voyager 2 on Dec. 15, 1977.
Voyager 1 began transmitting unreadable data on November 14, 2023. On December 12, 2023, NASA announced that Voyager 1 's flight data system was unable to use its telemetry modulation unit, preventing it from transmitting scientific data.
The team began once again receiving scientific data from Voyager 1 on May 19, and by June all of the science instruments on Voyager 1 had resumed sending usable data. Even so, Cofield added that ...
The region that Voyager 1 is traversing is sparser still. And for the most part, it's quiet. But every few years, as Voyager 1 records more data about the plasma and dust out here, it finds ...
Plasma data measured by Voyager 2 up through 27 June 2024 (2024/179) The outer atmosphere of the Sun expands outward to form the solar wind, with average speeds of 400 km/sec (roughly one million miles per hour). The Plasma Science Experiment on Voyager 2 measures that speed every 192 seconds, and that information is returned to Earth over the ...
The AACS controls the 45-year-old spacecraft's orientation. Among other tasks, it keeps Voyager 1's high-gain antenna pointed precisely at Earth, enabling it to send data home. All signs suggest the AACS is still working, but the telemetry data it's returning is invalid. For instance, the data may appear to be randomly generated, or does not ...
Voyager is a data visualization tool that blends manual and automatic chart specification in a unified system. It aims to support smoother gradations between open-ended exploration and more focused phases of analysis. Voyager augments a traditional drag and drop chart specification interface with two new partial view specification techniques.
Voyager 1 is now more than 15 billion miles away in interstellar space, still collecting data and sending it back to Earth. But late last year, Voyager 1 faced its biggest crisis yet.
The developer, VOYAGER OYUN YAZILIM SANAYİ TİCARET ANONİM ŞİRKET ... Data Used to Track You. The following data may be used to track you across apps and websites owned by other companies: Usage Data; Data Not Linked to You. The following data may be collected but it is not linked to your identity: Usage Data; Diagnostics;
Mem0 provides a smart, self-improving memory layer for Large Language Models, enabling personalized AI experiences across applications. Note: The Mem0 repository now also includes the Embedchain project.
Voyager Therapeutics last issued its earnings results on May 13th, 2024. The reported ($0.20) EPS for the quarter, topping analysts' consensus estimates of ($0.44) by $0.24. The company earned $19.52 million during the quarter, compared to the consensus estimate of $10.33 million.
Voyager 1 Returning Science Data From All Four Instruments. 5 min read. NASA's Voyager Will Do More Science With New Power Strategy. Article 1 year ago. 5 min read. NASA's Voyager Team Focuses on Software Patch, Thrusters. Article 9 months ago. 5 min read. Voyager, NASA's Longest-Lived Mission, Logs 45 Years in Space.