
Travel Vaccines and Advice for East and Southeast Asia

Seoul’s urban amenities, Japan’s countryside and China’s Great Wall are just a few of the reasons that millions of people visit East and Southeast Asia every year. With a wide variety of cultures, cuisines and historical sites, it is one of the most popular regions to visit.
Passport Health offers medications, immunizations and personalized consultations for your trip to East and Southeast Asia. See our What Vaccines… section to learn more.
Countries in this region include:
What Vaccines Do I Need for East and Southeast Asia?
The CDC and WHO recommend the following vaccinations for travelers to East and Southeast Asia: hepatitis A , hepatitis B , typhoid , cholera , yellow fever , Japanese encephalitis , rabies and polio .
Some routine vaccinations are also recommended, this includes: measles, mumps and rubella (MMR) , tetanus, diphtheria and pertussis (Tdap) , influenza , chickenpox , shingles , pneumonia , meningitis .
While rare, polio cases have been sporadicly reported in some parts of the region. While generally a routine vaccination, it may be recommended for your trip.
COVID-19 vaccination is recommended for travel to all regions, both foreign and domestic. Check with your local Passport Health clinic if immunization is offered in your area.
Proof of yellow fever vaccination may be required for some travelers, based on their specific itinerary.
See the table below for more vaccination information:
Customer Reviews
Passport health – travel vaccines for east and southeast asia, are there other health concerns in east and southeast asia.
There are a few additional health concerns for East and Southeast Asia that are not vaccine preventable.
Malaria is present in East and Southeast Asia. Antimalarial medication may be recommended based on your specific itinerary. Antimalarial resistance is also found in some areas, this may limit your medication options. Speak with a travel health specialist to learn more.
Dengue , chikungunya and Zika are found as well. Mosquito netting, repellents and protective clothing may be recommended. Avoid outdoor activities during high times for mosquito activity, especially at dusk and dawn.
Tuberculosis is common in some parts of the region. If you feel you may be exposed during your trip, or have returned and believe you were exposed, TB testing is available. Testing should be done upon return and within eight to ten weeks of the first test for long-term travelers.
Travelers’ diarrhea another common risk for travelers. While new cuisine is always fun to try, it may lead to some unpleasant side effects if not prepared safely. Bring a travelers’ diarrhea kit to help prevent illness and stop symptoms if they start.
What Are the Entry Requirements in East and Southeast Asia?
A visa may be required for some popular destinations like China and Cambodia. But, many others have minimal requirements. Check the table below for more information on your destination.
China’s visa rules for Hong Kong and Macao are very different from many other countries. Be sure to check the visa page if you are traveling to any of these regions.
Embassy information for each country is available on its own destination advice page.
Traveling to Another Destination?
Traveling outside of East and Southeast Asia? Learn more about your destination with our full compliment of destination advice pages!
- Afghanistan
- American Samoa
- Antigua and Barbuda
- British Virgin Islands
- Burkina Faso
- Canary Islands
- Cayman Islands
- Central African Republic
- Christmas Island
- Cocos (Keeling) Islands
- Cook Islands
- Cote d’Ivoire
- Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Dominican Republic
- Easter Island
- El Salvador
- Equatorial Guinea
- Falkland Islands
- Faroe Islands
- French Guiana
- French Polynesia
- Guinea-Bissau
- Liechtenstein
- Madeira Islands
- Marshall Islands
- Netherlands
- New Caledonia
- New Zealand
- Norfolk Island
- North Korea
- North Macedonia
- Northern Marianas
- Palestinian Territories
- Papua New Guinea
- Philippines
- Pitcairn Islands
- Puerto Rico
- Republic of the Congo
- Saint Barthelemy
- Saint Helena
- Saint Kitts and Nevis
- Saint Lucia
- Saint Martin
- Saint Pierre-et-Miquelon
- Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
- Sao Tome and Principe
- Saudi Arabia
- Sierra Leone
- Sint Eustatius
- Solomon Islands
- South Africa
- South Georgia & South Sandwich Islands
- South Korea
- South Sudan
- Switzerland
- Trinidad and Tobago
- Turkmenistan
- Turks and Caicos Islands
- U.S. Virgin Islands
- United Arab Emirates
- United Kingdom
- United States
- Wake Island
- Western Sahara
On This Page: What Vaccines Do I Need for East and Southeast Asia? Are There Other Health Concerns in East and Southeast Asia? What Are the Entry Requirements in East and Southeast Asia? Traveling to Another Destination?

- Records Requests
- Passport Health App
- Privacy Center
- Online Store
Vaccines for Traveling to Asia: The Complete Guide

This article gives an informative list of the vaccines necessary for traveling to China, East Asia and Southeast Asia.
Vaccines for Asia – Table of Contents
General situation of vaccines.
- Most common vaccines for traveling to Asia
Other diseases to consider
Coronavirus covid-19, precautions after your trip.
Before anything else, it is essential that you book an appointment with a specialist doctor at an approved international vaccination center or at a travel clinic (many public and private hospitals have one), preferably two months in advance of your departure date.
These are the only types of centers where you will receive up-to-date and detailed advice on all of the vaccines recommended for your trip.
I’m sure you can remember some of the controversies around vaccination that have arisen over the past decades. In the mid-1990s, a renowned British scientist concluded that the measles vaccine could trigger diseases such as autism or colitis.
Despite the fact that he was accused of data falsification and fraud in 2010, he currently has thousands of followers who support him across the globe, through the ever-expanding anti-vaccine movement.
However, official bodies such as the WHO, the pharmaceutical industry, the scientific community, and governments actively support and promote vaccination, in line with the conclusions of the latest science on the subject.
If we cast aside the political and economic interests that can be hidden behind these types of scandals, on the individual level, it is important to consider the risks of not getting vaccinated for potentially lethal diseases before making any decision. You also have to keep in mind that some vaccinations are subject to international regulations , such as the yellow fever vaccine. This means that countries have the power to require visitors to demonstrate that they have been vaccinated in accordance with national regulations if they want to enter the country.
This vaccine is only given at authorized international vaccination centers ( check here for the list of centers in US ), which provide you with an international vaccination certificate (also called a “yellow card”) recognized across the globe.
In any event, you will have to set aside a portion of your budget for vaccines , but keep in mind that the majority of these are for life, and in the worst case, you will have to remember to get a booster shot after a few years.
On the other hand, a distinction must be made between ordinary vaccination (the vaccination normally provided by governments following a specific schedule) and international vaccination (which is done when people go to another country).
Although there are slight variations, the vaccines normally given to the population in the majority of countries are the following: hepatitis B, diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough, polio, measles, rubella, and chickenpox.
It is very important to possess and periodically go over both vaccination histories (ordinary and international). Keep in mind that a large quantity of money and effort continues to be invested in improving existing vaccines and creating new ones.
Sometimes new evidence is published recommending changes in the period of effectiveness of a vaccine or in the frequency at which booster shots should be given, for example. Because of this, before any international trip, you should consider booking an appointment with a specialist to check that you are up-to-date with all of your vaccines.
Most common international vaccines for traveling to East Asia and Southeast Asia
This table shows the vaccines recommended for traveling to Asia by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the leading institution in the world in terms of international vaccination.
To summarize, the most commonly recommended vaccines are typhoid fever, tetanus, and hepatitis A and B . The latter is routinely given in many countries, but in any case, carefully go over your medical records and vaccination cards.
If you are not up to date, the best thing to do is to check with your family doctor. It’s possible to find out which vaccines you have through a blood test (which looks for the presence of antibodies).
Returning to the table, whether or not to get optional vaccines will depend on your itinerary, the duration of your trip, the sanitary conditions of your destination country, your age and your state of health , as well as the type of trip you are planning (adventure, business, volunteer work, family, etc.).
Because of this, it’s important to manage your vaccines long enough in advance, because in addition to potential waiting lists at authorized centers, some vaccines take up to three weeks to become effective .
Because of this, as suggested at the beginning of this article, the best thing is to start the procedure two months before your trip .
Yellow fever
This is a notifiable disease according to international regulations and is transmitted via the bite of an infected mosquito. “Notifiable” means that it is necessary to demonstrate that you are vaccinated to enter certain countries.
China and countries in Southeast Asia require travelers coming from countries endemic with yellow fever to present their international vaccination card containing the vaccination against this tropical illness at customs.
Because the vaccine takes ten days to become effective, vaccination is only considered legal once this time period has elapsed. Currently, a single injectable dose gives immunity for your entire life.
This is a disease that affects almost all tropical countries, including those of Southeast Asia and some of the southern provinces of China (but not Hong Kong and Macau). Just like yellow fever, it is transmitted through mosquito bites, but as opposed to yellow fever, there is currently no effective vaccine available for it.
What does exist is a preventive medication that can help mitigate the symptoms of malaria (in the event of infection). However, you should be aware that even by taking this medication, the possibility of developing malaria is not eliminated completely.
Another thing to keep in mind is that the strains of the parasite that cause illness vary from one region to another. Therefore, your route should be as clearly defined as possible in order for you to inform the international vaccination center of it.
This center is the only place where you will get precise recommendations on the prophylactic treatment of choice for the strain that you may encounter along your itinerary.
On the other hand, the majority of urban areas in the region are malaria-free. Therefore, if there isn’t a tangible risk, it’s most likely that your doctor won’t prescribe this treatment for you. The dosage schedule is strict and is followed before, during and after the trip, and the treatment is known for its side effects.
This is a viral infection once again transmitted by mosquito bites. It is also present in the majority of countries in Southeast Asia. It does not have a vaccine, and prevention is exclusively based on protection against mosquito bites .
This virus is fairly similar to the dengue virus. Zika also carries the recommendation that pregnant women abstain from traveling to countries where cases of Zika have been recorded. The transmission of the virus to fetal blood can cause irreversible damage.
Currently, there is no vaccine for the new coronavirus (COVID-19). However, and due to the global impact that this epidemic is having, the epicenter of which is in Wuhan (China), the scientific community is currently searching for an effective vaccine.
In any event, it is not expected to see the light of day for at least a year. Up until then, people are recommended to take extreme measures to avoid contagion , which takes place via inhalation. These measures include avoiding traveling to areas that are active hotbeds of disease transmission.
Currently, countries in Southeast Asia do not have restrictions on travelers related to the coronavirus. In any event, and considering the speed at which the virus is propagating, it is a good idea to confirm the current number of cases in the country that you plan to visit.
Last of all, you should keep in mind that some countries are applying restrictions to travelers coming from China. Therefore, check the order of your itinerary to avoid problems at customs.
Some infectious diseases do not present immediately, and can even show up a long time after you go back home. For any symptoms, it’s best to go to your family doctor and inform them of your itinerary and the dates of all of your trips over the past 12 months.
Photo Credits: Photo by fotoblend on Pixabay
About The Author
Andrea Lasheras
Related posts.

The Stone Forest and the legend of Ashima

From Lijiang to Lugu Lake: Chronicle of a Hectic Trip

Gubeikou: Hiking on the Wild Great Wall
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Privacy Overview
Get 3 Months FREE with EXPRESS VPN
+ Best VPN For China + 30-Day Money-Back Guarantee + 24/7 Live China Customer Support + 3 Months Free on 12 Months Package
- Vaccinations for Southeast Asia
- What Travel Vaccines Do I Need?
- Vaccinations for Asia
Information on this page is only intended as a guide to the travel vaccinations recommended for this country
Southeast Asia is a region of countries including Thailand , Vietnam , Cambodia , Laos , Indonesia and Philippines . The region is very popular with backpackers and tourists due to the abundance of different cultures, the wealth of exciting activities and the amazing natural beauty to be found in this part of the world.
Recommended Travel Vaccines for South-East Asia
*Vaccination schedules are approximate and are calculated based on the first dose. Schedules are subject to change depending on your individual needs and will be discussed in your appointment. These are the minimum times required to complete courses or for vaccines to become fully effective. You can always start your course of vaccinations earlier than stated, as vaccines work best when your body has time to process them. Your Travel Nurse will discuss any health implications in your appointment
Yellow Fever in Southeast Asia
There is a risk of Yellow Fever in Southeast Asia.
Some countries require arriving travellers to have certification of immunisation for Yellow Fever.
For country specific information on Yellow Fever choose from the list below
Malaria Risk in Southeast Asia
Malaria is present in some countries in Southeast Asia.
There is no vaccination for Malaria, we recommend you have a consultation with our expert Travel Nurses to talk through your Antimalarial medication options for specific countries.
For country specific information on Malaria choose from the list below
Other Health Risks
Chikungunya in southeast asia.
There is a risk of Chikungunya virus in this country. Spread by mosquitos, Chikungunya virus is widespread across Africa, South-East Asia, the Indian sub-continent and the Philippines. Occasionally, the virus can be found in other countries where the mosquito that spreads Chikungunya can also be found. There is no vaccination against Chikungunya, it is important to protect yourself with bite avoidance products like DEET. For more information – click here .
High Altitude in Southeast Asia
There are some high altitude areas. Travellers should take care to avoid Acute Mountain Sickness (AMS) by taking time to acclimatise properly. AMS can affect anyone, regardless of age, gender, level of fitness or training. At high altitude, extra precautions should be taken against the harsh conditions, which can cause damaging ultraviolet and cold exposure. All Nomad Travel Health Nurses are trained to advise on AMS, and it may be appropriate for you to take certain medications that may help with acclimatisation. Book an appointment to discuss health issues related to altitude, based on your specific itinerary. For more information – click here .
Leptospirosis in Southeast Asia
There is a risk of Leptospirosis. Leptospirosis infection is widespread throughout the world, but cases are most common in tropical climates, areas where the standard of hygiene is poor and in areas subject to flooding. The infection occurs when cuts or abrasions of the skin and mucous membrane (eyes, mouth) come into contact with flood water, moist soil, vegetation (particularly bamboo) and fresh water infected by animal urine and other secretions. Prevention is dependent on covering cuts, scratches and open skin lesions with waterproof plasters, avoiding swallowing or drinking potentially infected water and, where risk is high, protective clothing should be worn.
Dengue Fever in Southeast Asia
There is a risk of Dengue Fever. It is spread by a species of mosquito called Aedes aegypti, otherwise known as the ‘tiger mosquito’ which mainly bites during the day. The illness is widespread throughout the tropics and subtropics, affecting over 100 countries with approximately 50 million cases globally a year. Currently most infections occur in SE Asia, South and Central America, Mexico, Africa, Indian sub-continent, Hawaii and the Pacific. There is currently no vaccination against Dengue Fever, it is therefore important to protect yourself during the day with bite avoidance products like DEET. For more information – click here .
Schistosomiasis in Southeast Asia
There is a risk of Schistosomiasis in this country. A parasitic infection (also known as bilharzia), Schistosomiasis is transmitted to humans through contact with fresh water, when the parasitic worm enters through the skin. Usually, no symptoms are felt until 2-4 weeks after exposure, when fever, diarrhoea, cough or a rash can occur as the parasites move around the body. Long term disease can lead to damage of the bladder, kidneys, bowel, liver and genital tract. Prevention is dependent on avoidance of swimming, bathing or paddling in fresh water lakes and streams. For more information – click here .
We recommend you book a consultation with one of our specialist Travel Health Nurses to determine the exact vaccinations recommended for you based on a bespoke risk assessment that will take into account your itinerary, medical history, activities and length of travel, which are all risk factors affecting your immunisation recommendations. If you would like to book with us please call 01341 555 061 or click here . For the most up to date information, visit Fit For Travel and search for the countries you are travelling to.
- Burkina Faso
- Central African Republic
- Congo Brazzaville
- Cote d’Ivoire
- Sierra Leone
- South Africa
- South Sudan
BECOME A NOMAD - SUBSCRIBE TODAY
Join the Nomad community for updates and expert insight
Search for...
- Book Appointment
- Find a Travel Clinic
- Find a Travel Store

- Travel planning
Vaccinations and a medical kit
With a small dose of preparedness and planning you’ll be well positioned to handle any minor ailments you pick up in Southeast Asia—don’t forget to use your common sense!
Planning categories
Get an idea, get some money, get insurance, get your documents, get your gear, get packing, get the most out of your trip, get talking, get booking, get out alive, get working.
For travel in Southeast Asia, most medical experts recommend at least vaccinations for measles, mumps and rubella (MMR), typhoid, hepatitis A, chicken pox, diphtheria, tetanus and polio. Some of these you may have had when you were a child, but in some cases you will need a booster to get you back up to scratch. A doctor in your home country can offer advice on your personal situation.
You may also wish to consider shots for Japanese encephalitis, hepatitis B and rabies. Each has its own risk profile and will be dependent to an extent on what you’re doing during your travels. For instance, if you are spending a lot of time around animals then a rabies shot would be a good idea. Be sure to consult with a travel doctor or travel clinic (as well as your own doctor for whatever specific needs you may have) to decide which vaccinations are the right fit for you and your itinerary.
You’ll find useful information about vaccinations on the Travel Doctor website , the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the World Health Organisation (WHO) .
Travel medical kit
Generally you will be able to get medical attention and general medicines throughout Southeast Asia for most minor ailments, at local hospitals, medical clinics or pharmacies.
Treatment costs are reasonable by Western standards. If you are looking at major surgery or get seriously ill, get yourself to Bangkok, Singapore or home for treatment. You do have travel insurance, right?
Nevertheless, it's a good idea to take a small medical kit . There is not a region-wide prescription system, and much general purpose medication can be bought over the counter, though if you require specialist medication, bring your scripts as a local pharmacy may refer you to the hospital if they don’t have what you are after. Local chemists can be inconsistent, sometimes asking for a script or doctor’s letter, other times just handing the goods over.
While many of these are easily purchased in Southeast Asia, if you prefer to be prepared, in a general traveller medical kit we would recommend:
* Band aids, elastoplast dressing strip, steristrips, sterile gauze, cotton wool, thermometer, safety pins, safety scissors and tweezers * A wide spectrum antibiotic, antacids, Flagyl (for giardia), Imodium or Lomotil (for the runs), paracetamol, rehydration mixture and cough lozenges. * Antifungal cream, cetrimide antiseptic (Savlon), mosquito net, insect repellent (Muskol, Repellem, RID) and sunscreen.
Other items may include a torch/flashlight, a small bottle of hand sanitiser, and, if you think you might need them, condoms. Of course you'd pack sunscreen. While you can buy any of these items locally at the many chemist shops, quality sometimes varies. While the variety and quality of available tampons and pads are improving, they remain pricey so you may wish to bring a supply of your preferred brand in case a suitable substitute isn’t readily available.
Further reading
Planning well is an integral part of getting the most out of your trip. Be it picking the right backpack, the right vaccinations or the right country, the simple decisions are often the most important.
7 popular Southeast Asia tourist spots you can travel to in 2022

Mar 3, 2022 • 9 min read

Some Southeast Asian countries are preparing to loosen travel restrictions in 2022 © Getty Images
Many countries in Southeast Asia have been shut off from the world during the pandemic, either due to closed borders or strict entry rules. But that's starting to change in 2022 as many nations phase out restrictions and welcome travelers once again.
Vietnam is the latest country to announce a reopening date as it prepares to welcome tourists on March 15. There are positive movements toward reopening elsewhere as cases decline — or at least stabilize — across Southeast Asia. Tourists can apply to travel to Thailand without a seven-day quarantine as the country revives its Test-and-Go tourism plan. Bali lifted its travel ban in February, welcoming tourists from Australia, the UK, and the US once again. Furthermore, the Philippines ended its almost three-year leisure travel ban on February 10.
Though, not every country is throwing its doors open. Malaysia , for example, set out March 1 as a tentative reopening date but that day has come and gone and its border measures, some of the strictest in the world, remain in place. Currently, the island of Langkawi is the only place open to most foreign tourists under Malaysia's International Tourism Pilot Project .

Still, there are signs that travel in Southeast Asia is on the verge of a booming comeback, particularly in the destinations that have simplified entry protocols. Zina Bencheikh, managing director of Intrepid Travel , tells Lonely Planet that demand in the region is bouncing back with the tour company recording January 2022 as its busiest month since the start of the pandemic.
"Before the pandemic, Thailand, Cambodia and Vietnam were consistently among our top selling destinations at Intrepid. The region offers so much of what post-pandemic travelers are looking for; beautiful natural scenery, great local food and lots of opportunities to get active. Traffic to our website suggests there is huge pent-up demand for travel there [again]."
Similarly, Hostelworld is seeing a growth in Southeast Asia bookings in the past two months. The region overall recorded an average growth of 85% since October for the accommodation booking website, with the biggest increase (200%) being recorded in the months of December and January versus October and November.
"With more backpackers heading to Thailand and Cambodia to commence their epic adventures, we predict that Vietnam will also see a steady growth in bookings driven by its planned reopening," a spokesperson for Hostelworld says.

If you are thinking of a trip to Southeast Asia, book well in advance to secure the right trip for you. A last-minute getaway isn't feasible in many destinations, particularly with lengthy visa processing times and limited entry options. Whether you're booking directly with an airline, hotel or tour company, be sure to choose one that allows you to change your dates or destination without incurring a fee as entry protocols continue to evolve.
In the meantime, here's what you need to know about traveling to some popular tourist spots in Southeast Asia that are open right now.
1. Bali, Indonesia
Entry rules: Indonesian officials opened Bali to tourists from all countries in February. Vaccinated arrivals have to quarantine for five days in a government-approved hotel at their own expense, though this could be reduced to three in the coming weeks before being scrapped entirely in April. They must also show proof of vaccination and a negative COVID-19 test result before arrival. A second test is administered upon landing at the airport. Unvaccinated arrivals have to quarantine for seven days. All arrivals must provide proof of health insurance with COVID coverage.
How to get there: Borders are opening but getting there is another thing as there are limited international direct flights scheduled. Singapore Airlines—the first to return to Bali—resumed flights on February 16 and will operate daily flights to Bali from Singapore to "meet good demand". It's not clear whether foreign travelers can transit through another airport in Indonesia because the country is still largely closed off to non-residents and citizens . Travelers could fly into Jakarta but would have to undergo quarantine there before moving on to Bali.
What to see: For the first five days, travelers are restricted to quarantining in government-approved accommodation, which is typically a five-star resort or hotel in either tourist-friendly Nusa Dua , Jimbaran , Sanur or Ubud . Outside of that, most places are open, particularly in green (low COVID-19 risk) zones but expect shorter operational hours for restaurants and enhanced health and safety measures for attractions like Pura Tanah Lot and Uluwatu Temple . Masks are required and travelers have to download the PeduliLindungi contract tracing app to check into restaurants, bars and even beaches.

Entry rules: Traditionally one of the most isolated parts of Southeast Asia, Laos is open to tourists from select countries including the US, UK, Australia, Ireland, Israel, Denmark and Indonesia, among others, under the special Travel Green Zones and Trails programs. Other entry conditions include a health insurance policy with coverage no less than US$50,000 and a pre-departure COVID-19 test. A second test will be administered upon arrival.
How to get there: Laos is open to almost every country in Southeast Asia so if you want to include Laos in a multi-trip Southeast Asian vacation, it should be easy enough. However, the only way to enter Laos, regardless of where you're coming from, is through pre-arranged group tours with authorized agents under the Green Zone travel plans .
What to see: The designated Green Zones include the capital city of Vientiane ; Luang Prabang province; and the adventure destination of Vang Vieng in the north of the country. Tourists are restricted to these zones for now but more destinations will be added to the programs on April 1 before, it's hoped, the entire country will open up in July.
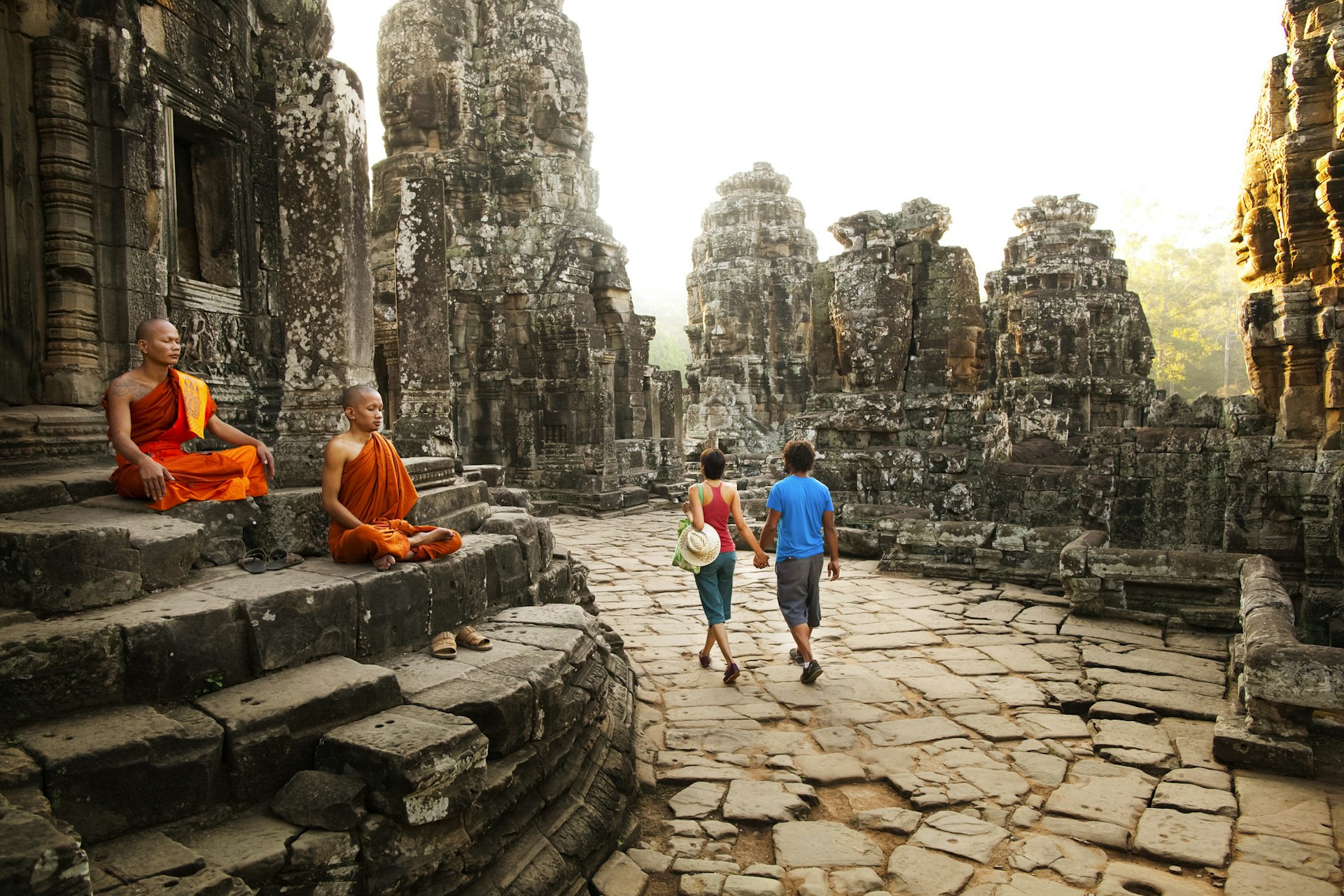

3. Cambodia
Entry rules: Cambodia reopened to vaccinated international tourists without quarantine back in November , though any traveler crossing the border must present proof of vaccination, a negative COVID-19 test result, then take a rapid antigen test upon arrival and await results at the airport.
How to get there: There are no direct flights from the US, UK or Australia to Cambodia but there are options with connections. However, according to the US Embassy in Cambodia , since it reopened, many travelers have reported unexpected flight cancellations and limited flight availability to Cambodia. The Embassy recommends US travelers book flights through a travel agency or direct with Korean Airlines or Asiana Airlines. UK travelers have additional options such as Swiss Airlines or Bangkok Airlines with stopovers.
It's not possible to enter Cambodia through land borders as the Cambodia-Laos, Cambodia-Thailand and Cambodia-Vietnam land borders are closed.
What to see: In tourist cities like Siam Reap , most places are open including the Unesco World Heritage site Angkor Wat . Hostels, hotels, restaurants and museums are open but masks are required in most places and some businesses may be operating at reduced hours so check ahead.
Angkor Wat: get to know Cambodia's most iconic temple

Entry rules: Tourists from approved countries are permitted to travel to Vietnam but are restricted to certain destinations under a pilot travel scheme potentially until March 15, 2022 . In the meantime, travelers who visit must present proof of vaccination, a negative COVID-19 test result and take out health insurance that covers COVID with a minimum of US$50,000 coverage.
How to get there: On February 15, Vietnam COVID-19 restrictions on international passenger flights and flights have resumed from San Francisco and Los Angeles in the US, as well as from Singapore, Thailand, Cambodia and more. When visiting Vietnam, tourists are required to book a tour package (package details are available on the tourism board's website ) and stay within their chosen destination for at least seven days. Once the seven days is complete, travelers can move to another approved destination, provided they test negative before traveling.
What to see: Tourists can choose from five beach destinations including Phu Quoc , Danang , Quang Nam, Khanh Hoa, and Quang Ninh, though starting March 15, it's expected the entire country will open to tourism with some restrictions in place.

5. Singapore
Entry rules: After putting the brakes on its Vaccinated Travel Lane (VTL) program in December, Singapore is open again to vaccinated travelers from select countries including the US, UK, Indonesia, Thailand, Australia and France. As of February 22, passengers no longer have to take a pre-departure COVID-19 test or isolate on arrival. Instead, they'll take a supervised test within 24 hours of arrival.
How to get there: Foreign visitors can bypass quarantine when arriving on a designated VTL flight , mainly through Singapore Airlines, KLM and Air France. However, the government notes that since these flights resumed on January 20 there has been reduced availability.
What to see: Most places are open but travelers will find museums and attractions operating at half-capacity and restaurants, coffee shops and hawker centers limiting dining to two people per group.

6. Thailand
Entry rules: Vaccinated visitors have two pathways into Thailand: the Test-and-Go and the Sandbox programs with some testing and quasi-quarantine requirements in place. Unvaccinated visitors have to quarantine for between seven to 10 days. You'll need to pre-book some accommodation and tests before traveling. Thailand also requires all visitors to apply for a Thailand Pass before visiting which can take about 60 days to process, so planning months ahead is essential.
How to get there: Commercial flights are operating to Thailand and the government has approved entry for travelers coming from most Southeast Asian countries, as well as the US, Australia, the UK, Canada, Ireland, France, Japan and more.
What to see: If you travel under the Sandbox program, you're restricted to destinations such as Phuket or Ko Samui . If you're eligible for the Test-and-Go scheme, you can travel all over Thailand. Most major destinations are classified as "blue zones" with relaxed restrictions. Museums, historical sites, and galleries are operating under some capacity limits. Restaurants are open but bars, karaoke venues and nightclubs remain closed.

7. Philippines
Entry rules: Borders reopened on February 10 . Fully vaccinated travelers from 157 visa-free countries are permitted to visit the Philippines without quarantine but they must test negative for COVID-19 prior to their trip.
How to get there: Flag carrier Philippine Airlines flies direct routes from Los Angeles, San Francisco, New York, London and nearby Asian countries but at reduced frequencies. According to Skift , flights from London's Heathrow only depart once a week now compared to four times before the pandemic. Australian airline Qantas will resume flights from Brisbane, Sydney and Melbourne to Manila later this month.
What to see: Tourists will be able to travel across the Philippines without being restricted to specific destinations. COVID-19 measures vary by region and some tourist spots such as Siargao are still in recovery mode following December's Super-typhoon Rai . After closing to visitors due to overtourism issues , the island of Boracay is back open.
You might also like: How to save money for your next big trip How to plan a big trip whether you have 2 months or 2 years How to pack like a pro for a backpacking trip
Safety recommendations and restrictions during a pandemic can change rapidly. Lonely Planet recommends that travelers always check with local authorities for up-to-date guidance before traveling during Covid-19 .
This article was first published Feb 2, 2022 and updated Mar 3, 2022.
Explore related stories

May 12, 2022 • 2 min read
It's one of Southeast Asia's most isolated countries but after more than two years of border closures, Laos has opened up to all international tourists…

Mar 8, 2022 • 2 min read

Mar 4, 2022 • 3 min read

Feb 16, 2022 • 2 min read

Jan 28, 2022 • 3 min read

Jan 21, 2022 • 4 min read

Jan 20, 2022 • 4 min read

Nov 30, 2021 • 6 min read

Nov 15, 2021 • 2 min read

- Português Br
- Journalist Pass
9 common questions about vaccines and travel
Joel Streed
Share this:

Travel does more than just transport you to a different place. It can broaden your perspective, increase your happiness, give you a chance to try new things, boost your creativity and help you recharge. Even planning a trip can be an exciting task. The anticipation of mapping an itinerary and scheduling your must-see attractions can bring a lot of joy and happiness.
One of the most important tasks before taking a trip is to make an appointment with a travel medicine specialist. These health care professionals help keep travelers safe and happy before and after their journeys.
Here are answers to common questions about travel medicine:
1. who should make an appointment with a travel medicine specialist.
Anyone planning a trip overseas can benefit from seeing a travel medicine specialist. However, a travel clinic appointment is critical if you are traveling to underdeveloped or developing countries where there's a higher risk of contracting severe communicable illnesses while abroad. It is also important for patients with certain medical conditions that make their immune systems weaker and more vulnerable to infectious diseases.
2. What vaccinations do I need to travel overseas?
All travelers should be vaccinated against the flu and current with COVID-19 vaccines and boosters.
In addition, it's important to complete the adult vaccination schedule that includes vaccinations for:
- Chickenpox (varicella)
- Diphtheria, tetanus and pertussis (DTP)
- Pneumococcal
- Measles, mumps and rubella (MMR)
Additional vaccines may be recommended depending on your travel itinerary. For example, hepatitis A vaccination is recommended if you are traveling to Southeast Asia. During your appointment, we can discuss which vaccines are appropriate for your itinerary.
3. Are there travel destinations that have different vaccination recommendations?
Yes. Infectious diseases thrive in different climates. If you travel to a new climate, you may be exposed to diseases to which you don't have any immunity.
Some infections are more prevalent in tropical settings compared to temperate climates. For example, typhoid and hepatitis A are more common in Southeast Asia because these communicable diseases can be spread through contaminated water. Some areas of Africa and South America have a higher prevalence of yellow fever and malaria, which are mosquito-borne infections.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has good information online for travelers for each travel destination.
Recommended vaccines may include:
- Hepatitis A
- Hepatitis B
- Japanese encephalitis
- Yellow fever
4. Can my primary care provider give me travel vaccinations?
It depends on your travel destinations and vaccine recommendations. I recommend starting the conversation with your primary care provider and reviewing the CDC recommendations .
If you have a complex itinerary with multiple countries or are traveling to Southeast Asia or Africa, it's better to make an appointment at the travel clinic. I also would recommend patients with organ transplants and immunocompromising conditions seek travel medicine consultation to reduce the risk of illness during travel. During that appointment, we will review your itinerary, provide necessary vaccinations and discuss ways to prevent mosquito-borne or tick-borne diseases.
5. How long before my trip should I go to the travel clinic?
Plan to have an appointment at least four weeks before you travel. Some vaccines require several weeks for immunity to develop, while others require more than one dose of vaccine for full protection.
If your trip is to an underdeveloped or developing country, you may need to schedule an appointment up to two months in advance to receive a complete set of immunizations. This gives your body time to produce the protective antibodies, so you are well protected when you land at your destination.
6. Can I only go to the travel clinic before I travel?
No. The Travel and Tropical Medicine Clinic is available before or after travel. The team can provide consultative services and treatment if you get sick after you return home.
7. I'm going to an all-inclusive resort. Will I have a lower risk of getting sick?
Maybe, but no traveler should take safety for granted. Even in an all-inclusive resort, knowing how food is prepared or the water supply quality is not possible. Mosquitos and other insects could still be a concern. It's important to take all necessary precautions and follow vaccination recommendations when you travel, regardless of your accommodations.
8. How do I lower my risk of malaria when traveling?
Malaria is a disease caused by a parasite. It's spread to humans through the bites of infected mosquitoes. Prophylactic malaria medications are available and are started before the travel, continued during the stay and for a certain duration after returning home. A travel medicine specialist can review the risks and benefits of all prevention and treatment options.
9. How do I stay healthy while traveling?
Nothing can ruin a trip like illness. Make sure all your vaccinations and boosters are up to date, and get any new vaccinations recommended for your destinations.
Food and water safety is important while traveling. Only eat well-cooked food. Avoid eating from roadside stands and uncooked foods, like salad and raw vegetables. Drink bottled beverages only, including bottled water. This is especially important if you travel in resource-limited regions, such as Southeast Asia or Africa.
Hand hygiene is important at home and overseas. Wash your hands often using soap and hot water. Avoid crowded places, follow respiratory etiquette and consider optional masking. Mosquitos and bugs can transmit parasites and diseases, like yellow fever and malaria. Use mosquito repellents. Mosquito nets may be appropriate in some parts of the world, as well.
As you make travel plans, schedule an appointment with a travel medicine specialist to get the vaccinations and information you need to be healthy and safe on your journey.
Raj Palraj, M.D. , is a physician in Infectious Diseases and Travel and Tropical Medicine in La Crosse , Wisconsin.
- Mayo Clinic Q and A: Thyroid nodules, cancer and treatment Mayo Clinic Minute: Dangers of late cervical cancer diagnosis in women of color
Related Articles


- About the Handbook
Vaccination for international travellers
Ensure that travellers are up to date with routine vaccines. Also consider other vaccines based on travel itinerary, activities and risk of disease exposure.
Recently added
This page was added on 09 June 2018 .
Updates made
This page was updated on 23 October 2023 . View history of updates
Millions of Australians travel overseas every year. More than half of these trips are to destinations other than New Zealand, North America and Europe. 1
This page helps with making decisions about travel vaccines. Also check the disease-specific chapters in this Handbook for details about specific vaccines.
See also Infographic. Vaccination for international travellers .
Health risks of overseas travel
Health risks associated with international travel include exposure to:
- infective agents
- altitude and temperature extremes
- other physical, psychological and environmental hazards
- poor-quality or limited access to clean water, shelter, hygiene and sanitation facilities, and health and medical care
The level of health risks depends on factors such as:
- the traveller’s underlying physical and mental health and physiological state
- the itinerary and activities undertaken
- the duration of exposure to various hazards during travel
Travellers at increased risk of serious travel-associated infections include:
- young children and infants
- pregnant women
- people with underlying medical conditions, especially immunocompromising conditions due to disease or medical treatment
- people spending extended periods in multiple regions with poor resources or in remote areas
- people participating in events where large numbers of people will gather, such as major sporting, cultural, social or religious events
- migrant families travelling back to their region of origin to visit friends and relatives
Those travelling to visit friends and relatives are more likely to: 2
- have closer contact with local populations
- stay in remote or rural areas
- consume higher-risk food and beverages
Those travelling to visit friends and relatives are less likely to: 2,3
- recognise the health risks associated with travelling
- seek pre-travel health advice
- obtain the recommended vaccines or prophylaxis
Common infections acquired by travellers
Exposure to infectious diseases is one of the many health hazards of international travel. Some of these diseases are vaccine preventable. Although some of these diseases are present in Australia, the risk of acquiring them overseas may be higher because of:
- higher disease incidence in other countries
- increased risk of exposure from participating in certain activities while travelling
Foodborne and waterborne infections
It is common for travellers to ingest contaminated food or beverages, resulting in an illness. 4-6 Practicing safe eating and drinking habits is essential to minimise the risk of contracting food and waterborne diseases while travelling. These include treating water or only drinking bottled water, avoiding undercooked meat, and avoiding raw fruit and vegetables (unless they can be peeled or washed in safe water prior to eating). Most infections are diarrhoeal diseases due to enteric pathogens, but some are due to extra-intestinal microorganisms, such as hepatitis A virus and Salmonella enterica serotype Typhi (causing typhoid).
Vaccines are available against hepatitis A, typhoid and cholera.
Vector-borne infections
Insect-borne — especially mosquito-borne — infections, such as malaria and dengue, are important causes of fever in Australian travellers returning from endemic areas, particularly Southeast Asia and Oceania. 4,6
A dengue vaccine (Dengvaxia) is available for the prevention of secondary dengue infections (not primary prevention of initial dengue infection ) in select individuals. See Clinical advice: ATAGI statement on use of Dengvaxia® for Australians .
Japanese encephalitis occurs throughout much of Asia and the Western Pacific region, including eastern Indonesia and Papua New Guinea. 7 Yellow fever occurs only in parts of Africa and South America, 8 and tick-borne encephalitis occurs in parts of Europe and Asia. 9
Vaccines are available against Japanese encephalitis , yellow fever and tick-borne encephalitis .
Some other vector-borne diseases and parasitic (including protozoal and helminthic) diseases are also important for international travellers. Some are preventable through appropriate barrier precautions and chemoprophylaxis (for example, malaria). 9
Aerosol-borne infections
Vaccine-preventable infections transmitted by aerosols and/or droplets include: 9
- influenza (the most common vaccine-preventable infection among travellers) 10
- meningococcal disease
- varicella (chickenpox)
The incidence of measles and mumps is higher in many overseas countries, including some developed countries, than in Australia.
Tuberculosis is a rare infection in travellers. 11 Expatriates who live in endemic areas for a long time are more likely to acquire tuberculosis than short-term visitors. 12
Vaccines are available against all of these diseases.
Bloodborne and sexually transmitted infections
Some Australian travellers may be at risk from bloodborne and sexually transmissible infections, such as chlamydia, gonorrhoea, hepatitis B, hepatitis C and HIV. In some areas, healthcare workers using non-sterile medical equipment or other poor infection control practices may transmit these viruses and other bloodborne agents.
Vaccines are available against hepatitis B.
Exotic infectious agents
Travellers may be exposed to a variety of other exotic infections, such as:
- rabies from bites or scratches from rabid dogs, bats and other mammals in many countries
- schistosomiasis from exposure to water infested with the parasites, especially in Africa
- leptospirosis through activities such as rafting or wading in contaminated streams
Of these diseases, vaccines are available only against rabies.
Recommending travel vaccines
Although recommending appropriate vaccines is important, it is not the only part of a pre-travel medical consultation. Travel vaccines — those relevant for travelling — include all relevant vaccines, not just the ones that prevent diseases that most commonly occur overseas.
Do not recommend a vaccine based only on the destination country, because there is no single ‘correct’ list of vaccines for travel to any particular country.
There are 3 categories of travel vaccines:
- routinely recommended vaccines (not specific to travelling overseas)
- selected vaccines based on travel itinerary, activities and likely risk of disease exposure
- vaccines required by the International Health Regulations 2005 (IHR) or for entry into specific countries
Questions for a pre-travel medical consultation
During a pre-travel medical consultation, ask questions about the traveller’s:
- personal information, including age and whether they are pregnant or planning pregnancy
- underlying medical conditions, particularly immunocompromising conditions, and current medicines
- vaccination history (including adverse events following immunisation) and allergy history
- purpose of travel and intended activities, especially those associated with various environmental risks and hazards
- plans for travel insurance
Also ask about their itinerary in detail, including:
- date of departure and time available for vaccinations
- specific localities and routes
- rural versus urban stay
- duration of stay
- likely access to health care and other services
- likelihood of changing the planned itinerary
This information helps to tailor recommendations about preventive vaccination or chemoprophylaxis for exposure risks during the proposed trip. It also allows the clinician to advise about other appropriate preventive health measures (for example, food and water precautions, avoiding bites from mosquitoes or other arthropods) and about managing possible health conditions during travel.
Organisational requirements for vaccination
Some overseas organisations, such as schools, colleges and universities, require evidence of vaccination or immunity against some vaccine-preventable diseases, such as measles and meningococcal disease. Consider these requirements when planning and scheduling vaccines before departure.
Routinely recommended vaccines (not specific to travelling overseas)
Vaccinate all prospective travellers according to the recommended vaccination schedule appropriate for their age, underlying health conditions, occupation and lifestyle. Vaccines might include, for example, pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine for an older person, or hepatitis B vaccine for a first aid officer.
Also ensure that all children are vaccinated according to the National Immunisation Program schedule. In exceptional circumstances, give the National Immunisation Program vaccines at the minimum age rather than the recommended age (see Table. Minimum acceptable age for the 1st dose of scheduled vaccines in infants in special circumstances ). Children vaccinated using the minimum age rather than the recommended age may need extra vaccine doses to ensure adequate protection. Observe the minimum interval requirements between doses (see Table. Minimum acceptable dose intervals for children <10 years of age ). The chances of being exposed to some diseases, such as measles and mumps, may be greater during overseas travel, even to other developed countries.
For some itineraries, it may be appropriate for the traveller to receive some booster doses earlier than the routine recommended time. An example may be diphtheria-tetanus booster.
Diphtheria, tetanus and pertussis
Vaccinate adult travellers against tetanus before departure, particularly if:
- their risk of sustaining a tetanus-prone wound is high
- there could be delays in accessing health services where they can receive tetanus toxoid boosters safely, if required
Offer dTpa vaccine during a pre-travel consultation if the traveller has never received a dose of dTpa . This provides protection against pertussis (see Pertussis ).
For high-risk travel, consider giving a booster dose of either dTpa or dT vaccine if more than 5 years have passed (see Tetanus ).

Hepatitis B
Most Australian children born since 2000 have been vaccinated against hepatitis B under the National Immunisation Program or state and territory school-based vaccination programs.
Hepatitis B vaccine is recommended for long-term or frequent travellers to regions of intermediate or high endemicity of hepatitis B, including:
- Central and South America
This is because travellers may be exposed to hepatitis B virus through bloodborne routes (including during emergency medical or dental procedures) or sexual routes. According to 1 survey, about half of Australian travellers who spent at least 3 nights in Southeast or East Asia participated in at least 1 activity that had a risk of hepatitis B transmission. 13
See also Hepatitis B .
Influenza and pneumococcal disease
Older travellers and those with any relevant underlying medical or behavioural risk factors should receive pneumococcal vaccine. See Pneumococcal disease for more details.
Consider influenza vaccine for all travellers, especially if they are travelling to a region during its influenza season. Influenza vaccine is particularly relevant if:
- there is an influenza epidemic at the traveller’s destination
- the person is travelling in a large tourist group, especially one that includes older people
- the person is travelling on cruises, where people are relatively confined for days to weeks
See also Influenza.
Measles, mumps and rubella
Inadequately vaccinated young adult travellers are responsible for most current measles outbreaks in Australia. This occurs when they acquire the infection overseas and bring it back to Australia. Some countries, regions or communities — including developed countries — have a higher incidence of measles and mumps than Australia. 9
Australians born during or since 1966 who have not received the recommended 2 doses of MMR (measles-mumps-rubella)–containing vaccines are recommended to receive MMR vaccine before travelling. This also applies to infants 6–12 months old travelling to areas with measles outbreaks or where measles is endemic . The exception is for pregnant women, because MMR is a live vaccine and is contraindicated in pregnancy.
People born before 1966 do not need to receive measles-containing vaccine (unless serological evidence indicates that they are not immune). This is because circulating measles virus and disease were prevalent before 1966, so most people would have acquired immunity from natural infection .
However, confirmed cases of measles have occurred in people born before 1966. 14 If in doubt about a person’s immunity, it may be faster and easier to vaccinate the person than conduct serological testing . See Serological testing for immunity to measles .
See also Measles .
Unvaccinated travellers are recommended to receive varicella vaccine if they either:
- have not had clinical disease, or
- have an uncertain history of clinical disease and serology shows a lack of immunity
The exception is for pregnant women, because varicella vaccine is a live vaccine and is contraindicated in pregnancy.
See also Varicella .
Meningococcal disease
Vaccination against meningococcal serogroups A, C, W-135, Y and B is recommended for certain age and population groups who are at increased risk of meningococcal disease.
In addition, MenACWY (quadrivalent meningococcal) vaccine is recommended for people who are:
- planning travel to, or living in, parts of the world where epidemics of serogroup A, C, W-135 or Y meningococcal disease occur, particularly the ‘meningitis belt’ of sub-Saharan Africa 15
- planning travel to mass gatherings, such as pilgrims travelling to the Hajj in Saudi Arabia
Seek up-to-date epidemiological information to determine whether a traveller needs meningococcal vaccination. See Accessing up-to-date travel information.
The Saudi Arabian authorities require that all pilgrims travelling to Mecca (for the Hajj or Umra) have evidence of recent vaccination with the quadrivalent meningococcal vaccine. 16 See Requirements for travellers to Mecca and Accessing up-to-date travel information .
See also Meningococcal disease .
Poliomyelitis
Ensure that all travellers are age-appropriately vaccinated against polio (see Poliomyelitis ).
If the person is travelling to a country where wild poliovirus is still circulating, they should receive inactivated poliovirus ( IPV ) vaccine if they have not completed a 3-dose primary course of any polio vaccine. Travellers who have completed the primary course should receive a single booster dose.
The World Health Organization (WHO) Global Polio Eradication Initiative website website has an up-to-date list of polio-affected countries.
Documented evidence of polio vaccination is not routinely required for travellers under the International Health Regulations. However, documented evidence of vaccination may be temporarily required according to WHO recommendations in response to new evidence of the spread of wild poliovirus (see Vaccines required by the International Health Regulations or for entry into specific countries and Documentation and certificates ).
International polio epidemiology and associated travel requirements can change. Check the Australian Government Department of Health website for current recommendations for Australian travellers .
Ensure that all travellers are age-appropriately vaccinated against COVID-19. Foreign governments may require evidence of COVID-19 vaccination before a traveller is allowed to enter. The Australian-issued International COVID-19 Vaccination Certificate is a secure way to prove COVID-19 vaccination history that has been developed to meet agreed international travel standards. Parents and carers of children <14 years of age, adolescents ≥14 years of age and adults can get a copy of their COVID-19 vaccination certificate at any time:
- using their Medicare online account through myGov
- through the Medicare Express Plus mobile app
- by calling 1800 653 809 (free call)
See also COVID-19 .
Vaccines based on travel itinerary, activities and likely risk of disease exposure
Use a risk assessment approach when recommending travel vaccines. Weigh the potential risks of disease exposure and protective benefits from vaccination against potential adverse effects, and the non-financial and financial costs of vaccination.
Prioritise vaccines for diseases that are:
- common and of significant impact, such as influenza and hepatitis A
- less common, but have severe potential adverse outcomes, such as Japanese encephalitis and rabies
Consider booster doses, where appropriate (see disease-specific chapters in this Handbook for recommendations). If the person is departing for travel soon, consider an accelerated schedule, if appropriate, such as for hepatitis B vaccine or the combination hepatitis A-hepatitis B vaccine (see Hepatitis A and Hepatitis B ). Although immunity may be established sooner with the accelerated schedule, people who receive an accelerated schedule need another dose about a year later to complete the course and ensure long-term protection.
Most travellers do not need cholera vaccine. 16,17 The risk of a traveller acquiring cholera is very low if they avoid contaminated food and water.
No country requires travellers to have certification of cholera vaccination. No country has official entry requirements for cholera vaccination
See also Cholera .
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A vaccine is recommended for all travellers ≥1 year of age travelling to moderately or highly endemic countries (including all developing countries). The exceptions are people who have evidence of natural immunity after previous infection .
Normal human immunoglobulin is no longer used to protect travellers against hepatitis A.
See also Hepatitis A .
Japanese encephalitis
While now considered an emerging disease in Australia, Japanese Encephalitis is more likely in travellers to endemic regions overseas. 18 Japanese encephalitis ( JE ) vaccine is recommended for travellers spending a month or more in endemic areas in Asia, Papua New Guinea or the outer islands of Torres Strait during the JE virus transmission season.
Consider JE vaccination for shorter-term travellers, particularly if:
- travel is during the wet season
- travel may be repeated
- the person will spend a lot of time outdoors
- the person’s accommodation has no air-conditioning, screens or bed nets
Check a reputable source before travel for information about JE virus activity — for example, Health Information for International Travel (the ‘Yellow Book’) . 19
A traveller’s overall risk of acquiring JE in these JE - endemic countries is likely to be low (<1 case per 1 million travellers). Determine the specific risk according to the: 17
- season of travel
- regions visited
- duration of travel
- extent of outdoor activity
- extent to which the person avoids mosquito bites
See also Japanese encephalitis .
Before travel to rabies- endemic regions, advise people about:
- the risk of rabies infection
- avoiding close contact with wild, stray and domestic animals — especially dogs, cats, monkeys and bats
- the importance of appropriate immediate wound care of all animal bites and scratches
See also Rabies and other lyssaviruses, including Australian bat lyssavirus .
Recommendations for rabies vaccination as pre-exposure prophylaxis
When deciding whether to give a pre-travel prophylactic rabies vaccination, assess the:
- likelihood of exposure to potentially rabid animals
- access to appropriate health care and availability of post-exposure prophylaxis , including rabies immunoglobulin , should there be an at-risk exposure
- timeliness of access to health care after exposure
Use a lower threshold for recommending rabies pre-exposure prophylaxis for children travelling to endemic areas.
Benefits of vaccination as pre-exposure prophylaxis
Pre-travel rabies vaccination:
- ensures that the traveller has received a safe and efficacious vaccine
- simplifies the management of a subsequent exposure because the person will need fewer doses of vaccine
- means that rabies immunoglobulin — which is often extremely expensive, and difficult or even impossible to obtain in many developing countries — is not needed
- reduces the urgency of post-exposure prophylaxis
Tick-borne encephalitis
Tick-borne encephalitis (TBE) is caused by a tick-borne RNA flavivirus. The disease may involve the central nervous system. TBE is prevalent in parts of central and northern European temperate regions, and across northern Asia. Travellers are at risk when hiking or camping in forested areas in endemic regions during the summer months.
Safe and effective vaccines are available. Vaccination is recommended only for people with a high risk of exposure.
TBE vaccine is not registered in Australia, but a small stock of vaccine may be available for use under the Special Access Scheme .
Tuberculosis
Vaccination with BCG (bacille Calmette–Guérin) vaccine is generally recommended for tuberculin-negative children <5 years of age who will be staying in high-risk countries for an extended period (3 months or longer).
Vaccinating older children and adults appears to be less beneficial. However, consider vaccinating tuberculin-negative children aged ≥5 years but <16 years who may be living or travelling for long periods in high-risk countries.
A high-risk country is one that has a tuberculosis incidence of >40 per 100,000 population.
For travellers who need BCG vaccine, consider the following precautions when scheduling their vaccination visits:
- If possible, give BCG vaccine at least 3 months before the person will arrive in an endemic area.
- Give other live viral vaccines (for example, MMR , varicella, yellow fever) at the same time or with a minimum 4-week interval after BCG vaccination.
- A tuberculin skin test (TST; Mantoux), performed by trained and accredited healthcare practitioners, is recommended before receiving BCG vaccine for all individuals (except infants aged <6 months).
- People may suppress reactions to tuberculin for 4–6 weeks after viral infections or live viral vaccines, particularly measles infection and measles-containing vaccines.
State and territory tuberculosis services can provide tuberculin skin tests and BCG vaccine.
See also Tuberculosis .
Typhoid vaccine may be recommended for travellers ≥2 years of age travelling to endemic regions, including:
- the Indian subcontinent
- most Southeast Asian countries
- several South Pacific nations, including Papua New Guinea
This advice is also relevant for those travelling to endemic regions to visit friends and relatives.
Inactivated parenteral and live oral typhoid vaccine formulations are available.
See also Typhoid fever .
Yellow fever
Yellow fever vaccine is recommended for all people ≥9 months of age travelling to, or living in, an area with a risk of yellow fever virus transmission. 20
To minimise the risk of introducing yellow fever, some countries require documented evidence of yellow fever vaccination for entry, in line with the International Health Regulations (see Vaccines required by the International Health Regulations or for entry into specific countries ).
When assessing the need for yellow fever vaccination, consider:
- the risk of the person being infected with yellow fever virus
- country entry requirements
- individual factors such as age, pregnancy and underlying medical conditions
Vaccination is generally not recommended for travel to areas with a low probability of yellow fever virus exposure — that is:
- where human yellow fever cases have never been reported
- where evidence suggests only low levels of yellow fever virus transmission in the past
However, consider vaccination for a small subset of travellers to lower-risk areas who are at increased risk of exposure to mosquitoes or who are unable to avoid mosquito bites. 20
People aged ≥60 years are at increased risk of severe adverse events after primary yellow fever vaccination. Weigh the adverse effects of vaccinating people in this age group against the potential for yellow fever virus exposure and, in turn, the benefits of vaccination. 17
See also Yellow fever .
Booster doses
Most people do not need a booster dose of yellow fever vaccine. A single dose induces protective antibody levels that last for many decades. However, certain people are recommended to receive a booster if their last dose was more than 10 years ago and they are at ongoing risk of yellow fever virus infection . See Yellow fever .
Vaccines required by the International Health Regulations or for entry into specific countries
Yellow fever requirements.
The International Health Regulations require yellow fever vaccination for travelling in certain circumstances. This is to:
- protect travellers who are likely to be exposed to yellow fever
- stop importation of the virus into countries that have the relevant vectors (see Yellow fever ).
Some countries may require documented evidence of yellow fever vaccination as a condition of entry or exit (see Planning and documenting vaccines ). This includes countries that do not currently have yellow fever circulating.
Australia’s yellow fever travel requirements are detailed in the Australian Government Department of Health’s yellow fever fact sheet .
Contact the relevant embassies or consulates in Australia to confirm the entry requirements for yellow fever vaccination for the countries a traveller intends to enter or transit through.
Requirements for travellers to Mecca
Each year, Saudi Arabia’s Ministry of Health publishes the requirements and recommendations for entry visas for travellers on pilgrimage to Mecca (Hajj and Umra). 16
For pilgrims travelling directly from Australia, only evidence of MenACWY vaccination is currently mandatory. However, check the current requirements when advising prospective Hajj and Umra pilgrims (see Meningococcal disease and Accessing up-to-date travel information ).
Temporary requirements
The International Health Regulations may temporarily introduce requirements for other vaccine-preventable diseases in response to changes in disease epidemiology that are of international health concern. An example is for polio vaccination.
Because country vaccination requirements are subject to change at any time, confirm all current vaccination requirements for the countries a traveller intends to enter or transit through before travel. See Poliomyelitis and Accessing up-to-date travel information .
Planning and documenting vaccines
Ideally, start vaccination courses early enough before departure to allow:
- monitoring of any possible adverse events
- time for adequate immunity to develop
Requirements for multiple vaccines
A traveller may need multiple vaccines before they depart. Apply the standard recommendations and precautions when giving multiple vaccines (see Administration of vaccines ).
A traveller may need more than 1 clinic visit if they need multiple vaccines or doses (for example, rabies pre-exposure prophylaxis or hepatitis B vaccine). Pay special attention to scheduling of these visits, and consider:
- dose interval precautions (for example, for multiple live vaccines)
- requirements for pre-vaccination tests (for example, tuberculin skin test)
- potential interference by some antimalarials, if relevant (for example, rabies vaccine)
Documentation and certificates
It is important to document travel vaccines:
- in the clinic’s record
- in the traveller’s record that they can carry with them
- on the Australian Immunisation Register
The record should also include all the other routinely recommended vaccines that the traveller has ever received.
For yellow fever vaccination, a traveller needs to have an International Certificate of Vaccination or Prophylaxis (ICVP), which only Yellow Fever Vaccination Centres can provide under the International Health Regulations (see Yellow fever ).
Travellers may also need an ICVP for other vaccine-preventable diseases, such as polio, based on temporary recommendations.
See also Accessing up-to-date travel information .
Vaccinating travellers with special risk factors
See Vaccination for women who are planning pregnancy, pregnant or breastfeeding , Vaccination for people who are immunocompromised and the disease-specific chapters in this Handbook for recommendations for travellers who are pregnant or immunocompromised.
Accessing up-to-date travel information
International travellers’ health risks constantly change. Up-to-date information, and knowledge of the changing epidemiology and current outbreaks of infectious and emerging diseases are essential. Reliable online information sources include:
- World Health Organization (WHO) for disease outbreak news, and its Travel and health section for specific advice on travel and health, including travel vaccination recommendations
- Travelers’ health , United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
- Travel health information , Australian Government Department of Health
- Smartraveller , the Australian Government’s travel advisory and consular information service, which provides up-to-date advice about health, safety and other risks of specific destinations for Australian travellers
The following resources have comprehensive technical advice on international travel and health, including vaccination:
- the latest edition of WHO’s International travel and health
- the CDC’s Health Information for International Travel (the ‘Yellow Book’)
- Australian Bureau of Statistics. 3401.0 – Overseas arrivals and departures, Australia, Mar 2018 (accessed May 2018).
- Paudel P, Raina C, Zwar N, et al. Risk activities and pre-travel health seeking practices of notified cases of imported infectious diseases in Australia. Journal of Travel Medicine 2017;24(5):tax044.
- Heywood AE, Watkins RE, Iamsirithaworn S, Nilvarangkul K, MacIntyre CR. A cross-sectional study of pre-travel health-seeking practices among travelers departing Sydney and Bangkok airports. BMC Public Health 2012;12:321.
- Chen LH, Leder K, Barbre KA, et al. Business travel-associated illness: a GeoSentinel analysis. Journal of Travel Medicine 2018;25.
- Angelo KM, Kozarsky PE, Ryan ET, Chen LH, Sotir MJ. What proportion of international travellers acquire a travel-related illness? A review of the literature. Journal of Travel Medicine 2017;24.
- Freedman DO, Weld LH, Kozarsky PE, et al. Spectrum of disease and relation to place of exposure among ill returned travelers. New England Journal of Medicine 2006;354:119-30.
- Halstead SB, Hills SL, Dubischar K. Japanese encephalitis vaccines. In: Plotkin SA, Orenstein WA, Offit PA, Edwards KM, eds. Plotkin's vaccines. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018.
- Staples JE , Monath TP, Gershman MD, Barrett AD. Yellow fever vaccines. In: Plotkin SA, Orenstein WA, Offit PA, Edwards KM, eds. Plotkin's vaccines. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018.
- World Health Organization (WHO). Chapter 6: Vaccine-preventable diseases and vaccines . In: International travel and health. Geneva: WHO; 2017.
- Steffen R. Travel vaccine preventable diseases-updated logarithmic scale with monthly incidence rates. Journal of Travel Medicine 2018;25.
- Denholm JT, Thevarajan I. Tuberculosis and the traveller: evaluating and reducing risk through travel consultation. Journal of Travel Medicine 2016;23.
- Lachish T, Tenenboim S, Schwartz E. 35 - Humanitarian Aid Workers. In: Keystone JS, Kozarsky PE, Connor BA, et al., eds. Travel Medicine (Fourth Edition). London: Elsevier; 2019. (Accessed 6 July 2023). https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780323546966000355
- Leggat PA, Zwar NA, Hudson BJ. Hepatitis B risks and immunisation coverage amongst Australians travelling to Southeast Asia and East Asia. Travel Medicine and Infectious Disease 2009;7:344-9.
- Winkler NE, Dey A, Quinn HE, et al. Australian vaccine preventable disease epidemiological review series: measles, 2012-2019. Commun Dis Intell (2018) 2022;46.
- World Health Organization (WHO). Epidemic meningitis control in countries of the African meningitis belt, 2017. Weekly Epidemiological Record 2018;93:173-84.
- World Health Organization (WHO). International travel and health: health conditions for travellers to Saudi Arabia for the pilgrimage to Mecca (Hajj) . 2017 (accessed May 2018).
- Freedman DO, Chen LH. Vaccines for International Travel. Mayo Clinic Proceedings 2019;94:2314-39.
- Furuya-Kanamori L, Gyawali N, Mills DJ, et al. The Emergence of Japanese Encephalitis in Australia and the Implications for a Vaccination Strategy. Trop Med Infect Dis 2022;7.
- Hills SL, Rabe IB, Fischer M. Infectious diseases related to travel: Japanese encephalitis . In: CDC yellow book 2018: health information for international travel. New York: Oxford University Press; 2017.
- World Health Organization (WHO). International travel and health (accessed Apr 2018).
Page history
Minor updates to clinical guidance around routinely recommended vaccines (not specific to travelling overseas), including the addition of advice regarding COVID-19.
Editorial update to reflect changes to pneumococcal vaccine recommendations for older adults and people with medical risk factors.
Guidance on vaccination of travellers against measles, mumps and rubella updated to reflect advice in the Measles chapter.
Help us improve the Australian Immunisation Handbook
Printed content may be out of date. For up to date information, always refer to the digital version:
Subscribe to receive notifications regarding updates to the Australian Immunisation Handbook and changes to immunisation policy.
Help us improve
We are always looking for ways to improve our website, the NICC and mobile app.
Provide feedback
Acknowledgement
The Department of Health and Aged Care acknowledges First Nations peoples as the Traditional Owners of Country throughout Australia, and their continuing connection to land, sea and community. We pay our respects to them and their cultures, and to all Elders both past and present.
© Commonwealth of Australia | Department of Health and Aged Care
Link , share or bookmark directly to this section of the page.
Travel vaccination advice
If you're planning to travel outside the UK, you may need to be vaccinated against some of the serious diseases found in other parts of the world.
Vaccinations are available to protect you against infections such as yellow fever , typhoid and hepatitis A .
In the UK, the NHS routine immunisation (vaccination) schedule protects you against a number of diseases, but does not cover all of the infectious diseases found overseas.
When should I start thinking about the vaccines I need?
If possible, see the GP or a private travel clinic at least 6 to 8 weeks before you're due to travel.
Some vaccines need to be given well in advance to allow your body to develop immunity.
And some vaccines involve a number of doses spread over several weeks or months.
You may be more at risk of some diseases, for example, if you're:
- travelling in rural areas
- backpacking
- staying in hostels or camping
- on a long trip rather than a package holiday
If you have a pre-existing health problem, this may make you more at risk of infection or complications from a travel-related illness.
Which travel vaccines do I need?
You can find out which vaccinations are necessary or recommended for the areas you'll be visiting on these websites:
- Travel Health Pro
- NHS Fit for Travel
Some countries require proof of vaccination (for example, for polio or yellow fever vaccination), which must be documented on an International Certificate of Vaccination or Prophylaxis (ICVP) before you enter or when you leave a country.
Saudi Arabia requires proof of vaccination against certain types of meningitis for visitors arriving for the Hajj and Umrah pilgrimages.
Even if an ICVP is not required, it's still a good idea to take a record of the vaccinations you have had with you.
Find out more about the vaccines available for travellers abroad
Where do I get my travel vaccines?
First, phone or visit the GP practice or practice nurse to find out whether your existing UK vaccinations are up-to-date.
If you have any records of your vaccinations, let the GP know what you have had previously.
The GP or practice nurse may be able to give you general advice about travel vaccinations and travel health, such as protecting yourself from malaria.
They can give you any missing doses of your UK vaccines if you need them.
Not all travel vaccinations are available free on the NHS, even if they're recommended for travel to a certain area.
If the GP practice can give you the travel vaccines you need but they are not available on the NHS, ask for:
- written information on what vaccines are needed
- the cost of each dose or course
- any other charges you may have to pay, such as for some certificates of vaccination
You can also get travel vaccines from:
- private travel vaccination clinics
- pharmacies offering travel healthcare services
Which travel vaccines are free?
The following travel vaccines are available free on the NHS from your GP surgery:
- polio (given as a combined diphtheria/tetanus/polio jab )
- hepatitis A
These vaccines are free because they protect against diseases thought to represent the greatest risk to public health if they were brought into the country.
Which travel vaccines will I have to pay for?
You'll have to pay for travel vaccinations against:
- hepatitis B
- Japanese encephalitis
- tick-borne encephalitis
- tuberculosis (TB)
- yellow fever
Yellow fever vaccines are only available from designated centres .
The cost of travel vaccines that are not available on the NHS will vary, depending on the vaccine and number of doses you need.
It's worth considering this when budgeting for your trip.
Other things to consider
There are other things to consider when planning your travel vaccinations, including:
- your age and health – you may be more vulnerable to infection than others; some vaccines cannot be given to people with certain medical conditions
- working as an aid worker – you may come into contact with more diseases in a refugee camp or helping after a natural disaster
- working in a medical setting – a doctor, nurse or another healthcare worker may require additional vaccinations
- contact with animals – you may be more at risk of getting diseases spread by animals, such as rabies
If you're only travelling to countries in northern and central Europe, North America or Australia, you're unlikely to need any vaccinations.
But it's important to check that you're up-to-date with routine vaccinations available on the NHS.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Speak to a GP before having any vaccinations if:
- you're pregnant
- you think you might be pregnant
- you're breastfeeding
In many cases, it's unlikely a vaccine given while you're pregnant or breastfeeding will cause problems for the baby.
But the GP will be able to give you further advice about this.
People with immune deficiencies
For some people travelling overseas, vaccination against certain diseases may not be advised.
This may be the case if:
- you have a condition that affects your body's immune system, such as HIV or AIDS
- you're receiving treatment that affects your immune system, such as chemotherapy
- you have recently had a bone marrow or organ transplant
A GP can give you further advice about this.
Non-travel vaccines
As well as getting any travel vaccinations you need, it's also a good opportunity to make sure your other vaccinations are up-to-date and have booster vaccines if necessary.
Although many routine NHS vaccinations are given during childhood, you can have some of them (such as the MMR vaccine ) as an adult if you missed getting vaccinated as a child.
There are also some extra NHS vaccinations for people at higher risk of certain illnesses, such as the flu vaccine , the hepatitis B vaccine and the BCG vaccine for tuberculosis (TB) .
Your GP can advise you about any NHS vaccinations you might need.
Find out about NHS vaccinations and when to have them
Page last reviewed: 16 March 2023 Next review due: 16 March 2026
You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.

Routine Vaccines
It’s important to be up to date on recommended routine vaccines prior to travel, including Flu, RSV and COVID-19.

Find a Clinic
Advice for Travelers
Personalized Health Information Tool for Global Travel
Disease Directory
Frequently Asked Questions
CDC Yellow Book
Pre-travel Rapid Evaluation Portal for Patients
Clinician Resources
Research and Surveillance
- Medical Tourism
- Cholera Information for Health Care Professionals
- COVID-19 Travel Information
- Travel Industry Resources
Learn about CDC’s Traveler Genomic Surveillance Program that detects new COVID-19 variants entering the country.
Sign up to get travel notices, clinical updates, & healthy travel tips.
See the full list of Travel Health Notices , including:
Level 2 - Practice Enhanced Precautions
- Global Polio April 26, 2024
- Diphtheria in Guinea April 23, 2024
- Chikungunya in Timor-Leste April 05, 2024
Level 1 - Practice Usual Precautions
- Updated Dengue in the Americas May 16, 2024
- Updated Dengue in Africa and the Middle East May 16, 2024
- Updated Dengue in Asia and the Pacific Islands May 16, 2024
There are no Warning , Alert, Watch, COVID-19 Very High, COVID-19 High, COVID-19 Moderate, COVID-19 Low, COVID-19 Unknown, Level 4, or Level 3 notices currently in effect.
File Formats Help:
- Adobe PDF file
- Microsoft PowerPoint file
- Microsoft Word file
- Microsoft Excel file
- Audio/Video file
- Apple Quicktime file
- RealPlayer file
- Zip Archive file
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to "About this site"
Language selection
Search travel.gc.ca.
Help us to improve our website. Take our survey !
Please help improve our website. See if you qualify .
Travel vaccinations
Measles cases are increasing worldwide.
Before travelling, check that you and your family have received the recommended measles vaccinations.
Do not travel if you have symptoms of measles or have been in contact with someone with measles.
If you develop symptoms of measles after your return to Canada, call a health care provider right away.
Global Measles Notice
When travelling outside Canada, you may be at risk for a number of vaccine preventable illnesses.
You should consult a health care provider or visit a travel health clinic preferably six weeks before you travel. This is an opportunity to:
- review your immunization history
- make sure your provincial/territorial vaccination schedule is up-to-date
- discuss any trip-related health concerns you may have
- assess your needs based on where you plan to travel and what you plan to do
You may need additional vaccinations depending on your age, planned travel activities and local conditions. Preventing disease through vaccination is a lifelong process.
Use the reference below to determine which vaccinations may be recommended or required for your destination.
Vaccination recommendations by destination
Yellow fever vaccination.
Some countries require proof that you have received a yellow fever vaccination before allowing you to enter the country. Consult an embassy or consulate of your destination country in Canada for up-to-date information on its entry and exit requirements before you travel abroad.
Other countries may require you to have been vaccinated for yellow fever if you have passed through an area where yellow fever may occur .
Proof of vaccination must be documented on an International Certificate of Vaccination or Prophylaxis . You must carry the original certificate with you.
In Canada, the vaccination is only given at designated yellow fever vaccination centres .
Immunization records
- Download the free CANImmunize app from the iOS App Store or Google Play, and manage your family’s vaccination records on the go.
- Carry copies of your family’s immunization records while you travel and leave the originals at home.
- Sickness or injury
- Travel Advice and Advisories
- If you get sick after travelling
- Receiving medical care in other countries
- Travel health kit
- Travel insurance
- Well on Your Way - A Canadian’s Guide to Healthy Travel Abroad
- Tips for healthy travel
- Yellow Fever Vaccination Centres in Canada , Public Health Agency of Canada (PHAC)
- Recommended Immunization Schedules , PHAC
Australian Government Department of Health and Aged Care
Immunisation for travel
It’s important to protect your health when travelling overseas. You can avoid diseases and other health conditions by planning ahead for any vaccinations you may need.
If you are looking for information COVID-19 vaccines, please visit the COVID-19 digital certificate page.
Vaccines needed for travel
If you travel outside Australia, you may get sick from a number of diseases that vaccination can prevent. Travellers can bring these diseases into Australia when they return and cause disease outbreaks.
You should always ask your doctor or travel health clinic about vaccinations before you travel.
Your immunity to some diseases may have changed or reduced with time – you may need a booster.
Different countries have different vaccination requirements. The recommended vaccines for travelling depend on a number of factors, including:
- pregnancy or planning pregnancy
- underlying medical conditions
- vaccination history
- season of travel.
When to get vaccinated
You should consult your doctor or visit a travel health clinic 6 to 12 weeks before you leave Australia.
It is important to see your doctor early. If you do need vaccinations:
- your body needs time to develop full immunity
- you may need several doses of a vaccine to achieve full immunity.
How to check your vaccination record
You may have already received recommended vaccines from previous travel or routine vaccinations. These may be recorded in the Australian Immunisation Register.
The Australian Immunisation Register (AIR) is a national register that records vaccines given to all people in Australia.
The AIR includes vaccines given:
- Under the National Immunisation Program
- through school programs
- privately, such as for flu or travel.
You can check your immunisation record :
- online on MyGov through Medicare
- via the Express Plus Medicare mobile app
- by calling 1800 653 809 (Monday to Friday 8 am to 5 pm).
Cost of vaccines
The vaccines you need for travel may not be covered by the National Immunisation Program. In this case, you will need to buy them. This may involve:
- getting a prescription for the vaccine
- buying it from a pharmacy
- returning to your doctor to give you the vaccination.
The cost of vaccines varies depending on the type, the formula and where you buy them.
Some doctors might have these vaccines available in their clinics. Some pharmacies also offer vaccination services.
Check with your provider when you book your appointment.
How to stay safe overseas
The vaccine information you find on various websites is only a guide. You should not rely on such information. Talk to your doctor or travel health clinic for advice on travel vaccines and how to stay safe while you are overseas.
Find more information:
- Travel Health Information for things to consider before you leave, while you are away and when you return.
- Smartraveller (Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade)
- Travellers’ health (US Center for Disease Control & Prevention)
Keep routine vaccinations up to date
Travel is an important time to check whether you and your children are up to date with your vaccinations. This includes routine childhood vaccinations and boosters. Some of these include:
- measles-mumps-rubella (MMR)
- diphtheria-tetanus-whooping cough (pertussis)
- chickenpox (varicella)
Influenza is the most common vaccine-preventable disease caught by travellers.
The chance of getting these diseases may be greater while travelling overseas. Travellers can bring these diseases into Australia. This can lead to disease outbreaks.
Get more about information about routine vaccinations:
- National Immunisation Program Schedule
- When to get vaccinated
Diseases to be aware of
Some countries require proof of immunisation for certain infectious diseases before you can legally enter that country. Ask your doctor or travel health clinic if you need proof of immunisation before you travel.
Read about some of the common vaccine-preventable diseases found in other areas of the world.
Cholera is found in places with poor water and waste facilities. It spreads through contaminated food and water and causes severe diarrhoea and dehydration.
Humanitarian disaster workers should get vaccinated for cholera because they are more likely to get infected. Most travellers do not need a cholera vaccination because the risk of getting cholera is very low.
Your doctor may recommend the cholera vaccine if you have a condition that puts you at greater risk of travellers’ diarrhoea.
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis A is one of the most common vaccine-preventable diseases caught by travellers. It is a liver disease spread by contaminated food and water. It is common in parts of India, Africa, Asia, South and Central America and the Middle East where there is poor sanitation and limited access to clean water.
You and your children over 1 year of age should get a Hepatitis A vaccination if you are travelling to an area where Hepatitis A is common.
Japanese encephalitis
Japanese encephalitis is a serious disease spread by mosquitoes in Asia and the Torres Strait region of Australia. We recommend vaccination against this disease if you are travelling to these parts and will be:
- travelling in rural areas
- undertaking certain activities with increased risk of exposure
- spending a month or more in the region.
You should avoid mosquito bites when you are in these areas.
Meningococcal
Meningococcal disease is a serious disease spread by close contact with an infected person. It is commonly found in sub-Saharan Africa.
Rabies is common to Central and South America, Eastern Europe, Africa and Asia. It is spread from infected animals to humans through bites, scratches and licks to open wounds. It is fatal when left untreated. The animal does not have to appear ill to have rabies. Infected animals can include dogs, monkeys, cats, rats, bats, foxes and chipmunks.
Ask your doctor if you need the rabies vaccine before you travel.
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is a serious disease spread by close contact with an infected person. It is common in developing countries.
We recommend the TB vaccine called BCG for children aged 5 years or under who are:
- travelling a lot
- spending a long time in countries where TB is common .
Typhoid is a disease spread through contaminated food and water. It causes diarrhoea and other symptoms. It is common in parts of India, Africa, Asia, South and Central America and the Middle East where there is poor sanitation and limited access to clean water.
Yellow fever
Yellow fever can be a serious disease. It causes fever, yellowing of the skin (jaundice) and damages the liver and kidneys. Mosquitoes spread yellow fever. It is found in Africa, the Caribbean and Central and South America.
You must be immunised for yellow fever before you can legally enter some countries. Only authorised yellow fever vaccination centres can give yellow fever vaccinations and certification. Ask your doctor about this.
Find more information: Yellow fever fact sheet
- Immunisation
- Travel health
Is there anything wrong with this page?
Help us improve health.gov.au
If you would like a response please use the enquiries form instead.
Travel Vaccines and Advice for East and Southeast Asia

Seoul’s urban amenaties, Japan’s countryside and China’s Great Wall are just a few of the reasons that millions of people visit East and Southeast Asia every year. With a wide variety of cultures, cuisines and historical sites, it is one of the most popular regions to visit.
Passport Health offers medications, immunizations and personalized consultations for your trip to East and Southeast Asia. See our What Vaccines… section to learn more.
Countries in this region include:
What Vaccines Do I Need for East and Southeast Asia?
The PHAC and WHO recommend the following vaccinations for travellers to East and Southeast Asia: hepatitis A , hepatitis B , typhoid , cholera , yellow fever , Japanese encephalitis , rabies and polio .
Some routine vaccinations are also recommended, this includes: measles, mumps and rubella (MMR) , tetanus, diphtheria and pertussis (Tdap) , influenza , chickenpox , shingles , pneumonia , meningitis .
While rare, polio cases have been sporadicly reported in some parts of the region. While generally a routine vaccination, it may be recommended for your trip.
Proof of yellow fever vaccination may be required for some travellers, based on their specific itinerary.
See the tables below for more vaccination information:
Are There Other Health Concerns in East and Southeast Asia?
There are a few additional health concerns for East and Southeast Asia that are not vaccine preventable.
Malaria is present in East and Southeast Asia. Antimalarial medication may be recommended based on your specific itinerary. Antimalarial resistance is also found in some areas, this may limit your medication options. Speak with a travel health specialist to learn more.
Dengue , chikungunya and Zika are found as well. Mosquito netting, repellents and protective clothing may be recommended. Avoid outdoor activities during high times for mosquito activity, especially at dusk and dawn.
Tuberculosis is common in some parts of the region. If you feel you may be exposed during your trip, or have returned and believe you were exposed, TB testing is available. Testing should be done upon return and within eight to ten weeks of the first test for long-term travellers.
Travellers’ diarrhea another common risk for travellers. While new cuisine is always fun to try, it may lead to some unpleasant side effects if not prepared safely. Bring a travellers’ diarrhea kit to help prevent illness and stop symptoms if they start.
What Are the Entry Requirements in East and Southeast Asia?
A visa may be required for some popular destinations like China and Cambodia. But, many others have minimal requirements. Check the table below for more information on your destination.
China’s visa rules for Hong Kong and Macao are very different from many other countries. Be sure to check the visa page if you are travelling to any of these regions.
Embassy information for each country is available on its own destination advice page.
Travelling to Another Destination?
Travelling outside of East and Southeast Asia? Learn more about your destination with our full compliment of destination advice pages!
- Afghanistan
- American Samoa
- Antigua and Barbuda
- British Virgin Islands
- Burkina Faso
- Canary Islands
- Cayman Islands
- Central African Republic
- Christmas Island
- Cocos (Keeling) Islands
- Cook Islands
- Cote d’Ivoire
- Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Dominican Republic
- Easter Island
- El Salvador
- Equatorial Guinea
- Falkland Islands
- Faroe Islands
- French Guiana
- French Polynesia
- Guinea-Bissau
- Liechtenstein
- Madeira Islands
- Marshall Islands
- Netherlands
- New Caledonia
- New Zealand
- Norfolk Island
- North Korea
- North Macedonia
- Northern Mariana Islands
- Palestinian Territories
- Papua New Guinea
- Philippines
- Pitcairn Islands
- Puerto Rico
- Republic of the Congo
- Saint Barthelemy
- Saint Helena
- Saint Kitts and Nevis
- Saint Lucia
- Saint Martin
- Saint Pierre-et-Miquelon
- Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
- Sao Tome and Principe
- Saudi Arabia
- Sierra Leone
- Sint Eustatius
- Solomon Islands
- South Africa
- South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands
- South Korea
- South Sudan
- Switzerland
- Trinidad and Tobago
- Turkmenistan
- Turks and Caicos Islands
- U.S. Virgin Islands
- United Arab Emirates
- United Kingdom
- United States
- Wake Island
- Western Sahara
On This Page: What Vaccines Do I Need for East and Southeast Asia? Are There Other Health Concerns in East and Southeast Asia? What Are the Entry Requirements in East and Southeast Asia? Travelling to Another Destination?

- PIPEDA Policy and Consent Form
- Privacy Policy
- Automatic Data Collection Statement

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Hepatitis A vaccine is highly recommended for travellers to Southeast Asia and is given as a single injection, with a booster (optional) 6-12 months, after the initial injection, that will then protect you for at least 20 years.
Vaccination (2-dose vaccine): Recommended for most travelers. --Administer 2 doses, at least 6 months apart. --At least 1 dose should be given before travel. Consultation: Advise patient to wash hands frequently and avoid unsafe food and water. Hepatitis B. Sexual contact, contaminated needles, & blood products, vertical transmission.
Advice. Travelers'. Diarrhea Kits. Available. Seoul's urban amenities, Japan's countryside and China's Great Wall are just a few of the reasons that millions of people visit East and Southeast Asia every year. With a wide variety of cultures, cuisines and historical sites, it is one of the most popular regions to visit.
Advice. Travellers'. Diarrhea Kits. Available. Seoul's urban amenaties, Japan's countryside and China's Great Wall are just a few of the reasons that millions of people visit East and Southeast Asia every year. With a wide variety of cultures, cuisines and historical sites, it is one of the most popular regions to visit.
What Vaccines Do I Need for Traveling to Southeast Asia? Home to Jakarta, Indonesia; Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam; and Bangkok, Thailand, Southeast Asia is a very popular destination for travelers.Prior to the COVID-19 pandemic in 2019, almost 40 million tourists visited Thailand, more than 26 million vacationed in Malaysia, and over 19 million spent time in Singapore.
Dosing info - Hep A. Hepatitis B. Recommended for unvaccinated travelers younger than 60 years old traveling to Thailand. Unvaccinated travelers 60 years and older may get vaccinated before traveling to Thailand. Hepatitis B - CDC Yellow Book. Dosing info - Hep B. Japanese Encephalitis. Recommended for travelers who.
Find out which travel vaccines you may need to help you stay healthy on your trip. Before Travel. Make sure you are up-to-date on all of your routine vaccines. Routine vaccinations protect you from infectious diseases such as measles that can spread quickly in groups of unvaccinated people. Many diseases prevented by routine vaccination are not ...
Injectable. For certain exceptional situations. This table shows the vaccines recommended for traveling to Asia by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the leading institution in the world in terms of international vaccination. To summarize, the most commonly recommended vaccines are typhoid fever, tetanus, and hepatitis A and B.
Recommended Travel Vaccines for South-East Asia. ALL TRAVELLERS: SOME TRAVELLERS: COURSE* Cholera: 6 weeks before travel 2 doses: Diphtheria: Anytime before travel 1 dose: Hepatitis A: ... These are the minimum times required to complete courses or for vaccines to become fully effective. You can always start your course of vaccinations earlier ...
For travel in Southeast Asia, most medical experts recommend at least vaccinations for measles, mumps and rubella (MMR), typhoid, hepatitis A, chicken pox, diphtheria, tetanus and polio. Some of these you may have had when you were a child, but in some cases you will need a booster to get you back up to scratch.
The country list is a compilation of key information to facilitate safe international travel. The country list is a compilation of key information to facilitate safe international travel. ... Americas; South-East Asia; Europe; Eastern Mediterranean; Western Pacific; When autocomplete results are available use up and down arrows to review and ...
3. Cambodia. Entry rules: Cambodia reopened to vaccinated international tourists without quarantine back in November, though any traveler crossing the border must present proof of vaccination, a negative COVID-19 test result, then take a rapid antigen test upon arrival and await results at the airport.
Asia; South America; The vaccine is usually given as a drink in 2 separate doses, taken 1 to 6 weeks apart. Children aged 2 to 6 years old should have a third dose taken 1 to 6 weeks after the second dose. You should make sure you have the final dose of this vaccine at least a week before you travel.
Pneumococcal. Measles, mumps and rubella (MMR) Polio. Shingles. Additional vaccines may be recommended depending on your travel itinerary. For example, hepatitis A vaccination is recommended if you are traveling to Southeast Asia. During your appointment, we can discuss which vaccines are appropriate for your itinerary. 3.
vaccines required by the International Health Regulations 2005 (IHR) or for entry into specific countries ... Central and South America; Africa; Asia; ... Hepatitis B risks and immunisation coverage amongst Australians travelling to Southeast Asia and East Asia. Travel Medicine and Infectious Disease 2009;7:344-9. Winkler NE, Dey A, Quinn HE ...
Travel vaccination advice. If you're planning to travel outside the UK, you may need to be vaccinated against some of the serious diseases found in other parts of the world. Vaccinations are available to protect you against infections such as yellow fever, typhoid and hepatitis A. In the UK, the NHS routine immunisation (vaccination) schedule ...
CDC Travelers' Health Branch provides updated travel information, notices, and vaccine requirements to inform international travelers and provide guidance to the clinicians who serve them. ... Updated Oropouche Fever in South America April 24, 2024; Dengue in Asia and the Pacific Islands April 18, 2024; More. Content source: ...
When travelling outside Canada, you may be at risk for a number of vaccine preventable illnesses. You should consult a health care provider or visit a travel health clinic preferably six weeks before you travel. This is an opportunity to: You may need additional vaccinations depending on your age, planned travel activities and local conditions.
Covid-19 Vaccines: South-East Asia Region. WHO South-East Asia Region. COVID-19 Vaccination Dashboard. South-East Asia Region. COVID-19 vaccines Weekly update. South-East Asia Region. Update on Pandemic Vaccine Deployment. Covid-19 Vaccines: Global. Information about Coronavirus (COVID-19) Vaccines.
The Australian Immunisation Register (AIR) is a national register that records vaccines given to all people in Australia. The AIR includes vaccines given: privately, such as for flu or travel. You can check your immunisation record: by calling 1800 653 809 (Monday to Friday 8 am to 5 pm).
Advice. Travellers'. Diarrhea Kits. Available. Seoul's urban amenaties, Japan's countryside and China's Great Wall are just a few of the reasons that millions of people visit East and Southeast Asia every year. With a wide variety of cultures, cuisines and historical sites, it is one of the most popular regions to visit.
Vaccines are widely recognized as one of the most cost-effective and successful public health interventions. Across the South-East Asia Region, immunization has prevented millions of deaths and disabilities, achieved dramatic declines in once highly-endemic diseases, stopped the transmission of wild poliovirus, eliminated maternal and neonatal tetanus, and significantly reduced the ...
The South -East Asia Region of WHO is made up of 11 countries, with over 1.8 billion people, with India's population of 1.2 billion. The diversity of people and health situations requires, on the demand side, a solid understanding of the emerging socio-economic, epidemiologic and demographic patterns and trends at both aggregate as well as ...