
UNWTO which stands for United Nations World Tourism Organizations. UN specialized and leading organization in the area of Travel and Tourism. UNWTO is formed in 1975, and its headquarter is in Madrid, Spain. This agency is responsible for the“promotion of responsible, sustainable and universally accessible tourism. At present it has 159 member states nad five hundred affiliate members around the globe.

History of UNWTO
The history of UNWTO dates back to the year 1920 when the “International Congress of Official Tourist Traffic Associations (ICOTT)” was established at The Hague, the Netherlands. The origin can also be linked to “International Union of Official Tourist Publicity Organizations (IUOTPO)”, although the UNWTO states that “the ICOTT became the International Union of Officials Tourist Publicity Organizations first in 1934”. After the brief discontinuity during the Second World War an International Conference was held in London that gave birth to The International Union of Official Travel Organization (IUOTO) in the year 1947 and IUOTO was finally transformed into an Intergovernmental organization called World Tourism Organization on January 2 1975. The headquarters was established in Madrid, Spain in January 1976. The resolution for setting up the headquarters was already taken in the first General Assembly of the WTO. The UN General Assembly decided to add UN before the World Tourism Organization in order to differentiate between World Trade Organization and World Tourism Organization. Finally, the organization was renamed as UNWTO on December 1 2005.
Also read Tourism
Promoting tourism as the driver for economic growth is the main work of this agency. While it offers leadership and support to the tourism sector in advancing knowledge and tourism policies worldwide, it promotes sustainable development and environmental sustainability. The UNWTO is an apex body in the field of tourism and it works with different governments on matters relating to tourism policy issues on a global basis. It provides a practical source of tourism knowledge and statistics for planners, researchers and academics alike. The Global Code of Ethics for Tourism were enforced by UNWTO to promote the sustainability in tourism operations. UNWTO aims to maximize the benefits of tourism to the society and economy of nations while minimizing the negative impacts of it.
Aims and Objectives of UNWTO
Following are the aims nad objectives of UNWTO:
Promotion and development of sustainable tourism that can contribute to the economy of countries
I nternational understanding to bring peace and prosperity
Development of universal respect for tourism
Working towards protection of basic freedom and human rights of citizens without any discrimination based on region, religion, language, race, or sex.
Functions of UNWTO
To accomplish the objectives, the UNWTO functions in the following six main areas:
1. Improving competitiveness in tourism industry
2. Promoting sustainable development
3. Promoting tourism for poverty reduction and development
4. Bringing up knowledge, education and capacity building
5. Creating partnership and mainstreaming
6. Achieving tourism which should be responsible, sustainable and universally accessible.
Also read History of Travel and Tourism
Activities of UNWTO
The UNWTO plays a vital role in development and promotion of tourism worldwide. It, therefore, undertakes a number of projects and activities for promoting and developing tourism, such as:
To conduct research related to the tourism market, industry, physical and financial planning and development, promotion and marketing, economic analysis and techniques.
To disseminate the data, research and study findings on various fields of tourism to its members.
To conduct studies about tourism trends, changes in the world economic and social conditions and their effects on tourism.
To conduct studies about the fluctuations in the market and preparing and maintaining standards within tourism sector.
To conduct courses and vocational training programmes aiming at human resource development especially in the developing countries.
To prepare drafts of international agreements on tourism.
To carryout systematic collection, analysis and dissemination of statistics and other data on various aspects of tourism.
To function like a data source to disseminate available information related to international, regional and domestic tourism; including statistics, legislation and policies, facilities.
To build a consortium of legislation, regulations and documents on all aspects of travel of various countries.
To work with different governments and competent specialized bodies in simplification of formalities for international travel and to remove barriers for the free movement between countries.
To organize international conferences, conventions, seminars, workshops, symposiums and meetings on contemporary aspects of tourism.
Structure of UNWTO
The UNWTO works through its various subsidiaries, having well defined responsibilities fixed for such subsidiaries.
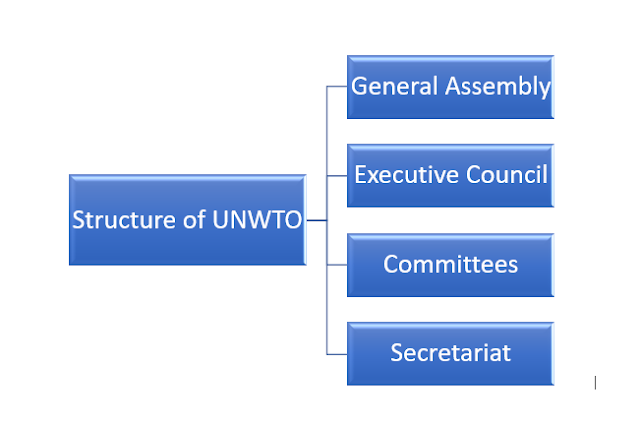
1. General Assembly: It is a composition of full members and associate members. It is a congregation of members to meet on a periodic basis of every two years to approve the amendments in policies, finalization budget and programme for the entire period. Contemporary and relevant issues are debated and discussed in it. The Affiliate Members and representatives of other International Organizations attend the General Assembly as observers. General Assembly elects a general secretary in every four years. Subsidiary organ of the general assembly is the “world committee on tourism ethics”.
2. Executive Council: This works as governing board for the UNWTO. This Council consists of full members elected by the General Assembly at a ratio of one member for every five. Representatives such as ‘One’ of Associate Members and ‘One’ of Affiliate Members represent the issues of their group. The Council ensures that the organization carries out its work and adheres to its budget. Spain as the host of UNWTO has a permanent seat in the Executive Council. The Council works in consultation with the Secretary General and it works towards the implementation of the resolutions in the General Assembly. The Council meets at least twice a year. There are some subsidiary organs created by Executive Council which meet on a regular basis to discuss the matters which fall within their jurisdictions and they report to the Council of the same. “The subsidiary organs are : Technical Committee for
GENERAL ASSEMBLY
EXECUTIVE COUNCIL
SECRETARIAT
Programme and Coordination(TCPC), Committee on Budget and Finance(CBF), Facilitation Committee, Environment Committee, Sub-Committee for the review of applications for affiliate membership, Sub Committee on Statistics and Joint WTOIATA Working Party”
You may read Tourism Product Concept
3. Committees . There are some specialized Committees of UNWTO members and the task of these committees is to advise the Executive Council on management and policies. The specialized committees are: The Programme Committee, The Committee on Budget and Finance, the Committee on Statistics and The Tourism Satellite Account, The Committee on Market and Competitiveness, the Sustainable Development of Tourism Committee, the World Committee on Tourism Ethics, The Committee on Poverty Reduction and the Committee for the Review of Applications for Affiliate Members.
4. Secretariat: The Secretariat of the organization is consisted of the Secretary General and the Staff Members. It is responsible for implementing the UNWTO’s programme of work and serving the needs of members. The responsibility of Secretary General is to carry out the general policy and work programme of the organization as directed by the General Assembly and the Executive Council. The Secretary General’s duty is to ensure the legal representation of the organization. The group is led by the Secretary General who supervises about 110 full-time staff at UNWTO’s Madrid headquarters. A full-time Executive Director supports and assists the Affiliate Members. The Secretariat has a Regional Support Office for Asia-Pacific in Osaka, Japan which is financed by the Japanese Government.
Members of UNWTO .
1. Affiliate Members: Public and private organizations working in the field of tourism can become Affiliate Members of UNWTO. These organizations contribute to the UNWTO in promotion and development of responsible, sustainable and accessible tourism. The members of the board meet at least twice a year. The organizational structure of affiliate members include mainly two organs such as: The Plenary: In this the Affiliate Members are represented and it consists of all the membership with each having voice and vote & The Board of the Affiliate Members: It is an advisory organ to the UNWTO Secretary General. It is responsible for the alignment of its members to the overall goals, mission and general programme. It also helps in the design and implementation of the policies of the Affiliate Members programme.
2. State Members: There are 156 State Members of UNWTO worldwide. It has 6 Associate Members and 2 Observers.
Regions of UNWTO.
There are six regions of UNWTO namely Africa, the Americas, East Asia, the Pacific, Europe and the Middle East. There are different regional programmes for different regions which are held considering mission and objectives of these regions.
You can read Tourism Product Concept
1. Regional Programme for Africa.
The mission of Regional Programme for Africa is to support and assist UNWTO African members. It also helps the stakeholders to develop the tourism industry in all spheres of sustainable development be it economic or social development. It ensures the members get full benefit from the services provided by the organization. There are objectives of the programme which are meant for the particular region. The objectives for Africa region are as follows:
To ensure the implementation of the programme within African region.
To work as a link between the Member States and The Secretariat through which all local, regional and national tourism needs and concerns are communicated.
To make the African countries more competitive, it strengthens the institutional capacity in various domains such as HRD, ICT, MARKETING AND PROMOTION, statistics and sustainable development of tourism.
To contribute to poverty reduction through the UNWTO ST-EP (Sustainable tourism- Eliminating Poverty) initiative.
To strengthen the presence of UNWTO in the region by increasing full and affiliate membership in the continent.
2. Regional Programme for the Americas .
The mission of “The Programme for The Americas” of UNWTO is to ensure that its members get full benefits from the transfer of technology generated by the activities done in the region and to enhance the quality and efficiency of development. It focuses on the needs of the local authorities and enterprises and National Tourism Administrations in the region. Topics and courses related to the tourism industry are also discussed in seminars and conferences.
There are two main objectives of Regional Programme for America the first one is Technical Cooperation Programme which helps the governments in the formulation of tourism policies and strategies, development of new product, marketing and HRD. Based on the policy of sustainability the programme concentrates on master planning at all levels such as founding tourism institutes, preparing marketing programmes, building national capacity for project management, strengthening the role of parliament in forming tourism policies and the economic measurement of the tourism. The
development of Tourism Satellite Account (TSA) helps in managing all such planning. The second one is the Sectoral Support Mission which is for shorter duration and works on the specific request of member countries in identifying, evaluating and describing specific technical assistance needs and provides policy advice in formation of project proposals. Funds for such mission are released by United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) or some other bilateral or multilateral financing agencies.
3. Regional Programme for Asia and the Pacific
This programme is restricted to the geographic region of Asia and the Pacific. The Regional Programme for Asia and The Pacific is the operational arm of world tourism organization. Its task is to implement general programme of work of UNWTO within the region. It is a direct link of UNWTO through which Member States are communicated to the Secretariat on the local, regional, and national needs and concerns for tourism development. It has got some objectives to perform within the region:
To bring up partnerships between private sector, government agencies and educational institutions by organizing seminars, conferences and workshops on contemporary tourism issues.
To support and assist Member States for promotion, management and development of the tourism industries so that Asia and the Pacific Region could maintain its endeavor in growth of tourism.
To increase full and affiliate membership of countries and private sectors in the region.
To promote the UNWTO ST-EP (Sustainable tourism- Eliminating Poverty) initiatives and make endeavors towards the UN Millennium Development Goals for the benefit of countries within Asia and the Pacific Region.
To supply with information and news and activities of UNWTO in the region and to its members.
To make different plans such as tailor- made contingency plan, crisis management plan in order to establish tourism – oriented warning system network which could be tapped by Member States when needed.
To establish networks of academicians, industry representatives and government officials in the region for the production of periodical Asia-Pacific market trends report.
4. Regional Programme for Europe
The mission of the Regional Programme for Europe is to achieve greater standards of performance in tourism governance and policy by framing sufficient contents in the UNWTO programme of work and publications. There are two important objectives.
To increase the participation of member states of UNWTO European region and maximize the benefits too within the region.
To work towards the synergy between the UNWTO and external institutions and businesses, by making policies and strategies for governance.
Activities of European Region include the development of strategies in the context of turbulent markets to help Member States use instruments which addresses the issues of quality and CRM. The preparation and implementation of the programmes relates to value addition such as novelty and innovation in the area of technology, HRD, capacity building etc.
You may be interested to read Aviation Industry in India
5. Regional Programme for Middle –East
The mission of Regional Programme for Middle-East is the regional representation for the Middle East and the objectives are as follows:
To work towards fulfillment of unique and specific needs of the tourism organizations and enterprises.
To organize workshops, seminars, meetings and conferences on relevant issues concerning tourism industry.
UNWTO’s Global Code of Ethics
The history UNWTO’s global code of ethics in tourism is a recent phenomenon. It was first proposed in International Association of Scientific Experts in Tourism Congress in the year 1992 held in Paris. It proposed the conception of a commission to deal with ethical problems in tourism. The Rio Earth Summit (Agenda 21) in 1992 called upon institutions to adopt codes of ethics in their organisational practices. Adherence to ethics is required to establish good relations and equation between hosts and guests.
The ethics of tourism are tied to human rights, environmental justice, equity, and virtue ethics. It encourages greater transparency in work that pays close attention to the ethical issues in gathering data and conducting research. The ethics builds an attitude of tolerance and respect towards the moral beliefs and philosophical issues. It builds cooperation between diversity of people in their religious belief.
It is the foundations of responsible and sustainable tourism as viewed by UNWTO Global Code of Ethics for Tourism. In the year 2001, UNWTO has established Global Code of Ethics that focuses on universal standards of addressing different aspects and traits such as cross-cultural tolerance, promotion of human rights, environmental and developmental sustainability, accessibility, economic growth, reduction of poverty, and self-education. However, ethical standards are purely voluntary.
Though it is not a legally binding document, there is a provision for voluntary implementation of ‘Global Code of Ethics for Tourism’. The different stakeholders’ institution and organisation may refer on a voluntary basis to the matter concerning the application and implementation of the code of ethics.
The role of the ‘World Committee on Tourism Ethics (WCTE)’ stands pre-eminent in the formulations and implementation of legal framework of tourism internationally. The WCTE is subsidiary organ that reports directly to the General Assembly of UNWTO. It has been assigned with tasks such as “promotion and dissemination of code of ethics and evaluation and monitoring the implementation of the ethics”.
The “Global Code of Ethics for Tourism” was adopted on October 1, 1999 in the meeting of General Assembly of United Nations World Tourism Organization in Santiago, Chile. This contains set of principles for the key players of the tourism industry including the governments, the travel industry, communities and tourist alike. It aims at “minimizing the negative impacts on environment, society and culture and maximizing economic benefits across the world”.
At the meeting, the UNWTO General Assembly recommended:
“States Members or non-members of WTO, without being obliged to do so, to accept expressly the principles embodied in the Global Code of Ethics for Tourism and to use them as a basis when establishing their national laws and regulations and to inform accordingly the World Committee on Tourism Ethics ”.
‘Global Code of Ethics for Tourism’ is a guide book of principles for all stakeholders, entrepreneurs, workers, local communities etc. worldwide. The idea of this Global code was conceived in 1997 when a committee was formed during the UNWTO General Assembly meeting in Istanbul.
The process of preparation involved wide ranges of discussion and consultation with all stakeholders of tourism industry for the benefit and development of tourism industry worldwide. More than 70 Members states and other entities sent their written comments on the concept of code.
The UNWTO meeting held in Santiago, Chile in October 1999 and finalised 10 principals of Global Code of Conduct for Tourism that was subsequently approved by UNWTO General Assembly in UNWTO resolution A/RES/406(XIII). Then in the year 2001 a draft resolution on ‘Global Code of Ethics for Tourism’ was adopted by the ‘United Nations Economic and Social Council’.
This ‘Global Code of Ethics for Tourism’ got final official recognition by United Nations General Assembly on 21 st of December 2001 through UN RESOLUTION A/RES/56/212. As per the directions of United Nations, the World Tourism organization has since then been promoting these code of ethics for implementation by member countries worldwide.
Not a legally binding document, it is purely voluntary which stakeholders may chose to implement for the long-term benefit of the industry. In the process of implementation of this global code of ethics, the World Committee on Tourism Ethics (WCTE) has gained its prominence as an Autonomous and Impartial Body of UNWTO.
The basic objectives of the ‘Global Code of Ethics for Tourism’ are to:
• Establish a synthesis of the documents, codes and declarations out of the available records or by comparing the aspirations of stakeholders published over the years.
• Complement the codes, documents and declarations with new considerations which would reflect the growth and development of the society.
• Serve as a term of reference for the stakeholders in the tourism industry.
2. World Committee on Tourism Ethics (WCTE)
Established in the year 2004, ‘World Committee on Tourism Ethics’ is an independent and impartial body of UNWTO. It directly reports to the General Assembly of UNWTO as a subsidiary organ. The members of this world Committee on tourism ethics are selected on their personal capacities rather than as officials or representatives of governments of member countries.
The Committee is responsible for interpreting, applying and evaluating the provisions of ‘The Global Code of Ethics for Tourism’ in promotion of sustainable and responsible tourism. The mandate of this Committee rests with tasks of ‘promotion and dissemination of code of ethics, evaluation and monitoring the implementation of the ethics.’
3. Global Code of Ethics for Tourism (GCET)
Global Code of Ethics for Tourism contains 10 Articles in which there are nine principles and the tenth article is a summary of all of others focused on the implementation part. These articles are further divided into sub-sections with laws, regulations and recommendations mentioned for various stakeholders of tourism. The Ten Articles are mentioned below.
• Contribution to mutual understanding and respect between peoples and societies
• Tourism as a vehicle for individual and collective fulfillment
• Factor of sustainable development
• A user of the cultural heritage of mankind and a contributor to its enhancement
• Beneficial activity for host countries and communities
• Obligations of stakeholders in tourism development
• Right to tourism
• Liberty of tourist movements
• Rights of the workers and entrepreneurs in the tourism industry
• Implementation of the principles of the Global Code of Ethics for Tourism”.

Article 1: “Contribution of Tourism to Mutual Understanding and Respect between Peoples and Societies”
This Article observes, Tourism sector is well known for developing goodwill and harmony among regions and countries. People’s motives to travel to a place can be judged over the selection of place or destination. While travelling, tourists or visitors come across different societies and tradition, they experience different culture and practices.
Therefore, they must maintain the dignity of other culture and must have a sense of respect for them. The tradition and culture of minorities and indigenous people must be observed. Tourist activities must be done in sync with the traditions and culture of the host community.
On the other hand, the host community must have respect for the tourists and they must supply them with all important information. They must not misguide or misbehave with them. The host community must provide a warm welcome and hospitality to the tourists.
Government or the concerned authorities must ensure the safety and security of the tourists. They must provide protection from illegal activities such as communal riots, war, kidnapping, murder, rape, snatching of goods, theft etc. Nonetheless the natural and cultural heritage must be preserved and conservation and preservation laws must be implemented. No criminal act should be allowed.
Misconduct with tourists must not be allowed. However, tourists must keep themselves away from any criminal activity. They must not indulge in any offensive act like smuggling, trafficking of valuable species etc.
Tourists must collect enough of information of rules and regulations, travel formalities and health information before the departure from their respective countries of residence.
Article 2: “Tourism as a Vehicle for Individual and Collective Fulfillment”
In any tourist destination whatever tourist activities take place that must be linked with rest and relaxation. It should provide learning about different culture of different people or society and of different region. There should not be any discrimination between men and women in any form, equality must be maintained. Cooperation of all states is mandatory in promoting human rights and it should be meant for all class of people without any discrimination.
Exploitation in any form must not be accepted and in case of any such thing, states should deal with it. Educating people about touristic activities and benefits of tourism like social and cultural benefits, economic benefits is also very necessary, on the other hand tourists must be told about the risks.
Article 3: “Tourism, as a Factor of Sustainable Development”
Article 3 enshrines about development that one thing always strikes our mind, whether it is sustainable or not? Sustainability must be maintained in all forms be it environmental or cultural or social or economic. Tourism development must safeguard natural environments for present as well as future growth.
Ecotourism should be promoted and natural heritage preservation should be given top priority. Priority should also be given to conserve energy at all levels such as; local, regional and national level. Destination carrying capacity should be maintained while conducting any tour or tourist activity. The infrastructural development in the name of tourism activities must be limited in order to protect natural heritage.
Also read on UNWTO
Article 4: “Tourism, as User of the Cultural Heritage of Mankind and a Contributor to its Enhancement”
Article 4 briefs the following ethics in its sub-sections . The local community plays a great role in protecting and enhancing cultural heritage. Tourism uses the cultural heritage of the local community as a product. Thus the local communities should have rights and obligations on the cultural heritage. They should protect the local culture, maintain its authenticity and pass this on to the future generation.
Government must make policies and activities for protection and they should also ensure that tourism should not affect any of the cultural heritage such historical monuments, or other structures. Revenue obtained from the visits to the heritage places, should be utilized for the development and conservation of the heritage.
Article 5: “Tourism, as a Beneficial Activity for Host Countries and Communities”
Article 5 comprehends the benefit of tourism to the host countries and communities. Tourism is a beneficial activity that brings prosperity in the society and local communities. Right from creation of jobs to implementation of policies, it plays a significant role in raising standard of living, quality of life, meeting the needs of the host communities and countries.
Therefore, the participation of the host community in providing activities and services to the tourists is mandatory for economic, cultural and social benefits. While framing policies, government or the concerned authorities must consider the local people and their social and economic growth. Economic growth is found less in coastal and hilly areas so that such regions must be given special attention because such places lag behind in development than the other accessible places.
On regular interval studies on impacts should be done by the authorities or its professionals keeping in view the objectives. Suitable corrections and changes in the policies need to be affected if negative impacts are noticed in the due course of development.
Article 6: “Obligations of Stakeholders in Tourism Development”
This Article includes obligations of stakeholders to be followed in tourism industry. Stakeholders pay a great contribution to the tourism industry as they provide good ambience for tourists’ quality of experience and supply tourists with valuable destination information. Stakeholders in tourism thus must provide accurate and genuine information of activities and services about a destination.
The information related to nature, price, quality etc. must be mentioned clearly in the documents given to the tourists at the time of booking. Such information should not be exaggerated so that the committed services are not different from the services being offered. In case of service deficiency provider should compensate the tourists against such deficiency in services.
The services offered must be in accordance with the national regulations at the same time they should show concern in cooperation with public authorities for safety and security, protection and food safety etc. Stakeholders must update tourists with the travel regulations and existence of insurance and assistance as tourists may face any adverse situation related to travel formalities while travelling abroad.
It is government’s duty to inform their nationals of any probable difficult situation faced by the tourists. Travel advisories should discuss regarding this with the host countries and concerned people beforehand. Media plays an important role in it so they should provide accurate, reliable, balanced and genuine information without disrespecting the rules and regulations of the host countries.
Article 7: “Right to Tourism”
Every human being has got some fundamental rights and “right to tourism” is discussed as a fundamental right in the Seventh Article of the global code. Tourism should be open to all habitants of the world without any discrimination for the proper utilization of leisure, be it disabled people or any other. Facilities must be provided to disabled at the same time they should be encouraged to travel.
For this, there ought to have the “right to rest and leisure including limitation in working hours and periodic holidays” so that there could be more and more participation of tourist in various tourism activities. Social tourism should be enhanced by providing facilities for travel and leisure activities. Public authority’ support is required in this way.
Article 8: “Liberty of Tourist Movements”
The sub-sections of Article -8 also relates to free movement of tourists. The growth of tourism industry cannot be imagined without tourists’ movements so there has to be freedom to move anywhere they wish, be it their own country or region or the other countries. There should not be too much of formalities which may tangle them. Formalities related to visa, entry, health etc. must be simplified for convenience.
There should be access to the places that tourists wish to visit and access to communication, stays, transits, legal and health services and access to allowances of convertible currencies for tourists. There should not be any discrimination and tourists should have the same rights as the citizens have in that particular country.
Article 9: “Rights of the Workers and Entrepreneurs in Tourism Industry”
In order to ensure a healthy work environment, the Global Code outlines ‘the rights of the worker and entrepreneurs in the tourism industry’ in the Article 9. Like right to tourism and right to tourism movements, workers and entrepreneurs have got some rights in the tourism industry. Every employee in the industry has right to get initial training which is provided by the firm.
There should be job security for the seasonal workers and they should be given social protection. There should be interaction programme for exchanging experience between executives and workers from different regions and different countries. Such interactions contribute to the development of the industry. The entrepreneurs should involve themselves in social development as partnership among various organizations and building relations between enterprises help in sustainable development and growth.
Article 10: “Implementation of the Principles of the Global Code of Ethics for Tourism”
Article 10 is the summarization of all the other articles of the code of ethics. The stakeholders who implement the principles need to be appreciated. Stakeholders should show their intentions to refer the disputes concerning interpretation of GCET. The article emphasizes public and private stakeholders to cooperate and complement each other in the implementation of code of ethics.
All players in tourism should respect apart from the guidelines of international law, the role of international tourism organizations such as the UNWTO and other non-governmental tourism organizations in all aspects of tourism activities. All stakeholders should approach the ‘World Committee on Tourism Ethics’ as an impartial third party to resolve any disputes amicably.

You Might Also Like

Airline Baggage, types & their handling procedures

Walking Tour

Stand By Passenger in Airlines

- Regional Support Office for Asia and the Pacific (RSOAP)
- Member States in Asia and the Pacific
- SUSTAINABLE TOURISM OBSERVATORIES (INSTO)

International tourism showed robust performance in January-September 2022, with arrivals reaching 63% of pre-pandemic levels in the first nine months of 2022. The results were driven by strong pent-up demand, lifting of travel restrictions of more destinations, as well as improvement of confidence levels.
Read more of the recent world tourism barometer here: UNWTO World Tourism Barometer, Volume 20, Issue 6, November 2022

Asia and the Pacific saw arrivals more than triple (+230%) from January to September 2022 compared to same period last year, reflecting the opening of many destinations in the region, including Japan.
Aside from increasing tourist arrivals, other industry indicators such as air capacity and hotel metrics are showing robust recovery for tourism. Air seat capacity on international routes (measured in available seat-kilometres or ASKs) in January-August reached 62% of 2019 levels, with Europe (78%) and the Americas (76%) posting the strongest results. Meanwhile, according to STR, global hotel occupancy rates reached 66% in September 2022, from 43% in January.
Industry metrics can be viewed collectively in UNWTO’s Tourism Recovery Tracker . The UNWTO Tourism Recovery Tracker is available for free and is a collaborative effort by a group of partners including the International Civil Aviation Organisation (ICAO), ForwardKeys, STR, Sojern, TCI Research and AIRDNA.
In terms of tourist numbers, the year 2022 is expected to close with over 900 million international arrivals, despite growing challenges pointing to a softening of the recovery pace.

- TourismBarometer
- TourismData
- WorldTourism
UNWTO becomes “UN Tourism”
World tourism barometer: january 2024, world tourism barometer: november 2023, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.


Most Popular
36th joint commission meeting of cap-csa and un tourism first regional forum on gastronomy tourism for asia and the pacific, 5th future tourism leaders workshop: sustainable tourism in best tourism villages, 5th future tourism leaders workshop (ftlw): application is open, recent comments, regional support office in asia and the pacific (rsoap), rsoap a to z.
- Sustainable Tourism Observatories(INSTO)
UNWTO A to Z
- About UNWTO
- Affiliate Members
- Member States
- Tourism in the 2030 Agenda
- World Tourism Day
- Technical Cooperation
- ASIA AND THE PACIFIC
- MIDDLE EAST
- RESOURCES/SERVICES
- Sustainable Development of Tourism
- Ethics, Culture and Social Responsibility
- Market Intelligence
- Tourism Data Dashboard
- Publications
- UNWTO Academy
Partners links

© UNWTO Regional Support Office for Asia and the Pacific (RSOAP)

- Bahasa Indonesia
- Eastern Europe
- Moscow Oblast
Elektrostal
Elektrostal Localisation : Country Russia , Oblast Moscow Oblast . Available Information : Geographical coordinates , Population, Altitude, Area, Weather and Hotel . Nearby cities and villages : Noginsk , Pavlovsky Posad and Staraya Kupavna .
Information
Find all the information of Elektrostal or click on the section of your choice in the left menu.
- Update data
Elektrostal Demography
Information on the people and the population of Elektrostal.
Elektrostal Geography
Geographic Information regarding City of Elektrostal .
Elektrostal Distance
Distance (in kilometers) between Elektrostal and the biggest cities of Russia.
Elektrostal Map
Locate simply the city of Elektrostal through the card, map and satellite image of the city.
Elektrostal Nearby cities and villages
Elektrostal weather.
Weather forecast for the next coming days and current time of Elektrostal.
Elektrostal Sunrise and sunset
Find below the times of sunrise and sunset calculated 7 days to Elektrostal.
Elektrostal Hotel
Our team has selected for you a list of hotel in Elektrostal classified by value for money. Book your hotel room at the best price.
Elektrostal Nearby
Below is a list of activities and point of interest in Elektrostal and its surroundings.
Elektrostal Page

- Information /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#info
- Demography /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#demo
- Geography /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#geo
- Distance /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#dist1
- Map /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#map
- Nearby cities and villages /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#dist2
- Weather /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#weather
- Sunrise and sunset /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#sun
- Hotel /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#hotel
- Nearby /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#around
- Page /Russian-Federation--Moscow-Oblast--Elektrostal#page
- Terms of Use
- Copyright © 2024 DB-City - All rights reserved
- Change Ad Consent Do not sell my data
View prices for your travel dates
- Excellent 6
- Very Good 11
- All languages ( 25 )
- Russian ( 25 )
- English ( 0 )
Own or manage this property? Claim your listing for free to respond to reviews, update your profile and much more.
ELEKTROSTAL HOTEL
Apart Hotel Yantar

View prices for your travel dates
Reviews we perform checks on reviews. tripadvisor’s approach to reviews before posting, each tripadvisor review goes through an automated tracking system, which collects information, answering the following questions: how, what, where and when. if the system detects something that potentially contradicts our community guidelines , the review is not published. when the system detects a problem, a review may be automatically rejected, sent to the reviewer for validation, or manually reviewed by our team of content specialists, who work 24/7 to maintain the quality of the reviews on our site. our team checks each review posted on the site disputed by our community as not meeting our community guidelines . learn more about our review moderation..
- Excellent 0
- Very Good 0
- English ( 0 )
Own or manage this property? Claim your listing for free to respond to reviews, update your profile and much more.
APART HOTEL YANTAR - Reviews, Photos
View prices for your travel dates
- Excellent 18
- Very Good 9
- All languages ( 43 )
- Russian ( 37 )
- English ( 4 )
- German ( 1 )
- Italian ( 1 )

Own or manage this property? Claim your listing for free to respond to reviews, update your profile and much more.
Apelsin Hotel - Reviews & Photos
UN Tourism | Bringing the world closer
- 25 Feb 2015
UNWTO report identifies common criteria for 4 and 5 star hotel classification
Share this content.
- Share this article on facebook
- Share this article on twitter
- Share this article on linkedin
PR No. : 15016
The new UNWTO report Hotel Classification Systems: Recurrence of Criteria in 4 and 5 Star Hotels , identifies the common criteria among 4 and 5 star hotels, providing valuable insights for destinations wishing to revise existing or establish new hotel classification systems.
Prepared jointly by UNWTO and Norwegian Accreditation (NA), an agency of the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Fisheries of Norway through its QualityMark Norway programme, the report reveals that despite the existence of many types of classification systems across the globe, there are more similarities than differences, both between geographic groups and between 4 and 5 star categories.
The report also provides a general overview of the existing types of hotel classifications, their benefits and challenges, and offers general guidance on areas to consider when setting up an official classification system.
Findings also suggest that more regular reviews of hotel classification systems can be useful to keep them up-to-date with rapidly evolving consumer needs, particularly with regards to technology and accessibility.
This is the second joint UNWTO/Norwegian Accreditation report on the topic of hotel classification, following Online Guest Reviews and Hotel Classification Systems: An Integrated Approach, published in 2014.
Useful links:
Full Report: Hotel Classification Systems: The Recurrence of Criteria in 4 and 5 Star Hotels Report: Online Guest Reviews and Hotel Classification Systems: An Integrated Approach UNWTO Regional Programme for Europe: Norwegian Accreditation
UNWTO Senior Media Officer: Marcelo Risi Tel: (+34) 91 567 81 60
UNWTO Communications & Publications Programme Tel: (+34) 91 567 8100 / Fax: +34 91 567 8218
Related Content
Unwto/unesco conference: cultural tourism sustains comm..., harness cultural routes and experiences for competitive..., sign up now: 1st hackathon for smart destinations (23-2..., innovation and digitalization top of european tourism agenda.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Tourism Statistics. Get the latest and most up-to-date tourism statistics for all the countries and regions around the world. Data on inbound, domestic and outbound tourism is available, as well as on tourism industries, employment and complementary indicators. All statistical tables available are displayed and can be accessed individually ...
The UNWTO Statistics Department is committed to developing tourism measurement for furthering knowledge of the sector, monitoring progress, evaluating impact, promoting results-focused management, and highlighting strategic issues for policy objectives.. The department works towards advancing the methodological frameworks for measuring tourism and expanding its analytical potential, designs ...
International Tourism and COVID-19. Export revenues from international tourism dropped 62% in 2020 and 59% in 2021, versus 2019 (real terms) and then rebounded in 2022, remaining 34% below pre-pandemic levels. The total loss in export revenues from tourism amounts to USD 2.6 trillion for that three-year period. Go to Dashboard.
In order to better understand accommodation demand and capacity in destinations, the World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) together with Telefonica has launched a dashboard on Accommodation - Demand and Capacity. The dashboard includes data on: Accommodation capacity. Establishments. Roomms.
These outline the Organization's budget and contributions of Members. Volume II - Staff Rules and Staff Regulations, contains the framework for duties, rights and benefits of employees. Volume III - Financial Regulations and Rules, constitutes the framework governing the budgetary and financial transactions of the Organization.
UN Tourism (UNWTO until 2023) is a specialized agency of the United Nations which promotes responsible, sustainable and universally-accessible tourism.Its headquarters are in Madrid, Spain.Other offices include: a Regional Support Office for Asia and the Pacific in Nara, Japan and a Regional Office for the Middle East in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.. UN Tourism serves as a global forum for tourism ...
These outline the Organization's budget and contributions of Members. Volume II - Staff Rules and Staff Regulations, contains the framework for duties, rights and benefits of employees. Volume III - Financial Regulations and Rules, constitutes the framework governing the budgetary and financial transactions of the Organization.
According to the first UNWTO World Tourism Barometer of the year, international tourism ended 2023 at 88% of pre-pandemic levels, with an estimated 1.3 billion international arrivals.The unleashing of remaining pent-up demand, increased air connectivity, and a stronger recovery of Asian markets and destinations, are expected to underpin a full recovery by the end of 2024 (UNWTO Tourism ...
The group is led by the Secretary General who supervises about 110 full-time staff at UNWTO's Madrid headquarters. A full-time Executive Director supports and assists the Affiliate Members. ... As per the directions of United Nations, the World Tourism organization has since then been promoting these code of ethics for implementation by ...
UN Tourism Secretary-General Zurab Pololikashvili took office in January 2018. Seeking to optimize the efficiency of the Organization, the Secretary-General has introduced a new leadership structure consisting of a Deputy Secretary-General and two Executive Directors, each one overseeing key structural areas and departments of the Organization, for increased efficiency in achieving UN Tourism ...
In 2019, people around the world were on the move. According to the United Nation's World Tourism Organization, there were 1.5 billion international tourist arrivals worldwide. A growing middle class with rising incomes and a desire for experiences has been fueling a travel boom. Gen Xers are entering their peak travel
International tourism showed robust performance in January-September 2022, with arrivals reaching 63% of pre-pandemic levels in the first nine months of 2022. The results were driven by strong pent-up demand, lifting of travel restrictions of more destinations, as well as improvement of confidence levels. Read more of the recent world tourism ...
recorded the largest decline in arrivals in the world in 2020, with the fewest travel restrictions eased over time, and more complete border closures in place for ... Sources: World Bank, South Pacific Tourism Organization, and IMF staff estimates.-100-80-60-40-20 0 20 40 Jan-19 Feb-19 Mar-19 Apr-19 May-19 Jun-19 Jul-19 Aug-19 Sep-19 Oct-19 Nov ...
International tourism up 4% in 2021 but still 72% below pre-pandemic levels Global tourism experienced a mild 4% upturn in 2021, with 15 million more international tourist arrivals (overnight visitors) than in 2020 but remained 72% below the levels of pre-pandemic year 2019 according to preliminary estimates. This follows a 73% plunge in international travel in 2020, the worst year on record ...
As such, international tourism can generate a tourism trade surplus when receipts exceed expenditure, or a deficit (vice versa) in the travel balance of countries. In 2019, the United States of America had the world's largest travel surplus with USD 62 billion, resulting from tourism receipts of USD 214 billion and expenditure of USD 152 billion.
Elektrostal Geography. Geographic Information regarding City of Elektrostal. Elektrostal Geographical coordinates. Latitude: 55.8, Longitude: 38.45. 55° 48′ 0″ North, 38° 27′ 0″ East. Elektrostal Area. 4,951 hectares. 49.51 km² (19.12 sq mi) Elektrostal Altitude.
BOTSWANA TELEVISION ENGLISH NEWS AT 1500HRS (CAT). #ikanyerona #kgasoyapopota #mindsetchange
Elektrostal Hotel, Elektrostal: See 25 traveler reviews, 44 candid photos, and great deals for Elektrostal Hotel, ranked #1 of 2 B&Bs / inns in Elektrostal and rated 4 of 5 at Tripadvisor.
The Apart-Hotel offers its guests free parking of the Yantar complex, 24-hour security and video surveillance, free WI-FI in rooms, a cozy Reception zone on the ground floor, two high-speed elevators making it pleasant and quick to go up to the 5th floor, where the apartments are located, the possibility of a continental breakfast in the restaurant "Around the World".
The bodies of the World Tourism Organization are the: General Assembly. General Assembly. The General Assembly is the principal gathering of the UN Tourism Organization. It meets every two years to approve the budget and programme of work and to debate topics of vital importance to the tourism sector. Every four years it elects a Secretary-General.
About Us. The World Tourism Organization (UN Tourism) is the United Nations agency responsible for the promotion of responsible, sustainable and universally accessible tourism. As the leading international organization in the field of tourism, UN Tourism promotes tourism as a driver of economic growth, inclusive development and environmental ...
The new UNWTO report Hotel Classification Systems: Recurrence of Criteria in 4 and 5 Star Hotels, identifies the common criteria among 4 and 5 star hotels, providing valuable insights for destinations wishing to revise existing or establish new hotel classification systems.
Total number of rooms reached 81. The hotel has got a number of significant advantages: comfortable location, luxury and standard hotel rooms, free parking, moderate prices and highly qualified staff. According the experts in the tourism and hospitality business the hotel is reckoned the leading middle class hotel in Moscow region.
PR No.: 15016. The new UNWTO report Hotel Classification Systems: Recurrence of Criteria in 4 and 5 Star Hotels, identifies the common criteria among 4 and 5 star hotels, providing valuable insights for destinations wishing to revise existing or establish new hotel classification systems. Benchmarking international accommodation standards can ...