

Horizontal and vertical integration: Made easy
Disclaimer: Some posts on Tourism Teacher may contain affiliate links. If you appreciate this content, you can show your support by making a purchase through these links or by buying me a coffee . Thank you for your support!
Horizontal and vertical integration are important concepts in all businesses, including those operating in the tourism industry.
An important management strategy, horizontal and vertical integration allows companies to be more competitive in the marketplace. But how does this actually work?
In this article I will teach you what horizontal and vertical integration is, discussing the advantages and disadvantages of both. I will also explain why such integration has happened/is happening and I will give you some examples of horizontal and vertical integration.
What is horizontal integration?
Advantages of horizontal integration, disadvantages of horizontal integration, horizontal integration in tourism examples, what is vertical integration, advantages of vertical integration, disadvantages of vertical integration, vertical integration in tourism examples, why has horizontal and vertical integration happened, horizontal and vertical integration: to conclude, further reading.
Horizontal integration is a competitive strategy that companies use. It refers to the acquisition of business activities that are at the same level of the chain of distribution in similar or different industries.
To put it simply, horizontal integration is when a related business merges with another business operating in the same level of the production chain. For example, a ski-based tour operator may merge with a tour operator which specialises in summer sun holidays.
These are different organisations, which operate at the same level.
There are many reasons that a company in the tourism industry may choose to integrate horizontally, such as:
- When the industry is growing
- When merges allows better value for money to be achieved
- When competitors lack expertise
- When the company can manage the operations of the bigger organisation efficiently, after the integration

Horizontal integration can be advantageous because it can enable economies of scale to be achieved (i.e. they can get better value for money). The bigger, horizontally integrated company can often achieve a higher production than the companies merged, at a lower cost.
Mergers help to provide organisations with increased power in the marketplace, whilst enabling the organisation with the opportunity to capture new markets. The company becomes larger, has a bigger marketshare and has less competition.
Horizontal integration can also allow organisations to penetrate new markets in different geographical areas. This is particularly relevant in travel and tourism , where operations occur around the globe.
Whilst there are benefits of horizontal integration, however, there are also disadvantages.
Organisations often encounter problems when they grow. Allowances need to be put in place for restructures and recruitment of new staff where appropriate.
There are also legal implication when merging companies. These differ in different countries. It is important that the organisation looks into any legal requirements that will be expected of them.
The decision whether to adopt vertical or horizontal integration has a long-term effect on the business strategy of a company and therefore the decision to do so must not be taken lightly.
Travelopia is a great example of a tourism organisation with lots of horizontal integration.
Travelopia is the world’s largest collection of specialist travel brands. This means that the organisation can offer a variety of products, which are at the same level in chain of distribution. So, whilst Aus Travel and American Holidays may be totally different companies, they are both at the same level (tour operators) under the Travelopia umbrella.

Another good example of horizontal integration in travel and tourism is the Virgin Group.
The Virgin Group have owned many different companies throughout the years and some have been more successful than others.
A good example of horizontal integration within Virgin Atlantic is their airlines based in different parts of the world. Virgin Atlantic is based in the UK, Virgin Australia is based in Australia and Virgin America (which ceased to continue after 2018) was based in the USA. All of these companies are/were at the same level of the distribution chain, but are/were different companies.

You can learn more about the Virgin brand here .
Vertical integration is the opposite of horizontal integration.
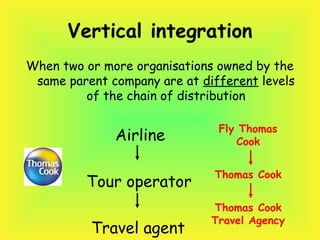
Vertical integration is a competitive strategy identified when a company takes over one or more other companies that are at different levels in the chain of distribution.
Many companies choose to opt for integration to allow for total control of all aspects of their business. This may include the manufacturing of their products right through to sales, for example.
There are several benefits of vertical integration in travel and tourism.
By maintaining control of the supply chain, organisations have greater control. They can regulate and manage all aspects.
For example, Tui holidays puts together their holidays via their tour operations and then sells them via their travel agents. They then put tourists on aircraft that are owned by TUI and tourists are greeted in their destination by TUI representatives- this demonstrates a smooth and consistent process throughout, where all aspects are owned and managed by TUI.
Vertical integration allows more scope for the highs and lows of business and enables the organisation to diversify their income. If one part of the business isn’t doing so well, there is the hope that the other areas of the business can compensate for this or to help absorb the loss. Likewise, if one area is doing particularly well, the money made from this can be invested in any areas of the business that require investment.
Vertical integration can also increase barriers for new entrants and help to reduce competition.
There are also some downsides of vertical integration.
Less competition means that prices may rise for consumers and that standards may drop.
The organisation may also have less flexibility as they must maintain a level of production in order to continue operations.
It can also be difficult for an organisation to be good at everything. Sometimes an organisation can do one thing particularly well, but then other areas may not have the same high standards (i.e. they may be great at making delicious sandwiches but not so great at offering customer service at the dining table).
Read also: – International tourism: What, where and why – Components of tourism: Structure of the tourism industry – The history of tourism – The Importance of tourism | Understanding the tourism industry – What is ABTA and how does it work?
TUI is one of the biggest travel companies in the world. Since the collapse of Thomas Cook, TUI has a monopoly of tour operator operations within the United Kingdom and other parts of the world.
You can learn more about the organisation TUI and its different branches here .
Within the umbrella organisation, TUI owns many different companies. Some are at the same level (horizontal integration) and other are at different levels (vertical integration).
As I described earlier, TUI has many companies that are at different levels of the chain of distribution. This includes their tour operations, travel agents, airline and in-destination services.

Disney is another organisation that has a history of both horizontal and vertical integration. You can learn all about this in the video below.
Horizontal and vertical integration has happened throughout all sorts of business around the world, including travel and tourism.
One reason for this is because the suppliers who work with companies or the distributors who work with the end product are unreliable. Therefore some organisations see it as easier to simply do these things themselves.
Money is also an important factor. Working with outside companies can often be more costly than doing it yourself. Suppliers and distributors may have big profit margins and this is money than can be saved of organisations take over these operations themselves.
Some companies simply have enough resource for horizontal and vertical integration to occur so… why not?
And lastly, when a specific industry grows considerably, as the travel industry did for many years prior to COVID-19, then there is more scope for organisations to expand through horizontal and vertical integration.
As you can see, horizontal and vertical integration is a competition strategy often used in business. Whether a company seeks to merge with other companies at the same (horizontal) level or at different (vertical) levels, there are many advantages both to the consumer and to the organisation itself. There are, however, also some disadvantages that need to be managed also.
If you’re studying travel and tourism then I highly recommend the following texts to support your learning:
- An Introduction to Tourism : a comprehensive and authoritative introduction to all facets of tourism including: the history of tourism; factors influencing the tourism industry; tourism in developing countries; sustainable tourism; forecasting future trends.
- The Business of Tourism Management : an introduction to key aspects of tourism, and to the practice of managing a tourism business.
- Tourism Management: An Introduction : gives its reader a strong understanding of the dimensions of tourism, the industries of which it is comprised, the issues that affect its success, and the management of its impact on destination economies, environments and communities.
Liked this article? Click to share!

What Is a Vertical Integration in Travel and Tourism?
By Michael Ferguson
In the world of travel and tourism, vertical integration is a term that is often used to describe the way in which different businesses work together to provide a complete travel experience for customers. Simply put, vertical integration refers to the process of combining two or more stages of the travel supply chain under one ownership or management structure.
What is Vertical Integration?
Vertical integration can take many different forms in the travel and tourism industry. At its most basic level, it involves combining different elements of the travel supply chain to create a seamless experience for customers. For example, a tour operator might own its own hotels, airlines, and transportation companies, allowing them to offer end-to-end packages that include everything from flights and accommodations to tours and activities.
There are many benefits to vertical integration in travel and tourism. By consolidating different parts of the supply chain under one roof, businesses can often save money on overhead costs like marketing and administration. Additionally, they can create a more streamlined experience for customers by ensuring that all aspects of their trip are coordinated and integrated seamlessly.
Types of Vertical Integration
There are several different types of vertical integration that are commonly used in the travel industry. These include:
Forward Integration
Forward integration refers to a situation where a business moves downstream in the supply chain towards the end customer. In other words, they take over functions that were previously performed by wholesalers or retailers. One example of forward integration in the travel industry might be a tour operator that opens its own retail stores or online booking platforms.
Backward Integration
Backward integration is when a business moves upstream in the supply chain towards their suppliers. In other words, they take over functions that were previously performed by wholesalers or manufacturers. An example of backward integration in the travel industry might be an airline that acquires its own fuel providers or aircraft maintenance companies.
Full Integration
Full integration is when a business owns or controls every aspect of the supply chain, from production to distribution. In the travel industry, this might involve a company that owns its own airlines, hotels, and transportation companies.
- Pros of Vertical Integration
There are several advantages to vertical integration in the travel and tourism industry:
- Cost savings: By consolidating different parts of the supply chain under one roof, businesses can often save money on overhead costs like marketing and administration.
- Increased control: With vertical integration, businesses have more control over their operations and can ensure that all aspects of their trip are coordinated and integrated seamlessly.
- Better customer experience: By offering end-to-end packages that include everything from flights and accommodations to tours and activities, businesses can create a more streamlined experience for customers.
- Cons of Vertical Integration
However, there are also some potential drawbacks to vertical integration:
- Risk concentration: By owning multiple elements of the supply chain, businesses may be exposed to greater risks if one part of their operation fails or experiences difficulties.
- Inflexibility: Vertical integration can sometimes make it harder for businesses to adapt to changes in the market or consumer preferences.
- Potential antitrust issues: In some cases, vertical integration may raise antitrust concerns if it creates too much market power for one company.
The Bottom Line
Vertical integration is a common strategy in the travel and tourism industry. By combining different elements of the travel supply chain under one ownership or management structure, businesses can create a more seamless experience for customers while also potentially saving on costs.
9 Related Question Answers Found
What is difference travel and tourism, what is the relationship between travel and tourism, what's the difference between travel industry and tourism industry, what is the difference between travel and tourism, what is difference between travel and tourism, what is geographic segmentation in tourism, what is difference between tourism and travel industry, what is difference between travel and tourism industry, what is the difference between travel industry and tourism industry, backpacking - budget travel - business travel - cruise ship - vacation - tourism - resort - cruise - road trip - destination wedding - tourist destination - best places, london - madrid - paris - prague - dubai - barcelona - rome.
© 2024 LuxuryTraveldiva
404 Not found

Linkages and Integrations in Travel Business
During the recent past, all businesses have become highly competitive and the travel industry is no exception in this context. Such competition has compelled the travel agencies and tour operators to seek ways to become more efficient and profitable in this direction. Since the tourism product is not an independent product rather it is a dependent product, which is formulated by the ‘tour manufactures’ by assembling various tourism product components – airline seats, hotel rooms, transportation, culture, and so on from other sectors of the economy. Essentially, travel industry has to maintain a close tie with the air industry, hotel industry, cultural and entertainment organizations. Such linkages are vital for the travel or tour operation industry to serve the diverse needs and demands of tourists
Below figure describes the linkages in travel trade business. The figure reveals that accommodation, transportation, recreation entertainment organizations, airlines, hotels have occupied a pivotal place in the travel industry and are supporting the travel agency business. In fact, travel agency or tour operators are creating demand for travel, lodging, food, shopping, entertainment and other tourism sources. Accommodation includes all forms of lodging, even camping and caravanning and all types of food and beverage services, transportation encompasses – airline, rail, road and sea; shopping includes any form of retail purchase such as souvenirs, arts & crafts, clothing and other. Banking and insurance companies offer financial and insurance services; tourism associations offer an opportunity to solve tourism industry problems and follow tourism business ethics; tourism educational institutions provide /supply right kind and quality human resource to operate and manage travel industry in a professional manner. Keeping in view the above mentioned aspects, one can say that, the linkages in the travel industry or the constituents of the travel industry are dependent on each other not only in terms of their business but also in relation to determining their marketing strategies. For example; a tour company will be able to package a tour with the help of transportation sector, accommodation sector, destination attraction, destination organizations, and so forth. Hence, all tourism services have a direct impact on the product of the tour operator. Figure 1. Describes the linkages in travel Trade :
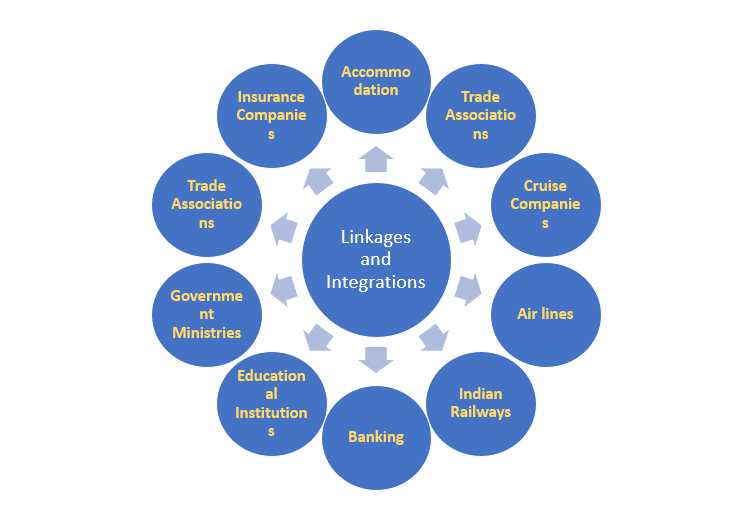
- Airlines: International Air Transport Association (IATA) operates a network by which travel agencies sell airline tickets and receives Commission. Thus the sale of airline tickets is highly regulated and strictly controlled. The agency commission range from 5 to 8 percent but most major airlines offer additional incentives i.e. cash bonuses and over ride commission. However, in some cases when a travel agency purchases air tickets in bulk the margin of commission will be high. This largely depends on relationship between the two organizations. The producer of sale of domestic airline tickets is different from country- to country and even the rate of commission also varies. Today, airline ticketing and reservation is almost entirely automated.
- Accommodation Companies : Most hotels and other lodging companies including major Indian and international hotel chains pay commission to the travel agencies, (the rate varies from hotel to hotel) however hoteliers in dealing with travel agencies are more information and less regulated than the airline companies. Interestingly many hotels and hotel chains participate in computer reservation system (CRS) permitting hotel reservation to be made at the same terminal, which is used to sell airline tickets. The commission received from hotels is the second largest component of total agency’s revenue. But if the purchase is made in bulk than the profit is based on the negotiated prices and accordingly the profit may be higher or lower.
- Cruise Companies: The cruise companies are informally regulated by its Own governing body i.e. cruise lines association which must approve any travel agency that. Desires to sell booking on behalf of any member of a cruise company the raise companies also offer a complete package including sea travel accommodation food entertainment and sometime air travel also. The commission varies room 10 to 20 percent. However most cruise package tour are sold to the public through travel agencies. It was Thomas cook who brought first group of foreign tourist in India through sea rout.
- Insurance Companies: Today many travel companies have included travel insurance in their package tour like Thomas cooks. The company insured the travellers to protect them against accident, loss of baggage and missing flights. Successful travel agency management has to make close contact with Insurance companies to obtain insurance policies for its clients. Recently the Oriental Insurance Company has introduced two new travel policies for domestic as well foreign tourist i.e. ‘Suhana
Safar’ for domestic travellers And ‘Videsh Yatra Mitra’ for foreign travellers. Incidentally the foreign policy is an upgraded version of overseas medical insurance.
- Banking Companies: Travel agencies offer banking facilities to the traveller like clearance of traveller cheques and arrangement of foreign currency. Only those travel agencies, which are authorized by the reserve bank of India under Foreign Exchange Regulation Act 1973, can deal with foreign currency. Banking companies give commission to travel agencies on traveller cheques and currency exchange.
- Educational Institutions: An agency’s success depends almost entirely on the competence of management and expertise of the staff. It develops manpower planning in such a way that will help to conduct on campus selection and match the student to the requirements of the company. The linkage between travel Companies and tourism education institutions will solve the problem of human resource requirements of present and future. Therefore a travel company needs to maintain close contact and interface with tourism Education intuitions. Many chief executives from the industry are the members of the advisory board of the intuitions.
- Travel Trade Associations: These associations provide a common platform to solve many problems of the members such as training, common code of conduct airlines commission to any other. There are a number of travel trade associations like TAAI, ICAO, ASTA, IATA, and PATA, WTO, that are quite active in the Promotion of travel trade at global. Essentially every travel company should be this association to avail financial and non – financial incentives and commissions from the airlines, hotels, railways etc.
- Tour operators / destination companies : The travel agencies need to maintain close ties with many other organizations offering travel related service like cultures and entertainment organizations foreign tour companies’ regional passport office, department of tourism both at centre and states sports operators transport operators food and beverage business etc. in fact these organizations play a vital role in making travel a complete product. Travel companies provide business to above cited organization and in return receive commissions. However there are few other originations that help the agency to run travel business smoothly and promote India as a tourist Destination. Technically a Travel Company cannot work in isolation but is interdependence with other travel related enterprises.
Keeping in view the above mentioned aspects, one can say that, the linkages in the travel industry or the constituents of the tourism industry are dependent on each other not only in terms of their business but also in relation to determining their marketing strategies. It can be supported with an example; a tour company will be able to package a tour with the help of transportation sector, accommodation sector, destination attraction, destination organizations, and so forth.
Meaning of Integration in Travel Trade
As a lay man integration refers to the end result of a process. The integration aims to sew up together different subsystems so that the data contained in each system becomes part of a more comprehensive system that will share ideally, quickly and easily information when required. However, as per business perspective, business integration defined as a strategy whose goal is to synchronize information technology (IT) and business cultures and objectives and aligns technology with business strategy and goals. Business integration is a reflection of how IT is being absorbed as a function of business. It is also used to cross-train management and employees reduce ineffective communication and cut supplier costs. As you analyze your company operations, think of the different ways you can integrate processes to save the company time and money. Thus, integration is the process by which a business can strengthen its arms both financial and economically.
Types of Integration in travel trade
1. horizontal integration : .
Horizontal Integration occurs when two companies merge together; it is where one business which offers a product takes over another business who offers similar products/services. An example of horizontal integration is the First Choice Group and this is because they own First Choice Hypermarket as well as First Choice Travel Agency. The reason why they are part of the horizontal integration is because looking at the buying chain they are on the exact same level. Moreover, when two travel agencies merged to form a new travel agency or one takeover the business of another is known as Horizontal Integration.
2. Vertical Integration
Vertical Integration is when one company expands its business into a variety of different areas; the company buys another similar organisation however it is on a different level of the chain. An example of vertical integration is a hotel company starts travel division to diversify its product line towards tourism. In the travel industry two companies take over one another in order to find out different ways to sell their products and services to their customers. Moreover, when two are more organisations owned by the same parent company are at different levels of the chain of distribution is known as Vertical Integration.
You Might Also Like

World Major Airports with Official Codes

Tourist Circuits of India Part-I

Tourism Destination Development
This post has one comment.
Pingback: What Is Horizontal Integration In Travel And Tourism? – Fallsgardencafe
Comments are closed.

- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Vertical Integration
- How It Works
- Pros and Cons
- Vertical vs. Horizontal
The Bottom Line
- Corporate Finance
Vertical Integration Explained: How It Works, With Types and Examples
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
Katrina Ávila Munichiello is an experienced editor, writer, fact-checker, and proofreader with more than fourteen years of experience working with print and online publications.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/KatrinaAvilaMunichiellophoto-9d116d50f0874b61887d2d214d440889.jpg)
What Is Vertical Integration?
Vertical integration is a strategy that allows a company to streamline its operations by taking direct ownership of various stages of its production process rather than relying on external contractors or suppliers. Companies can achieve vertical integration by acquiring or establishing their own suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, or retail locations rather than outsourcing them. Vertical integration can be risky due to the significant initial capital investment required.
Key Takeaways
- Vertical integration requires a company's direct ownership of suppliers, distributors, or retail locations to obtain greater control of its supply chain.
- The advantages can include greater efficiencies, reduced costs, and more control along the manufacturing or distribution process.
- Vertical integration often require heavy upfront capital that may reduce a company's long-term flexibility.
- Forward integration occurs when a vendor attempts to acquire a company further along the supply chain (i.e. acquire a retailer).
- Backward integration occurs when a vendor attempts to acquire a company prior to it along the supply chain (i.e. a raw material provider).
Investopedia / Mira Norian
How Vertical Integration Works
Vertical integration occurs when a company attempts to broaden its footprint across the supply chain or manufacturing process. Instead of sticking to a single point along the process, a company engages in vertical integration to become more self-reliant on other aspects of the process. For example, a manufacturer may want to directly source its own raw materials or sell directly to consumers.
The supply chain or sales process typically begins with the purchase of raw materials from a supplier and ends with the sale of the final product to the customer. Vertical integration requires a company to take control of two or more of the steps involved in the creation and sale of a product or service. The company must buy or recreate a part of the production , distribution, or retail sales process that was previously outsourced.
Companies can vertically integrate by purchasing their suppliers to reduce manufacturing costs. They can invest in the retail end of the process by opening websites and physical stores. They can invest in warehouses and fleets of vans to control the distribution process.
All of these steps involve a substantial investment of money to set up facilities and hire additional talent and management. Vertical integration also ends up increasing the size and complexity of the company's operations.
As a company engages in more activities along a single supply chain, it may result in a market monopoly. A monopoly that occurs due to vertical integration is also called a vertical monopoly.
Types of Vertical Integration
There are a number of ways that a company can achieve vertical integration. Two of the most common are backward and forward integration.
Backward Integration
A company that chooses backward integration moves the ownership control of its products to a point earlier in the supply chain or the production process.
This form of vertical integration is aptly named as a company often strives to acquire a raw material distributor or provider towards the beginning of a supply chain. The companies towards the start of the supply chain are often specialized in their distinct step in the process (i.e. a wood distributor to a furniture manufacturer). In an attempt to streamline processes, the furniture manufacturer would try to bring the wood sourcing in-house.
Amazon ( AMZN ) started as an online retailer of books that it purchased from established publishers. Although it continues to do so, it also became a publisher. The company eventually branched out into thousands of branded products. Then, it introduced its own private label, Amazon Basics, to sell many of them directly to consumers.
Forward Integration
A company that decides on forward integration expands by gaining control of the distribution process and sale of its finished products.
A clothing manufacturer can sell its finished products to a middleman , who then sells them in smaller batches to individual retailers. If the clothing manufacturer were to experience forward vertical integration, the manufacturer would join a retailer and be able to open its own stores. The company would aim to bring in more money per product, assuming it can operate its retail arm efficiently.
Forward integration is a less common form of vertical integration because it is often more difficult for companies to acquire others that are further along the supply chain. For example, the largest retailers at the end of the supply chain often have the greatest cash flow and purchasing power . Instead of these retailers being acquired, they often have the capital on hand to be the acquirer , which is an example of backward integration.
Balanced Integration
A balanced integration is an approach to vertical integration where a company aims to merge with companies both before it and after it along the supply chain. A company must be the middleman and manufacture a product to engage in balanced integration. That's because it must both source raw materials as well as work with retailers to deliver the final product.
Consider the supply chain process for Coca-Cola ( KO ) where raw materials are sourced, the beverage is concocted, and bottled drinks are distributed for sale. Should Coca-Cola choose to merge with both its raw material providers as well as retailers who will sell the product, the company is then engaging in balanced integration.
Though most costly and risky due to the diversified nature of business operations, balanced integration also poses the greatest upside as a company is more likely to have greater (if not full) control over the entire supply chain process.
Although vertical integration can reduce costs and create a more efficient supply chain, the capital expenditures involved can be significant.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Vertical Integration
Vertical integration can help a company reduce costs and improve efficiency. However, when executed poorly, vertical integration may have negative consequences on the company.
The primary goal of vertical integration is to gain greater control over the supply chain and manufacturing process. When performed well, vertical integration may lead to lower costs, economies of scale , and a lower reliance on external parties.
Vertical integration may lead to lower transportation costs, smaller turnaround times, or simpler logistics if the entire process is managed in-house. This may also result in higher quality products as the company has direct control over the raw materials used through the manufacturing line.
Companies may sometimes find themselves at the whim of suppliers who have market power. Through vertical integration, companies can circumnavigate external monopolies . In addition, a company may gain insights from a retailer on what goods are selling best; this information may be very useful in making manufacturing and product decisions.
Disadvantages
Companies can't vertically integrate overnight. In fact, it is a long-term process that requires widespread buy-in. This also includes heavy upfront capital expenditure requirements to acquire the proper company, integrate new and existing systems, and ensure that staff is trained across the entire manufacturing process.
By vertically integrating, companies do sacrifice some degree of flexibility. This is because they commit capital to a specific process or product. Instead of being able to decline purchasing from an external vendor , a company will likely have committed money that can not be easily recovered. In addition, a company may lose the opportunity to gain unique knowledge through different external vendors .
Vertical integration may also have several social impacts. Companies may end up trying to do too much and lose focus on their ultimate goal. In addition, customers may not support the culture of a large manufacturer also interfacing directly with customers.
Long-term cost saving due to favorable pricing and minimal supply chain disruptions
Economies of scale, which increase efficiency
Reduces or eliminates the need to rely on external parties/suppliers
Greater control over the product, inputs, and process, which may lead to superior products
Requires large upfront capital requirements to implement
Reduce a company's long-term flexibility
Loss of focus on a company's primary objective or customer
Displeased customer base that would prefer to work with smaller retailer

Vertical Integration vs. Horizontal Integration
Vertical integration involves the acquisition of a key component of the supply chain that the company has previously contracted for. It may reduce the company's costs and give it greater control of its products. Ultimately, it can increase the company's profits.
Horizontal integration , on the other hand, involves the acquisition of a competitor or related business. A company may do this to accomplish any or all of the following:
- Eliminate a rival and cut out its competition
- Improve or diversify its core business
- Expand into new markets
- Increase its overall sales
While a vertical integration strategy stretches a company along a single process, horizontal integration is a more pointed approach that causes a company to become more specific or niche within a certain market. For example, instead of engaging in all aspects of a supply chain ranging from materials sourcing, manufacturing, or retail, a company can choose to master only one of those facets by acquiring similar companies to engage in horizontal integration.
Much analysis has gone into reviewing when it is more optimal to simply contract with another company as oppose to acquire them. Published modern economic theory on the matter dates back decades.
Examples of Vertical Integration
Netflix ( NFLX ) is a prime example of vertical integration. The company started as a DVD rental business before moving into online streaming of films and movies licensed from major studios. Executives then realized they could improve their margins by producing some of their own original content like the hit shows "Grace & Frankie" and "Stranger Things." It also produced some bombs, like 2016's The "Get Down," which reportedly cost the company $120 million.
The company now uses its distribution model to promote its original content alongside programming licensed by studios. Instead of simply relying on the content of others, Netflix performed vertical integration to become more engaged in the entertainment development process earlier.
Fossil Fuel Industry
The fossil fuel industry is a case study in vertical integration. British Petroleum ( BP ), ExxonMobil ( XOM ), and Shell ( SHEL ) all have exploration divisions that seek new sources of oil and subsidiaries that are devoted to extracting and refining it. Their transportation divisions transport the finished product. Their retail divisions operate the gas stations that deliver their product.
Live Nation & Ticketmaster
The merger of Live Nation and Ticketmaster in 2010 created a vertically integrated entertainment company that manages and represents artists, produces shows, and sells event tickets. The combined entity manages and owns concert venues, while also selling tickets to the events at those venues.
When Is an Acquisition Considered Vertical Integration?
An acquisition is an example of vertical integration if it results in the company's direct control over a key piece of its production or distribution process that had previously been outsourced.
A company's acquisition of a supplier is known as backward integration. Its acquisition of a distributor or retailer is called forward integration. In the latter case, the company is often buying a customer, whether it was a wholesaler or a retailer.
Is Vertical Integration Good for a Company?
Whether vertical integration makes sense for a company depends on what's good for it in the long run. If a company makes clothing with buttons, it can buy the buttons or make them. Making them eliminates the markup charged by the button-maker. It may give the company greater flexibility to change styles or colors while eliminating the frustrations that come with dealing with a supplier.
Then again, the company would have to set up or buy a whole separate manufacturing process for buttons, buy the raw materials that go into making and attaching buttons, and hire people to make the buttons along with a management team to manage the button division.
What Is the Difference Between Vertical Integration and Horizontal Integration?
Vertical integration is the practice of acquiring different pieces along a supply chain that a company does not currently manage. Horizontal integration is the practice of acquiring similar companies to further master what it already does. Vertical integration makes a company broader while horizontal integration may help it penetrate a specific market further.
Why Do Companies Use Vertical Integration?
Companies use vertical integration to have more control over the supply chain of a manufacturing process. By taking certain steps in-house, the manufacturer can control the timing, process, and aspects of additional stages of development. Owning more of the process may also result in long-term cost savings (as opposed to buying outsourced goods at marked-up costs).
Vertical integration is the business arrangement in which a company controls different stages along the supply chain. Instead of relying on external suppliers, the company strives to bring processes in-house to have better control over the production process. Though vertical integration may result in increased upfront capital outlays, the goal of vertical integration is to streamline processes for more efficient and controlled operations in the long-term.
Harvard Library. " The Costs and Benefits of Ownership: A Theory of Vertical and Lateral Integration ."
Variety. " Inside the Troubled Production of Baz Luhrmann's 'The Get Down,' Netflix's Most Expensive Series Yet ."
U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. " Form 10-K, Netflix, Inc. ," Page 30.
U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. " Live Nation and Ticketmaster Entertainment Complete Merger ."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1402948131-b5d3c90e09cb43248f4264d3e9fcfab9.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
examples of vertical integration in travel and tourism industry
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Vertical-integration-7a31b884b9564a139c5ec2f7885ff3f0.jpg)
Vertical integration travel and tourism. Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of vertical integration within a tourism context 2022-11-08
Vertical integration is a business strategy that involves a company owning or controlling all aspects of the production and distribution of a product or service. In the travel and tourism industry, vertical integration can take many forms, such as a hotel chain owning its own airline, or a tour operator owning its own travel agencies.
One advantage of vertical integration in travel and tourism is that it allows a company to have more control over the quality of its products and services. For example, if a hotel chain owns its own airline, it can ensure that its guests have a comfortable and seamless travel experience from the moment they leave their homes to the moment they arrive at their destination. This level of control can help a company differentiate itself from its competitors and attract repeat customers.
Another advantage of vertical integration in travel and tourism is that it can lead to cost savings. By owning all aspects of the production and distribution process, a company can eliminate the need to pay intermediaries, such as wholesalers or agents. This can result in lower prices for the end customer and increased profits for the company.
However, there are also potential drawbacks to vertical integration in the travel and tourism industry. For example, a company that is heavily integrated may have a limited range of products and services to offer, as it only controls a specific part of the supply chain. This can limit the company's flexibility and its ability to adapt to changing customer preferences or market conditions.
Additionally, vertical integration can lead to increased risks for a company, as it is more reliant on its own internal operations. If any part of the production or distribution process breaks down, the entire business may be affected. This can be particularly problematic in the travel and tourism industry, where customer expectations are high and any disruptions can have serious consequences.
Overall, vertical integration in travel and tourism can offer many benefits, including greater control over the quality of products and services, cost savings, and increased efficiency. However, it is important for companies to carefully consider the potential risks and limitations of this strategy before fully committing to it.
Essays on vertical integration in travel and tourism. Free essay topics and examples about vertical integration in travel and tourism
It to provide a tourism and their Forward, or downstream, vertical integration occurs when the company joins with or creates businesses whose role in the production of its goods occurs after its own; the products move forward after the company has finished its share of the manufacture. One of the firm's most prominent successes is its vertical integration strategy. Together they sell about of the package holidays bought in the K. They are divided into: Hierarchical relationships ensure unity of action, giving the enterprise, from this point of view, the operational departments, hierarchically subordinated them. . This work called "Sports tourism" describes the impacts of sports tourism, the players in this sector and their roles, and also the impacts of the games as a tourism venture. Demographics deals with the study population and the population is important for tourism organizations for two reasons: First, the population is a key factor influencing demand for tourism organizations.
Vertical and horizontal integration in tourism.
. After their content, the relationships within an organization are: Relationships determines the effective exercise of authority. Then again, the company would have to set up or buy a whole separate manufacturing process for buttons, buy the raw materials that go into making and attaching buttons, hire people to make the buttons, and hire a management team to manage the button division. . But if the purchase is made in bulk than the profit is based on the negotiated prices and accordingly the profit may be higher or lower. Explain the difference between forward vertical and backward vertical integration.
Horizontal And Vertical Integration Made EASY! Advantages, disadvantages and examples. [video]

The size of the tourism market and ease of entry of competitors led to fierce competition. Changes in consumer behavior gave rise to new tourism. . However apple have very cleverly vertically integrated the production of apps for the apple IOS systems by only supplying one… HomeStyle Hotels 1. This form of vertical integration is aptly named as a company often strives to acquire a raw material distributor or provider towards the beginning of a supply chain.
Linkages and Integrations in Travel Business » Tourism Beast
Regardless of the position they occupy, it is clear that the scope of activities influence people life, growing up over time. Additionally, the company has been able to comply with the laid down laws and regulations that govern operations of travel and tourism firms. Rarely used other alternative energy sources. Through vertical integration, companies can circumnavigate external monopolies. Travel Agencies are exclusive caterers who provide services embodied to tourism for suppliers like airlines, car rentals, cruise lines, railways, hotels and package tours. Collaboration in tourism planning is viewed as an interactive approach that requires participation and physical interaction between responsible an organization, the unit of governance and the stakeholders.
Vertical Integration: Clipping the wings of the Seychelles Tourism Industry

Business integration is a reflection of how IT is being absorbed as a function of business. Our engineering specialists follow the paper instructions and ensure timely delivery of the paper. The hospitality sector in UK boost its profitability with a series of events like Olympic Games 2012 and will be delivering world class service to the Ryder Cup and Commonwealth Games in 2014 and the Rugby World Cup in 2015. . Vertical integration allows more scope for the highs and lows of business and enables the organisation to diversify their income. Information technology is thus applied in areas that require management and distribution of information on travel and tourism. Opportunities resulting from technological development can be found in cheaper supplies in improvement of goods and services or to better marketing.
Vertical integration and the effect on the travel and tourism

. An example of horizontal integration is the First Choice Group and this is because they own First Choice Hypermarket as well as First Choice Travel Agency. This paper examines the historic developments of travel and tourism with reference to the contribution of technological and economic developments, including the industrial revolution over the last two years, tells about the role of national authority governments in the development of tourism. There are Vertical and horizontal integration within the tourism and hospitality industry also allow for the consolidation of branding, for example, the expansion of the References Hargrave, A. .
Vertical Integration Explained: How It Works, With Types and Examples
Companies use vertical integration to have more control over the supply chain of a manufacturing process. Tour Operators will earn less money than usual; this means there will be less work for travel agents therefore they will get bored easily as no customers are entering the store. . Is an estimate that over 500,000 people are employed in the industry. . In 2013, she was hired as senior editor to assist in the transformation of Tea Magazine from a small quarterly publication to a nationally distributed monthly magazine. It is also thought that in the tourists eyes a company combining all aspects of the tourism experience will be of more use and more popular with tourists.
Integration of Travel and Hospitality Companies
. . . Horizontal and vertical integration occurs in the travel and tourism industry and in other industries all around the world. . Networking across these business sectors is called vertical integration, which is done through large scale cooperation among different service chains such as acquisitions, mergers, joint ventures or other similar levels of partnership. The client can ask the writer for drafts of the paper.
Vertical Integration and the Effect on the Travel and Tourism Essay Example
- Pages: 2 (537 words)
- Published: February 10, 2018
- Type: Case Study
Vertical Integration and the Effect on the Travel and Tourism Industry When two scalar companies such as two hotels, are offering very similar products and are In a strong competing situation, Integration Is a popular move. It can be a voluntary decision by both companies or it can be the take-over of one company by another. Benefits include greater sales, which result in larger revenue and expansion opportunities.
Complimentary reasons tend to be the realization that one hotel offers something that the other hotel doesn't and vice versa.
If the two combined it would create one stronger hotel. The vertical in the supply structure represent examples of vertical integration. This the merging of two companies up or down the chain as opposed to across the same level of the cha
Moving down the chain Is known as forward vertical integration. An example of this would be a tour operator buying a chain of travel agents. Backward Integration Is moving up the chain. An example of backward Integration would be a tour operator buying a principal, such as an airline.
It Is understood that as you go up he chain each level costs more to buy. This is why forward vertical integration is more commonly found because a travel agency would rarely have enough capital to buy a principal, which is at the top of the chain. Company expansion is the major reason for this type of merging. A tour operator with its own airline will be much higher in the chain than a tour operator without its own airline. It is also thought that in the tourists eyes a company combining all aspects of
the tourism experience will be of more use and more popular with tourists.
This Is because It would mean that a tourist could buy al the aspects of their holiday from the one company.
Some strong vertical Integration has taken place In the travel and tourism Industry since the asses. The largest travel groups such as Thomson, Riotous (now known as Moderately) and Thomas Cook own the tour operators who are responsible for putting together the package holidays. The travel agencies who sell these package holidays to customers are also owned by these travel groups, as are the airlines which take the resists to their destinations.
This means that the travel agent at places like Thomas Cook or LUHN Poly will prefer to sell their own tour operators' holiday rather than those of others. These companies may also have links with car hire companies and hotel chains. So they can get these holidays at the cheapest prices possible and make a large profit from the customer.
The four largest tour operators In the UK dominate the holiday market. Together they sell about of the package holidays bought in the K. This makes it difficult for or the customer.
The recent takeover of Thomson by the German travel giant Presage for almost DMS$6 billion (US$2. 9 billion) shows that takeovers will carry on and the larger companies will continue to grow.
This means that there will be less competition in the market. Questions: . What is integration? Explain the difference between vertical and horizontal integration. 2. Explain the difference between forward vertical and backward vertical integration.
- Investigating Travel And Tourism Analysis Essay Example
- The car hire market in the UK evolves around the tourism industry Essay Example
- SWOT Analysis of the Vegas Tourism Industry and Marketing - College Essay Example
- Marketing In Tourism And Travel Tourism Essay Example
- Travel And Tourism Industry Of Pakistan Tourism Essay Example
- Amazing Thailand Essay Example
- Destination Marketing Essay Example
- Amazing and Strategic Changes of Tui Essay Example
- Allowing knowledge to students Essay Example
- Marketing In Travel And Tourism Essay Example
- Marketing Uk Tourism Analysis Essay Example
- SWOT Analysis of the Vegas Tourism Industry and Marketing Essay Example
- Pushing them physically Essay Example
- Strategies in Theme Park Marketing Essay Example
- Perspective of Tourism Marketing in the Post-War Jaffna Essay Example
- Advertising essays
- Audience Theory essays
- Competitor Analysis essays
- Consumer essays
- Marketing Management essays
- Marketing Mix essays
- Marketing Plan essays
- Marketing Research essays
- Marketing Strategy essays
- Point Of Sale essays
- Price essays
- Procurement essays
- Product essays
- Product Differentiation essays
- Promotion essays
- Promotion And Marketing Communications essays
- Retailing essays
- Trademark essays
- Anheuser-busch essays
- Brands essays
- Detergent essays
- Product Placement essays
- Research Design essays
- New Product Development essays
- Advertisement essays
- Brand essays
- Sales Promotion essays
- Advertising campaign essays
- Consumer behaviour essays
- Offer And Acceptance essays
- Wal-Mart essays
- Discover essays
- Cultural Tourism essays
- Accounting essays
- Andrew Carnegie essays
- Automation essays
- Business Cycle essays
- Business Intelligence essays
- Business Model essays
- Business Operations essays
- Business Software essays
- Cooperation essays
- Cooperative essays
- Corporate Social Responsibility essays
- Corporation essays
- Customer Relationship Management essays
- Family Business essays
- Franchising essays
- Harvard Business School essays
- Harvard university essays
Haven't found what you were looking for?
Search for samples, answers to your questions and flashcards.
- Enter your topic/question
- Receive an explanation
- Ask one question at a time
- Enter a specific assignment topic
- Aim at least 500 characters
- a topic sentence that states the main or controlling idea
- supporting sentences to explain and develop the point you’re making
- evidence from your reading or an example from the subject area that supports your point
- analysis of the implication/significance/impact of the evidence finished off with a critical conclusion you have drawn from the evidence.
Unfortunately copying the content is not possible
Tell us your email address and we’ll send this sample there..
By continuing, you agree to our Terms and Conditions .
404 Not found
Quick-Advices
Add custom text here or remove it
What is an example of horizontal integration in travel and tourism?
Table of Contents
- 1 What is an example of horizontal integration in travel and tourism?
- 2 Is Disney vertically or horizontally integrated?
- 3 What is horizontal integration in tourism industry?
- 4 Is Coca-Cola horizontal integration?
- 5 Which is the best example of a merger?
- 6 Why is it important to look at mergers?
Another good example of horizontal integration in travel and tourism is the Virgin Group. The Virgin Group have owned many different companies throughout the years and some have been more successful than others.
How is TUI horizontal integration?
TUI. TUI has an horizontal integration this is where businesses at the same level in the chain of distribution merge together or are purchased by another. TUI has this one as TUI own part of major airlines which helps them have a interrelationship with different companies.
What are some examples of horizontal integration?
Three examples of horizontal integration are the merger of Marriott and Starwood Hotels in 2016, the merger of Anheuser-Busch InBev and SABMiller in 2016, and the merger of The Walt Disney Company and 21st Century Fox in 2017.
Is Disney vertically or horizontally integrated?
Arguably the largest vertical integrator is the Walt Disney Company, which owns the companies that create and produce film and television properties, and are then marketed and distributed by Disney throughout the world, who therein broadcast on affiliated networks, such as ABC and other channels and platforms like ABC. …
Is British Airways horizontally integrated?
British Airways (BA) boss Willie Walsh has said the planned merger with Iberia is “great news for British Airways, our customers and our shareholders”[1] British Airways is a flag carrier of the UK. This merger can be classified as ‘Horizontal integration’ where two organisations join in the same level of production.
What is Horizontal integration in tourism industry?
Horizontal Integration Occurs when companies are bought out or merged at the same level in the chain of distribution, such as travel agencies buying each other.
What is horizontal integration in tourism industry?
What companies use horizontal and vertical integration?
- Heinz and Kraft Foods merger is an example of Horizontal Integration.
- A store like Target, which has its own store brands, is an example of Vertical Integration.
What is horizontal mergers?
A Horizontal merger is a merger between firms that produce and sell the same products, i.e., between competing firms. Horizontal mergers, if significant in size, can reduce competition in a market and are often reviewed by competition authorities.
Is Coca-Cola horizontal integration?
As part of their Horizontal Integration strategy, Coca-Cola acquired del Valle in 2007. In this way, Coca-Cola was able to cover other fronts by taking over the manufacture of substitute products such as energy drinks in the first instance as occurred with the launch of Powerade and juices.
Is Amazon horizontal or vertical integration?
The operational model of Amazon is to do vertical integration using its scale.
Who are British Airways integrated with?
We are a member of oneworld® along with Alaska Airlines, American Airlines, Cathay Pacific, Finnair, Iberia, Japan Airlines, Malaysia Airlines, Qantas, Qatar Airways, Royal Air Maroc, Royal Jordanian, S7 Airlines and SriLankan Airlines.
Which is the best example of a merger?
Which is an example of horizontal integration in tourism?
When do horizontal mergers and acquisitions take place?
Why is it important to look at mergers?
Privacy Overview

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Horizontal integration in tourism examples . Travelopia is a great example of a tourism organisation with lots of horizontal integration. ... There are several benefits of vertical integration in travel and tourism. By maintaining control of the supply chain, organisations have greater control. They can regulate and manage all aspects.
Vertical integration is a common strategy in the travel and tourism industry. By combining different elements of the travel supply chain under one ownership or management structure, businesses can create a more seamless experience for customers while also potentially saving on costs. However, there are also potential drawbacks to vertical ...
Vertical integration in the travel and tourism industry is a popular business strategy. This describes the integration of airlines, hotel operators, car rental services and tour packager and other ...
Vertical integration in tourism examples. TUI is one for the biggest travel company in the world. Since the collapse of Thomas Cook, TUI has a monopoly of tour operator operations within the United Kingdom and other parts from the world. ... If you're studying travel and tourism then I highly share who followed texts to support your learning ...
2. Vertical Integration. Vertical Integration is when one company expands its business into a variety of different areas; the company buys another similar organisation however it is on a different level of the chain. An example of vertical integration is a hotel company starts travel division to diversify its product line towards tourism.
The asset-heavy business strategy, one of vertical integration, recently has resurfaced with many global travel companies. They are forming their own hotel ownership and management divisions. The ...
The failure of vertical integration across tourism's component sectors can be attributed in considerable part to the contrasting forms of organization in each. Airlines have strongly Fordist characteristics, whereas hotels tend towards both pre-Fordist (in smaller establishments) and post-Fordist operations (in large, international-standard ...
The topic of vertical integration in the European tourism sector was investigated by [41]. Jin et al. [41] looked into how customer decision behavior in similar package tours was affected by the ...
Literature has classified the tourism sector into eight vertical and horizontal integration: hotels, adventure and leisure, attractions, events and conferences, food and beverage, transportation ...
Abstract. This paper addresses two interrelated issues in tourism development: horizontal integration within tourism's component sectors and attempts at vertical integration between them. The paper employs a conceptual framework adapted from regulation theory, to assess the dynamics of these processes, particularly in relation to airlines and ...
2. Consumer Electronics | Samsung. The South Korean MNC is a more traditional example of both forward and backward vertical integration. Through its various divisions, Samsung is actively involved in the manufacture of various components, such as LCD and AMOLED displays, antennas, Li-ion batteries, camera modules, and semiconductors.
This paper addresses two interrelated issues in tourism development: horizontal integration within tourism's component sectors and attempts at vertical integration between them. The paper employs ...
Vertical integration-. Vertical integration is when businesses at one point in the chain purchases a business at a higher or lower level of the chain of distribution. An example of vertical integration is when the tour operator Thomson merged with First Choice Holidays in September 2007. This enabled Thomson (which is now part of the TUI group ...
Vertical integration is a strategy where a company expands its business operations into different steps on the same production path, such as when a manufacturer owns its supplier and/or ...
Vertical integration occurs when two companies at different levels in the chain of distribution merge or are bought. This may be backwards integration- for example, a tour operator buys a hotel - or forwards integration, for example a tour operator may buy a travel agency. Tour operators have bought or created airlines, hotels and travel agencies.
Vertical Integration. Vertical Integration is when one company expands its business into a variety of different areas; the company buys another similar organisation however it is on a different level of the chain. An example of vertical integration is Virgin Trains which is owned by Virgin Group and also in partnership with the stagecoach.
What Is a Vertical Integration in Travel and Tourism? By Michael Ferguson. In the world of travel and tourism, vertical integration is a term that is often used to describe the wa
Horizontal plus vertical integration: Built easy. 11th February, 2023. Horizontal and vertical integration are key concepts in all businesses, including those operating in the promotion industry. Certain important administrator strategy, horizontal and vertical integration allows our to be more competitive in aforementioned marketplace.
The strategies considered are the vertical integration of tour operators with travel retailers and airlines, pricing and contracting systems in the resort, and developments in market segmentation.
Essays on vertical integration in travel and tourism. Free essay topics and examples about vertical integration in travel and tourism. It to provide a tourism and their Forward, or downstream, vertical integration occurs when the company joins with or creates businesses whose role in the production of its goods occurs after its own; the products move forward after the company has finished its ...
An example of this would be a tour operator buying a chain of travel agents. Backward Integration Is moving up the chain. An example of backward Integration would be a tour operator buying a principal, such as an airline. It Is understood that as you go up he chain each level costs more to buy. This is why forward vertical integration is more ...
Vertical Integration Travel And Tourism Example. Landside Integrates is whereas two industries merge together; it is where one business which offers a product holds over another enterprise who offers similar commodity. An show of horizontal integrat
Which is an example of horizontal integration in tourism? Horizontal integration in tourism examples Travelopia is a great example of a tourism organisation with lots of horizontal integration. Travelopia is the world's largest collection of specialist travel brands.