

31 Niche Tourism Groups
If you thought that Niche Tourism covers just a handful of interest groups, think again. In the 5th edition of his book ‘ Marketing Tourism in South Africa ‘ , Richard George identified 20 distinct Special Interest or ‘Niche’ tourism groups, and we’ve added 11 more to this growing list.
Table of Contents
Special interest tourism (SIT) to South Africa has increased rapidly in the last few years. Special interest tourists are motivated by the desire to go on holiday and take part in a current interest or develop a new interest in a new or familiar location.
Special interest tourism is a niche market, similar to adventure tourism, but it differs in that it involves little or no physical exertion. The special interest may be a one-off interest (for example, going on a safari, white-water-rafting or shark-cage-diving) or an ongoing interest (for example, spiritual tourism).
Some of the most popular special interest tourism products include the following:
1. Agri-tourism
Agri-tourism (aka agro-tourism or farm-based tourism) involves activities such as fruit-picking. Tourists may go on tours of working farms or on established tourist routes such as brandy or wine routes. They may visit factories that process farm produce (for example, jam) and may stay overnight in farmhouse B&Bs.
2. Ancestry tourism
Tourists travel to destinations with the aim of learning more about and possibly tracing their ancestors.
3. Architourism (or architectural tourism)
Tourists are attracted by the design and buildings of a destination.
4. Avitourism (or birding tourism)
Birdwatching is a popular hobby all over the world. Southern Africa is one of the richest birding regions, with a network of birding routes. BirdLife South Africa, a membership-based non-profit organisation, represents the birding tourism sector in South Africa.
5. Battlefields tourism
Tours to former battlefields have grown in popularity. Popular battlefields sites in South Africa include Isandlwana in KwaZulu-Natal and the Western Front (Normandy, the Somme) in Europe.
6. Eco-tourism (or wildlife tourism)
Tourists view the flora or the game of an area. This includes whale-watching.
7. Gambling tourism
Tourists visit casino destinations and holiday in gambling cities that have many casinos.
8. Gastronomy tourism (or food tourism)
“Foodies” visit a destination in order to experience cuisine and food festivals. Gastronomy tourism is defined as travel that has food as the primary factor of influence in travel behaviour and in the decision-making process.
9. Lighthouse tourism
Tourists visit and sometimes stay in lighthouses that provide accommodation for tourists.
10. Military tourism
Tourists who visit war memorials, battlefields, forts and war museums.
11. Nostalgia tourism
Tourists return to a destination for sentimental reasons. For example, they go back to a destination where they had a memorable childhood holiday, or where they lived or studied in their younger years.
12. Photographic tourism
Tourists visit Africa’s natural and cultural attractions in order to take photographs.
13. Property tourism
Tourists travel to holiday destinations to purchase residential property. The property tourism operator who organises the tour may reimburse all or a portion of the cost of the holiday that was taken in order to view the property if the tourist purchases the property.
14. Rural tourism (or Cultural tourism)
This includes home-stays so that tourists can experience rural life and food.
15. Safari tourism
Tourists participate in art safaris and rail safaris.
16. Spa tourism
Tourists visit mineral or hot springs. This type of niche tourism is not bound to any season. It is a year-round activity.
17. Wedding tourism
This involves honeymooners and couples who travel to destinations to have their wedding ceremonies. Wedding tourists tend to travel in quite large numbers.
18. Wellness tourism (or Spiritual tourism)
Tourists come to a destination in order to unwind and enjoy reflexology and massages, for example.
19. Wildlife tourism
Tourists participate in activities such as safaris, viewing marine wildlife and photographing wildlife.
20. Wine tourism
Tourists visit wine-growing regions and wine routes, vineyards, wineries (cellar tours and tasting rooms), wine festivals and so on, for the purpose of consuming or purchasing wine.
South Africa has excellent wine regions and offers a variety of additional benefits to wine tourists, including natural and cultural visitor attractions. The country’s wine routes are ranked as the fourth most popular visitor attraction for international and domestic tourists.
The Winelands in the Western Cape, Napa Valley in California , the USA and Adelaide in Australia are examples of world-class wine tourism destinations.
More Specialist Tourism Groups:
Here are more niche tourism groups to add to the above list – Editor.
21. Accessible tourism
Accessible tourism is ‘Tourism For All’. It’s about making travel and hospitality more reachable and pleasurable for travellers with universal access requirements. It’s also about sensitising yourself to the language of disability.
22. Adventure tourism (or Adventure travel)
Adventure travel is a type of tourism, involving exploration or travel with perceived (and possibly actual) risk, and potentially requiring specialized skills and physical exertion. Adventure tourism is rapidly growing in popularity, as tourists seek different kinds of vacations.
23. Art Tourism
Art tourism is a term that is used when people travel in order to visit, explore and engage in activities related to art. It includes travelling to art festivals, art galleries, music concerts, and dance and book festivals, and to explore the homes of famous artists, musicians, writers, and poets.
24. Cruise tourism
Cruise tourism is a great way to expose a country’s beauty and culture and also a nice way to travel the world giving tons of jobs and employment to places that it visits, mostly “ports of call”.
25. Cultural tourism
This kind of tourism normally occurs in urban areas with particular historical significance or cultural facilities, such as museums and theatres.
Cultural tourism also highlights the various traditions of indigenous communities through observing their rituals, customs as well as their values and lifestyle. Tourism, therefore, serves as the carrier of culture and cultural tourism has become the platform for cultural consumption.
26. Environmental Tourism (or Green tourism)
Environmental Tourism, – also referred to as Ecotourism, Sustainable Tourism and Responsible Tourism – are terms rooted in the concept of development that “meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.”
27. Film Tourism
Film tourism is a growing phenomenon worldwide, motivated by both the growth of the entertainment industry and the increase in international travel. Film-induced tourism explores the effects that film and TV-productions have on the travel decisions made when potential tourists plan their upcoming holiday or visit to a destination.
28. Luxury Tourism
According to Statista, luxury tourism as a niche market is defined as revenues derived by a destination from acquisitions of consumer goods, services, and valuables for and during trips by individual tourists who have net assets of over one million U.S. dollars (read our article ‘ Growth Forecasts for Luxury Tourism Market’ via the links at the end of this article).
29. Voluntourism (Volunteer travel or volunteering)
Voluntourism is a form of tourism in which travellers participate in voluntary work, typically for a charity or cause.
A good example of volunteer programmes in the wildlife conservation space is Ashia Cheetah Sanctuary . Their reciting of Benjamin Franklin’s famous quote: “Tell me and I’ll forget; Show me and I may remember; Involve me and I’ll understand” encapsulates the ethos behind voluntourism.
30. Youth tourism (or Youth travel)
Youth tourism is defined as people aged between 15 to 30 who take independent trips of less than one year.
31. Red-tape tourism
OK, this one is more tongue-in-cheek! Could Home Affairs offices, licencing departments and similar facilities in small towns compete on service delivery to create a new domestic tourism niche? Read th is article: Red-tape tourism .
If you have any other niche tourism groups to add to the list just COMMENT below.
About the Author: Richard George is an Associate Professor and Research Director at the School of Management, University of Cape Town. For more information Telephone: +27 (0)21 650 4245 or Email [email protected]
Read more on this topic:
- Avitourism in South Africa
- Cruise Tourism Potential in South Africa
- A Guide to Cultural Tourism
- Ecotourism: A Case Study
- Environmental Tourism – Part 1
- Environmental Tourism – Part 2
- Environmental Tourism – Part 3
- Film Tourism: Exploring the benefits
- Food Tourism: How to Get Your Slice of the Pie
- Growth Forecasts for Luxury Tourism Market
- Voluntourism: Keeping it Sustainable
- Volunteerland: The Worlds Largest Adult Traveller Population

Tourism Tattler
Related articles, youth tourism trends, how to apply responsible tourism practices.

Cape Town now an international trail running Mecca for tourists

Accessible Tourism Manual
Privacy overview.

How to choose a travel niche: Exploring niche tourism in the travel Industry
- June 2, 2023

Niche markets in the travel industry are specialised segments that cater to specific interests, demographics, or travel styles. They help businesses in the industry target their offerings and better cater to their customers’ needs.
This article aims to explore the concept of these niche markets. It seeks to illustrate how they function, their increasing popularity, and their role in shaping the future of tourism.
What is niche tourism?
Niche travel and niche tourism refer to specialised travel experiences catering to a specific interest, activity, or demographic group. Rather than offering broad, one-size-fits-all travel experiences, niche tourism providers deliver tailored services and packages to accommodate their target market’s unique preferences and needs. This can encompass numerous specialisations, from adventure or eco-tourism to wellness, cultural, and food tourism.
Importance of choosing a travel niche
Choosing a travel niche is important for both travel providers and travellers for several reasons:
- Customer satisfaction: Tailored services and packages increase the likelihood of customer satisfaction as they align more closely with individual interests and expectations
- Market differentiation: In a highly competitive industry, carving out a niche allows businesses to distinguish themselves from competitors, positioning them as experts in a particular area
- Increased loyalty: Niche travel experiences can foster increased customer loyalty, as customers who have had their specific needs and interests met are more likely to return
- Sustainable business growth: Focusing on a niche can help travel providers achieve sustainable business growth. They can better understand their market, streamline their offerings, and refine their marketing strategies, leading to more efficient operations and stronger customer relationships
- Enhanced experiences for travellers: Choosing a niche allows them to have more personalised and enriching experiences. They can immerse themselves more deeply in their interests and activities, resulting in more fulfilling journeys
Understanding niche travel
Niche travel is hugely significant for both travellers and travel industry providers for several reasons:
- Personalisation: Niche travel allows for customised experiences that cater to specific interests, creating a more personalised and enjoyable travel experience
- Expertise: Niche travel companies often have a high level of expertise in their particular area, enabling them to provide in-depth experiences and knowledge
- Community: Travellers with shared interests can form a sense of community, enhancing their overall travel experience
Differentiating niche travel from mainstream tourism
Niche travel and mainstream tourism differ in several key aspects:
- Broad vs Specialised: Mainstream tourism caters to a wide audience and typically includes popular destinations, attractions and experiences. Niche travel, on the other hand, is specialised, targeting a specific demographic, interest, activity or offbeat destination
- Mass market vs Personalised: Mainstream tourism is often mass-market-oriented with broad appeal, whereas niche travel focuses on delivering personalised experiences
- Generic vs Unique: Mainstream tourism often offers generic, one-size-fits-all experiences. In contrast, niche travel focuses on unique experiences tailored to the specific interests or needs of the traveller
Exploring the concept of experiential and specialised travel
Experiential and specialised travel, often considered a subset of niche travel, prioritises unique, immersive experiences:
Experiential travel
This form of travel prioritises personal and unique experiences over sightseeing. The goal is to immerse oneself in the local culture, meet the locals, and engage in activities characteristic of the destination.
Specialised travel
Specialised travel focuses on a specific interest or activity, such as wine tasting, skiing, horse riding, cooking, yoga, dancing, wildlife photography, or yoga retreats. These tours are typically led by experts in the field and offer a deep dive into the particular interest.
In both experiential and specialised travel, the emphasis is on creating meaningful, personal experiences rather than just visiting a destination.
Benefits of choosing a travel niche
There are many benefits to be gained from choosing a travel niche to focus on.
Personal fulfilment and passion-driven travel experiences
Choosing a travel niche allows for deeply personal, fulfilling experiences that cater to one’s passions and interests. A culinary enthusiast may opt for food tourism, for example, immersing themselves in the local cuisine of different regions, thereby enriching their gastronomic knowledge and skills. The connection between personal passion and travel provides a unique, deeply satisfying experience that extends beyond typical sightseeing.
Building expertise and becoming an authority in a specific area
When individuals or businesses focus on a travel niche, they can develop in-depth knowledge and understanding of that area, becoming experts in that field and enhancing their reputation and credibility. For instance, a travel agency specialising in eco-tourism can accumulate a wealth of knowledge about sustainable travel practices and destinations, setting them apart from generalist competitors.
Targeting a specific audience and creating unique travel offerings
Choosing a travel niche allows businesses to target a specific audience with unique travel offerings. This specificity can aid in designing marketing campaigns and packages that speak directly to a defined group’s interests, needs, and expectations, thereby improving the effectiveness of marketing efforts. For example, a company with a niche in adventure tourism can tailor its offerings to thrill-seekers and outdoor enthusiasts, providing experiences that general travel agencies might not offer.
Opportunities for collaboration and networking
Focusing on a travel niche opens opportunities for collaboration and networking. Businesses can collaborate with other organisations, cross-promote each other, and engage with influencers or thought leaders to enhance their visibility and credibility. For example, a travel agency focusing on wellness tourism might partner with yoga studios or wellness coaches to offer retreats or workshops, enhancing their services and strengthening their network.
Identifying niche markets in the travel industry
Adventure and outdoor travel.
Adventure and outdoor travel cater to individuals who crave physical activity, exploration, and nature-based experiences. It’s a broad category that can include anything from mountain climbing and hiking to off-the-beaten-path tours and camping in remote locations. Adventure travel can also involve paragliding, rock climbing, or white-water rafting, appealing to thrill-seekers and those hunting an adrenaline rush.
Culinary and food tourism
Culinary and food tourism is all about exploring a region’s culinary traditions and food culture. This type of travel involves food tours, cooking classes, wine tastings, and farm-to-table experiences. Culinary tourism allows travellers to dive deep into local food scenes, taste authentic dishes, and learn about the history and tradition behind regional cuisines.
Wellness and spa retreats
Wellness and spa retreats focus on relaxation, self-care, and holistic experiences. This market includes yoga retreats, meditation workshops, spa treatments, and other health-oriented activities that aim to rejuvenate the body, mind, and spirit. Wellness retreats often occur in serene environments such as beach resorts or mountain lodges, offering travellers an escape from their daily routine and stress.
Cruise travel
Cruises are a popular niche market that offers unique sea experiences and can vary greatly in destinations, sizes, and themes, from luxurious world cruises to river cruises, from family-friendly cruises to expedition cruises for adventure seekers. Cruises often offer comprehensive packages that include accommodation, food, entertainment, and excursions, providing an all-in-one travel solution for many tourists.
Ski tourism
Ski tourism targets winter sports enthusiasts. Travellers might head to mountainous regions for skiing, snowboarding, and other winter activities. Ski resorts often provide comprehensive services, including equipment rental, ski lessons, accommodation, and après-ski entertainment, making it a popular choice for winter holidaymakers.
Scuba diving holidays
Scuba diving breaks cater to those who are interested in underwater exploration. Travellers often visit exotic locations known for their coral reefs, marine wildlife, and clear waters. This niche market includes the diving experience itself and often offers diving instruction, equipment rental, and other related services.
Sustainable, environmental and eco-tourism
Sustainable and eco-tourism is a rapidly growing niche in the travel industry, focusing on responsible travel practices. This niche promotes travelling in a way that respects local culture and environment, minimises impact on nature, and contributes to conserving natural and cultural heritage. Eco-tourism often involves visiting pristine, fragile, and relatively undisturbed natural areas, contributing to their preservation. Sometimes it also incorporates volunteer holidays where people spend their time helping conserve the environment.
Sports and sporting events tourism
Sports and sporting events tourism is a niche market that attracts sports enthusiasts and fans. This can involve travelling to participate in sporting activities like golf, cycling, or swimming or attending major sporting events such as the Olympics, the World Cup, or the Super Bowl. This niche often provides related services such as ticket booking, transportation, and accommodation.
Medical and wellness tourism
Medical and wellness tourism combines medical treatments with leisure travel. This niche caters to individuals who travel to receive medical treatments such as surgeries, dental procedures, or wellness therapies that may not be easily accessible or affordable in their home country. After receiving medical treatment, these travellers often take the opportunity to recuperate and relax at their destination.
Factors to consider when choosing a travel niche
When deciding which travel niche to specialise in, there are several considerations.
Personal interests, passions, and expertise
When choosing a travel niche, it’s essential to consider one’s interests, passions, and areas of expertise. If you deeply understand and love a particular area, this can enhance your services, make your work more enjoyable, and resonate strongly with your target audience.
Market research and demand analysis
Conducting thorough market research and demand analysis is essential. Travel agents must understand the trends in the travel industry, identify which niches are growing, and assess the demand for different travel experiences. It’s also essential to consider your potential customers’ demographics, preferences, and behaviours.

Competition analysis and identifying gaps in the market
It’s important to research what other providers in your potential niche offer and identify market gaps. If there is an underserved area that aligns with your interests and expertise, this could present a unique business opportunity.
Accessibility and feasibility of the niche
Accessibility and feasibility are other crucial factors to consider. Some niches may require more resources or specific expertise to execute successfully. For instance, arranging adventure travel experiences might require extensive knowledge of safety protocols and outdoor survival skills. Assessing the feasibility of your potential niche ensures you can provide high-quality, reliable services.
Potential profitability and sustainability
While a niche might be personally fulfilling and have a good demand, it must also be financially viable for it to be a good business choice. It’s also important to consider the sustainability of the niche. Some niches may be trendy but have little long-term potential, while others, such as eco-tourism, align with long-term trends towards more sustainable and responsible travel.
Steps to choosing your travel niche
So, how do you choose your particular travel niche?
1. Research and explore different niche markets
Your journey to choose a travel niche should start with broad research to explore different niche markets in the travel industry. This step involves learning about various travel niches, understanding what they entail, and identifying the ones that resonate with you.
2. Evaluate your personal interests, skills, and experiences
Next, evaluate your interests, skills, and experiences. Reflect on the types of travel that excite you, and consider your strengths and experiences that might contribute to success in a particular niche. This step is about identifying where your interests align with potential niche markets.
3. Analyse market trends and demand for specific niches
After identifying potential niches, you’ll want to analyse market trends and demand. Examine current trends in the travel industry, understand consumer behaviours and preferences, and determine which specialisations have strong growth potential. Market research can provide valuable insights into the demand for specific travel experiences.
4. Consider the potential challenges and opportunities within each niche
Assess the competition within the niche, identify potential entry barriers, and explore possible partnerships or collaborations. Considering challenges and opportunities can help you gauge your chosen niche’s feasibility and potential profitability.
5. Seek advice from industry experts
Contact people already operating within your potential niche, attend industry events, or join relevant online communities. Experienced industry professionals can provide valuable insights and practical advice, helping you to avoid potential pitfalls and make informed decisions.
6. Make an informed decision based on your information
Review your research, reflect on your interests and skills, and consider the advice you’ve received. Choose the travel niche that best aligns with your passion, skills, and market demand. Remember, your chosen niche should be a viable business opportunity and something you’re excited about pursuing.
Embrace the power of niche tourism
Choosing a travel niche holds immense potential for success in the ever-evolving tourism industry. Embracing a niche that aligns with your interests and passions, and has a robust market demand, can lead to gratifying experiences and a thriving business.
The power of niche tourism lies in its ability to provide personalised, in-depth, and unique experiences beyond conventional tourism. As a franchisee with The Travel Franchise , you have the opportunity to harness this potential and can offer travel options that cater to specific interests, from adventure and outdoor activities, culinary explorations, and wellness retreats, to eco-tourism and more.
As you embark on this exciting journey in niche tourism, remember to continually monitor market trends, adapt to your customers’ evolving needs, and stay true to your passion. In doing so, you’re ready to create meaningful travel experiences that resonate with your audience and stand the test of time in this dynamic industry.
You might also like...

Part-time duo from Doncaster race ahead with our Partners in Travel Scheme

Made redundant at 59… now a homeworking travel consultant with a £60k booking under her belt and a dream house in Cyprus. Meet Marietta

14 years in the business and now with a team by her side. Agata shares her tips and explains why she still loves being a personal travel consultant

Useful links
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
Get in touch
Our friendly team are on live chat if you have any questions..
- [email protected]
- 0800 084 8128
© The Travel Franchise. We reserve right to change our packages at any time.
Learn how it works instantly!
Your instant access to all our presentations is one e-mail away!

- Privacy Overview
- 3rd Party Cookies
This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
You can read our Privacy Policy here .
This website uses Google Analytics to collect anonymous information such as the number of visitors to the site, and the most popular pages.
Keeping this cookie enabled helps us to improve our website.
Please enable Strictly Necessary Cookies first so that we can save your preferences!

What is special interest tourism and why is it so popular?
Disclaimer: Some posts on Tourism Teacher may contain affiliate links. If you appreciate this content, you can show your support by making a purchase through these links or by buying me a coffee . Thank you for your support!
Special interest tourism is growing, and it’s growing fast! Have you heard the term special interest tourism a lot? And do you wonder why people are choosing special interest tourism more than mass-market? Well here, I will explain the meaning of special interest tourism and why it’s becoming more popular.
What is specialist interest tourism?
Characteristics of special interest tourism, the growth of special interest tourism, health tourism , adventure tourism, dark tourism, food tourism, spiritual/ religious tourism, rural tourism, wildlife tourism, sports tourism, special interest tourism- further reading.
Special interest tourism (also known as specialist tourism or SIT), is a branch of niche tourism and alternative tourism . Essentially, special interest tourism is tourism which is tailored to a specific interest.

There are many tour operators who focus their business on special interest tourism (and this number is growing). There are typically smaller companies that specialise in specific types of package holidays; they are seen as package holidaymakers that are perfectly customising holidays with preferred activities or destinations that the customer chooses as they want their needs and preferences to be met.
There are many different types of special interest holidays. An example would be an active family with teenage boys who are looking to travel somewhere like Australia to take part in adventurous activities like bungee jumping, mountain biking, or zip-lining. Another example would be a couple who are looking to travel for their honeymoon to an exotic romantic destination, like the Maldives .
Many people would describe special interest tourism as the law of changing nature, meaning people are changing normal everyday items for better-improved items. In other words, people are moving away from the traditional mass tourism model and towards more niche, specialist products that better satisfy their individual desires, interests and needs. This happens in many different ways, from the tourists visiting different destinations, for example by swapping a trip to the beaches in Spain for an adventure across Jordan or by switching their day by the pool for a specialist painting holiday.
Special interest tourism is seen as both tangible (something you can touch, like a hat) and intangible (something you can’t touch, like air); even though when customers are booking their holidays they can’t physically touch their holidays and see what it feels like, however, when they hop on the plane and go to their resort, or when they go to the pools or when they go to the beach, etc – all of those things they can touch, and they can even take stuff with them for memories.

There are many reasons for the rapid growth of special interest tourism, the first one being, socioeconomic. The customer’s level of income will dictate the choice of their holiday and the level of service that is wanted. Nowadays there are more people who have more money to spend on their holidays, which increases all tourism, not just special interest tourism!
However, it is the change in consumer attitudes that has really influenced the growth of the special interest tourism market. Many more people nowadays want to experience bungee jumping, line walking, mountain biking, and more fun activities; they want to do something crazy and different from their normal life and mainly to get their mind off their workplace. People want to pursue their hobbies in alternative contexts and to experience culture in a way that they have not previously done.
All of this creates this demand and thus the rise of special interest tourism as more people are now interested in doing something different. This is especially the case since COVID-19, when people developed a true appreciation for the opportunities that are presented to them outside of the confines of their homes.
Another reason for the growth of special interest tourism is due to trends – trends are always changing, which means that special interest tourism has to be updated and developed to follow these trends for their customers. An example of a trend would be the development of technology; which has a high impact as everyone has access to the internet, which leads to everyone having and being on social media and the growth of tourism forms such as Insta tourism , smart tourism and virtual tourism !

Furthermore, social media platforms are used globally with billions of people using them; people can post pictures of themselves, families, places, and their hobbies, and they can comment on our people’s posts (where they are following each other), this has led to people changing and wanting more things; which is caused by some social media influencers (who have a lot of followers who will look up to them); they are paid employees who are working on social media to post pictures and inspire people to try what they are doing; which is good for the companies like travel – because there is a demand and an increase in destinations as these influencers will go to certain places and they will post these amazing catching pictures that will lead to people wanting to travel in that destination).
Examples of special interest tourism
There are over 150 types of tourism that tour operators specialise in. Some of the main types of special interest tourism include:

Health tourism allows customers to go to a destination with a purpose for things like medical treatments, visiting spas, wellnesses, and physical activities (yoga, swimming, fitness) – to ‘clear’ and focus on their mindset and body; most of the destinations seem like relaxing and calm place to go, however, some destinations may be seen as expensive, exotic place to travel (meaning most of the destinations are long haul flights), popular destinations include Asia, Middle East, Indian Ocean and many more.
Adventure Tourism is seen as a fantastic and energetic place with adventure activities, like mountain hikes, snorkeling, skiing, bungee jumping, zip-lining, etc. The holidaymakers will go to places with the most fun things that the customers can do and experience (and can tick off on their bucket list), which includes destinations like Australia , Africa, Thailand, and many more.
Dark touris ts will travel to destinations where certain (bad) things have happened. Dark tourism generally means that tourists will visit places where a high amount of death has occurred; some people go to these places to remember their loved ones who were involved and to honour them (to pay their respect) and others go there to learn more about what has happened and see the experience. They can visit places like battlefields, prisons, castles, Chernobyl, Auschwitz, and the 9/11 memorial site.
Food tourism allows tourists to go aboard and do things that involve doing food & beverage testings; to get the authentic experience of trying new things. Some people go to another destination to learn how to cook the country’s famous dishes from the locals and others go aboard just to try the dishes around the world, which includes going to the destinations like: France, Italy , Korea, Middle East, USA, and more (some people will have a sit-down meal, some will try street food, some will share meals with the local people, some will go to the food festivals, some will visit the local food market, etc)
Spiritual/ religious tourists can go abroad and connect with the world (meaning with god and with religions) and even with themselves; meaning spiritual tourism is not always connecting with specific religions, it means that people can also be connecting their bodies, mind, and soul; while religious tourism is to seek blessings from God based on the religious faiths and beliefs; some destinations include: the Middle East, Spain, India, United Kingdom and more – most of the tourists will visit pilgrims, churches, sacred sites, and other will visit places where there are quiet and calm areas; somewhere like at the top of the cliff, Greenland (somewhere with a lot of grass area).

Rural tourists can travel somewhere in the country-side; meaning the tourists can experience the country life, the culture, the beliefs, and religion, and take part in the activities that take place in the country life like farming, hand-picking vegetables, riding tractors to crop the soils, etc; it means that the tourist will not stay in expensive hotels, tourists will likely be spending their nights in a small house that is located in the village with local tourists around, or they will likely be sleeping in tents and camps, the destinations include Poland, Middle East, Philippines and more.
Wildlife tourists can travel abroad to see and interact with animals that they don’t see on the daily basis, it includes visiting places like the zoo, safari, animal shows (although this is very controversial and I do not recommend it). Wildlife tourism destinations include Africa, India , Sri Lanka, Spain, and more.
Sports tourism occurs when tourists travel aboard to watch or take part in sports or sports events. Sporting events include things like the Olympics, Formula One, etc. Sporting activities may include playing football, golf, volleyball, taking part in car races, etc. Popular sport tourism destinations include Germany, Italy, Middle East, Spain, Belgium and more.
If you have enjoyed this article on special interest tourism, I am sure that you will love these too!
- What is adventure tourism and why is it so big?
- What is alternative tourism and why is it growing so fast?
- The fascinating history of tourism
- What is industrial tourism and why is it so popular?
Liked this article? Click to share!
The Rise of Niche Tourism
- Post author By SnC
- Post date April 16, 2022
Niche tourism is a new work I recently came across. When looking more into it, it was difficult pinning down a specific definition. I later read that Niche Tourism is actually a collective term used to group a number of types of tourism – which explained why there’s no one definition. However, it being an umbrella term allowed me to gain a broad understanding of this concept and make sense of it through multiple mediums.
First, I think it’s important to understand what ‘niche’ means. According to Merriam Webster, niche is a “place, employment, status, or activity for which a person thing is best fitted,” or more simply, a specialized market. Niche tourism covers a range of types of tourism where products and services serve a specialized segment of the tourism industry. A way to better understand this concept is by looking at the exact opposite of niche tourism – mass tourism. Mass tourism includes large group tours (cruises) and all-inclusive holiday resorts.
Below, you can find a list of different types of niche tourism:
Niche tourism has recently become more popular because of changes in consumer behavior. Consumers have become more sophisticated with their wants and needs, therefore all-inclusive, one-size-fits-all is no longer a fan favorite. One interesting thing I read that resonated with my tourism habits is that we want more than a nice pool and some evening cocktails from our vacations. There are things we want to see and learn about from different cultures. People have become more globalized and educated therefore wanting education, culture, and adventure.
This article from Yahoo Finance discusses how companies are taking advantage of this new phenomenon. Recently, mainstream holiday providers have identified niche tourism as a potential growth area.
Niche tourism is a critical element to consider as consumer attitudes shift towards more special interest travel. This consumer behavior has become more relevant among Millennials and GenZ. The tastes of GenZ and Millenials are helping take niche tourism to the next level.
Handbook of Niche Tourism
- School of Business and Law
Research output : Book/Report › Book - edited › peer-review
- niche tourism
- sustainable tourism
- sustainability
- post-covid19
- Sustainable development
Other files and links
- https://www.e-elgar.com/shop/gbp/handbook-of-niche-tourism-9781839100178.html
Fingerprint
- Niche Arts & Humanities 100%
- Handbook Arts & Humanities 95%
- niche Earth & Environmental Sciences 91%
- Tourism Arts & Humanities 89%
- tourism Earth & Environmental Sciences 85%
- Sustainable Development Arts & Humanities 18%
- Wellness Tourism Business & Economics 14%
- Religious Tourism Business & Economics 14%
T1 - Handbook of Niche Tourism
AU - Novelli, Marina
AU - Jones, Adam
AU - Milano, Claudio
A2 - Cheer, Joseph
A2 - Dolezal, Claudia
PY - 2022/9
Y1 - 2022/9
N2 - This Handbook provides a critical analysis of the evolution of the contemporary niche tourism phenomenon. By framing discussions around sustainable development thinking, concepts and practical applications, each chapter provides specific reflections on niche tourism trends, successes and/or failures, and the challenges and opportunities that destinations that pursue tourism as a vehicle for sustainable development face around the world. The Handbook includes a blend of academic and practitioner contributors providing a balance of theoretical, conceptual and empirical elaborations on the topic, with case studies from across the globe. It covers a broad range of critical thematic areas, including: nature-based tourism, rural tourism, heritage and culture based tourism, dark tourism, spiritual, religious and wellness tourism, and social and inclusive tourism. Chapters also examine the latest developments in niche tourism, including the impact of Covid-19.This invigorating and comprehensive study of niche tourism will benefit sustainable tourism scholars, as well as tourism researchers and students more broadly. It will also be useful to policy makers and tourism practitioners seeking a better understanding of this increasingly important field.
AB - This Handbook provides a critical analysis of the evolution of the contemporary niche tourism phenomenon. By framing discussions around sustainable development thinking, concepts and practical applications, each chapter provides specific reflections on niche tourism trends, successes and/or failures, and the challenges and opportunities that destinations that pursue tourism as a vehicle for sustainable development face around the world. The Handbook includes a blend of academic and practitioner contributors providing a balance of theoretical, conceptual and empirical elaborations on the topic, with case studies from across the globe. It covers a broad range of critical thematic areas, including: nature-based tourism, rural tourism, heritage and culture based tourism, dark tourism, spiritual, religious and wellness tourism, and social and inclusive tourism. Chapters also examine the latest developments in niche tourism, including the impact of Covid-19.This invigorating and comprehensive study of niche tourism will benefit sustainable tourism scholars, as well as tourism researchers and students more broadly. It will also be useful to policy makers and tourism practitioners seeking a better understanding of this increasingly important field.
KW - niche tourism
KW - sustainable tourism
KW - sustainability
KW - post-covid19
KW - Sustainable development
UR - https://www.e-elgar.com/shop/gbp/handbook-of-niche-tourism-9781839100178.html
M3 - Book - edited
SN - 9781839100178
BT - Handbook of Niche Tourism
PB - Edward Elgar Publishing

Top 40 Travel and Tourism Niches: Which One Are You?
Not too long ago, travel and adventure meant going out of your small town (be it even to the nearby woods ). You left the comfort and safety behind and took significant risks, especially if you traveled solo.
Today, numerous travel niches have become popular, each with its own tourism appeal and unique perspective that it offers.

In this post, I will list the major types of travels that I consider to be broad enough to deserve a mention as a travel niche. These tourism niches have big enough market demand to sustain as an independent category on their own.
Travel Niches & Trends
- Adventure Travel – Adventure tourism is the fastest growing and biggest travel niche today
- Nature and Wildlife Tourism (aka Ecotourism) – another trend which will continue to grow
- Cultural Tourism – traveling for the purpose of exploring various culture, and cultural & world heritage sites
- Medical, Dental, & Fertility Tourism – traveling for medical purposes
- Wellness Tourism – traveling to seek tranquility, healing, meditation, and nature retreats
- Music (and Music Festivals) Tourism – popular with young adults
- Culinary Tourism – traveling for food, to eat well is to live well
- Wine, Cheese, & Beer Tourism – traveling to taste different wines from different regions
- Nightlife and Party Tourism – traveling to various party destinations
- Roadtripping – traveling by car with a group of friends
- Extreme Sports Tourism – traveling to mountains
- Highpointing – Hiking, climbing, or driving to the highest elevation point of a state, country or continent
- Sports Tourism (Golf, etc.) – either to play or watch
- Shopping Tourism – traveling exclusively for shopping purposes
- Religious Pilgrimages – walking, biking, or traveling to religious & spiritual sites

- Off-the-Grid Travel – traveling to and living off the grid in a minimalistic way
- Scenic Train Travel – touristy scenic train rides with focus on dining & wining
- Space Tourism – exploring the outer atmosphere, earth from above, and outer space
- Bookstores & Literary Tourism – visiting cool bookstores and fictional or real sites related to books and authors
- Tolkien Tourism – exploration of Tolkien’s middle earth and LOTR related sites
- Volunteer Travel – traveling & volunteering to work on non-profit charity projects
- Film & TV Tourism – traveling to various film and TV series filming sites (eg. Game of Thrones )
- Archaeology & History Tourism – traveling to ancient ruins, archeological sites, and historical places
- Ghost, UFO, & Haunted Tourism – traveling to haunted places and UFO siting sites
- Genealogy Tourism – tracing or returning to your roots
- Jungle Tourism – traveling and camping in the deep and remote jungles
- Underwater Tourism – exploring the marine life and ocean through Scuba, Snuba, Snorkeling
- Shark Tourism – seeking underwater thrills & shark encounters across the globe
- Rural and Village Tourism – countryside relaxation
- Astronomy Tourism – visiting sites that provides excellent views of the stars and night sky
- Inner city Tourism – exploring your own town or city in great details
- Weekend Tourism – traveling every weekend (mostly nearby attractions)
- Ghetto Tourism – traveling & exploring the living conditions in slums and ghetto
Deviant & Sad Trends

A beautiful ruin
I was debating at first whether to lost the following sad trends or not? Listing them will give them more exposure, so at first, I thought I will leave them out. But then I thought, these trends are actually growing (financially speaking) so closing my eyes to these problems will not help solve these issues.
The best thing I can do is to use this platform and bring public awareness about these. Some of these may sound harmless or even exciting (drugs and sex for example), but please understand that both drugs and sex causes overall more damage, deaths, and harm to innocent lives (including children).
The best way you can help is first by not participating in them and therefore cutting off the financial incentive. Second, you can be aware that these problems exist and thus help to spread the word. (Fact: Even in Prague or Amsterdam , most of the girls working in the red light district are there against their will via deception, bribery, and manipulation.)
- Drug Tourism – mostly illegal and unsafe, please use common sense
- Sex Tourism (Male, Female, Trans) – again, please use common sense. Do not do anything that hurts other humans
- Dark Voyegeristic Tourism (Underground shady fights, deaths, & stuff) – please do not support or fund this industry by partaking in it. Anyone can be the next innocent victim of it
- War & Disaster Tourism – visiting sites with tragic past for pleasure (War, disaster, & genocidal sites, Nazi camps, etc.)
- Suicide Tourism (Important: if you are feeling suicidal, know that you’re not alone and confidential help is available for free. Please seek help. US Helpline | HelpGuide | Resource Center )
- Hunting Tourism ( The Big 5 Games ) – traveling to mainly Africa ( South Africa , Tanzania , Kenya , Zimbabwe , Botswana , etc.) to hunt rare and endangered species such as Elephants, Lions, Rhinos among others. *Hunting* is very common in North America and Europe .
*Hunting is a personal choice. It’s a complex issue and would need an entire blog to discuss the various impacts and issues surrounding it. If you are not a hunter, please do not partake and support this industry.
As a starting point, please follow the first rule of life, do not kill life unless it is for your own or your family’s survival and safety . Also, the above category is about hunting the big animals (man of them endangered and at the point of extinction).
March 2, 2018 12:09 pm Published by Art Of Travel 3 Comments
Join the Travel Club
Categorized in: Trip Ideas , Travel Inspiration , Travel FAQ , Did You Know
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Resources and Links
- Write for Us
- Advertising
- Apply Tourist Visa
- Global Travel Alerts
- World Climate Guide
- Adventure Travel
- Press Bio/Media Kit
- Useful Travel Resources
- Common Travel Questions
- List of All Blogs
- Travel Bucket List
- Couple Goals

The Emerging Trend of Niche Tourism: Impact Analysis
Journal of marketing research and case studies.

Corina Larisa BUNGHEZ
Bucharest university of economic studies, bucharest, romania, academic editor: alexandra cristina dinu, cite this article as: corina larisa bunghez (2021), “ the emerging trend of niche tourism: impact analysis", journal of marketing research and case studies, vol. 2021 (2021), article id 134710, doi : 10.5171/2021.134710, copyright © 2021. corina larisa bunghez. distributed under creative commons attribution 4.0 international cc-by 4.0.
This research paper addresses the current tourism global market shift towards a niche tourism approach and focuses on some of the most significant tourism forms in this growing sector, analyzing both the current development and future evolution of these tourism trends, also taking into account the current global pandemic situation. The enormous versatility and potential of the selected niches are assessed, and the impact that these activities will have on mainstream tourism is highlighted, both economically and socially, as this trend continues to expand and integrate itself in the tourism global marketplace. The niche sectors analyzed in this research paper will fundamentally transform the tourism industry in the near future and, inevitably, alter the consumer experience by bringing more services and experiences into the mainstream tourism sector.
Introduction
Mass tourism is an important part of our daily lives; niche tourism is also growing at a rapid pace. Started as an expensive and elitist concept, targeting sophisticated travelers, who were enthusiastically interested in pursuing a diverse range of activities, niche tourism is now readily accessible to most people, being one of the fastest growing sectors within the domain of tourism.
The term niche tourism has been borrowed mostly from the term niche marketing, which has adopted the concept from a newer discipline, ecology. Hutchinson is considered to be the first who used the term niche, referring to a region in a vast area that is characterized by environmental factors which disturb the welfare of species (Hutchinson, 1957). In this sense, niche tourism can be linked to the particular natural and anthropogenic resources of a region, to the characteristic lifestyle of the tourists that engage in this type of activity and to their social status and their financial resources, etc. The niche tourism market, which is characterized by its name, targets a small number of consumers when compared to mass tourism, but, at the same time, it is a constant tourism market. Niche tourism is more identified with what tourists are doing than their number in a particular destination, at a particular time.
Any discussion of niche tourism needs to be considered against the other extreme of mass tourism. The rise of mass tourism, fueled by the growth in the aviation sector in the 1950s and 1960s, also gave rise to the backpacker tourist who later became the highly specialized and sophisticated middle-class traveler of the developed world (Lew, 2008).
Over time, the transition from mass tourism to niche tourism has been a slow and cumbersome process that necessitated a large amount of material and human resources in order to develop the much needed new and specialized infrastructure. The development of this infrastructure in the past decades has allowed people to reach destinations all over the world in record time. Keeping with the accelerated technological advancement, tourism will continue to expand its digitalization process. There are more and more applications for niche services nowadays, that are extremely personalized. These special applications perfectly know their target consumers and offer them suggestions based on their budget, their family structure and their traveling and browsing habits. On the other hand, for destination managers and traveling planners, who want to use tourism as a mechanism for economic growth, focusing on niche tourism offers greater opportunities because this attracts consumers that are willing to spend more money.
In order to position niche tourism products, Novelli considers the notion of an increasingly experienced group of tourists demanding specialist holidays to meet their specific desires (Novelli, 2005). The presence of activities, tourist attractions, settlements, food services and other facilities make up the fundamental components of niche tourism regarding mixed destinations, being aware of consumer needs and wants. The focal point of the niche tourism market is the focus on the demands and the expectations of the customers. The relation between supply and demand is well taken into consideration because tourists are in a never-ending search for a more satisfying experience during their holidays (C.T., 2010). In a world in which monotony is becoming more pronounced due to globalization, niche tourism is defined by its diversity and by new ways in which it can differentiate itself from the competition. Niche tourism doesn’t have the negative implications that mass tourism has gotten along with its expansion, namely the negative impact on the environment and the degradation of socio-cultural relations.
If mass tourism is a standardized product aimed at a large segment of the market, niche tourism is situated at the opposite end of the tourism spectrum, being heterogeneous by nature and based on a larger demand for a more exclusive, unique and distinctive product.
The consumer is actively involved in the formation of a specific niche through its own consumerist practices. Because of this, in order to escape from the competition of mass tourism, the producer is no longer the sole identifier of adequate niche markets, because these niches are formed and developed by both producers and consumers, who act in a symbiotic mode in order to mutually benefit by it (Richards, 2011).
Over time, the different types of niche tourism have been presented in specialty literature in a random fashion. There are, however, some authors that have categorized them based on different criteria.
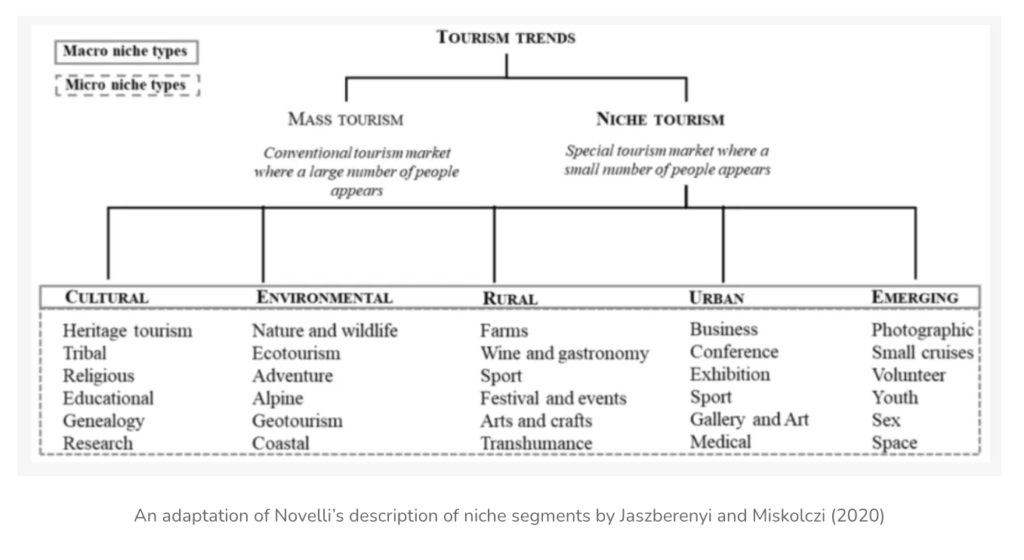
In order to better analyze the impact that certain types of niche tourism have over mass tourism, the classification made by Alex Papathanassis in his book, The Long Tail of Tourism, will be utilized (Paapathanassis, 2011). Tourism niches are built on persisting social trends such as:
- Sustainability (e.g. Eco-, Inclusive-, Agro-tourism)
- Experience-economy (e.g. Space-, Sport- & Extreme-, Military-, Film-, Dive-tourism)
- Self-development & individuality (e.g. Cultural-, Educational-tourism)
- Hedonism & voyeurism (e.g. Armchair-, Drug-, Sex-, Dark-tourism)
- Consumerism (e.g. Shopping-tourism)
- Conscious living (e.g. Health- & Medical, Religious-, Wellness-tourism)
Consumer experience in tourism is defined as a conglomerate of personal reactions and emotions associated with tourism activities (Sugathan & Ranjan, 2019). The creation of memorable experiences is necessary in order to attract new consumers and to keep the ones you already have loyal. All of the aforementioned tourism forms satisfy this requirement.
The impact of these forms of tourism is presented and analyzed in the following sections of the article, focusing on one form of tourism in each of the categories presented.
Ecotourism is considered to be a niche segment that targets a small category of tourists, when compared to mass tourism. Nevertheless, ecotourism is the sector with the biggest growth in all the niche tourism markets.
The consequence of broadly defining the borders of what constitutes to be ecotourism is the cause behind the difficulty of properly measuring and assessing the market share and the size of this segment. Even so, estimates tell us that ecotourism makes up for roughly 20% of the tourism global market.
The eco tourist is the individual who visits the less developed areas with an appreciative, participatory and selfless attitude. This type of tourist interacts in a noninvasive way with local flora and fauna and uses natural resources in a conscious, reserved manner, while contributing through voluntary work or funds that are directed to the preservation of the area and the economic welfare of the local community (Ziffer, 1989).
Ecotourism has two specific components: specialized operations and non-specialized operations. The non-specialized ones include all common elements characteristic to all forms of tourism: tourist guides, adequate clothing, tourism agencies, hotels and transportation. The specialized ones are those which refer to the specific activities of ecotourism: eco cabins and hotels in urban or more secluded areas (resorts), protected areas, eco thematic attractions, services in other inaccessible areas by interesting means and local tour operators (natives).
There are independent groups successfully promoted as ecotourism products: aboriginal/indigenous tourism (related to cultural tourism), ornithology, celestial ecotourism (aurora borealis, astronomical observations, astrophotography), hiking and nature observation, landscapes photographing, outdoor education and research, etc. (Weaver, 2008).
Ecotourism attractions are primarily based on biodiversity and natural habitats that are, for the most part, unaffected by human activities. Thus, taking place in relatively isolated places, the current pandemic crisis will not impact this sector as severely as others. On the contrary, people will tend to visit more isolated places and ecotourism could benefit by this crisis. These zones require a specific conduct, in order to properly preserve and protect the tourism destinations so that they may keep their natural qualities and their sense of wilderness.
Ecotourism could indirectly compete with two tourist segments in terms of content and characteristics of the tourism product. These are cultural tourism and adventure tourism and they form, together with the ecotourism, what we call alternative tourism (Papathanassis, 2011).
It is estimated that the future development of ecotourism in terms of application will depend on several factors, such as: revenue growth; increasing the education level; increased leisure time; population growth; easier, cheaper, faster and safer access to ecotourism destinations; greater care for the natural environment and people’s feeling of alienation from it because of increasing urbanization and the development of technological elements.
Beyond all these elements, there is a necessity for properly trained people to educate the general tourists regarding the importance of nature conservation. Also, practicing ecotourism in these areas brings significant financial benefits that can be directed to further develop and maintain the natural parks and protected areas within the zone. Thus, ecotourism is a viable alternative for sustainable economic growth in these communities.
Space Tourism
Space tourism is an industry with extraordinary potential, but at present is limited by the conditions in which it can be done, because the prices are huge. Until the year 2019, the cost of a trip to the International Space Station aboard the Russian Soyuz spacecraft was 30 million dollars/flight. At present, the collaboration between NASA and SpaceX will inevitably lead to a commercial development. Axiom Space has already started the selling of tickets aboard the SpaceX capsule, at the price of 55 million dollars/ticket. The trip will last 10 days and will be directed to a privately funded orbital space station. Further technological advancement will massively lower the prices for space travel, starting with the amount of $200,000 that Virgin Galactic assigned in the beginning. Space travel will become more accessible to a greater number of people, especially in relation to the results of a market analysis, which has found that potential consumers are very price sensitive (Goehlich, 2005). A study shows that at least 10 million people from around the world would be willing to spend a year’s salary for space travel (Smith, 2001).
It is expected that the number of space travelers will grow somewhere to a million per year when the price of a ticket will be under $ 10,000. According to research, rich and adventurous young people seem to form the most suitable target market due to their care-free rebellious character and the low comfort level that they are willing to accept in order to be among the first passengers in space (Crouch, et al., 2008). A study made by Futron Corporation in 2002 made the prediction that by 2021, the suborbital flight market will reach 15.000 passengers/annually, bringing in revenue of about 700 million dollars (Futron, 2002). We are in 2021 and this approximation is totally unattainable in the current global context. But it can be safely assumed that the number is not unachievable and we may see this happen in a few years. Another study made in 2006, in which 783 high income Australian respondents participated, showed that those who were mostly interested in space travel were thrill-seeking young men (Devinney, et al., 2006).
The economic potential of the development of space tourism is extraordinary. This type of tourism will bring massive economic and social benefits in the future, because it can be estimated that it will undoubtedly surpass aviation on Earth.
The progress of the space tourism sector would generate, alongside the indirect technological and scientific advancements, an important direct economic component that will lead to the exponential growth of this sector. Because space tourism has the potential of becoming its own branch in the tourism industry, the effects of this economic development will be significant, both for the companies and industries involved in the process, and for the evolution of our society as a whole. In this type of endeavor, the investor’s primary concern is the return of the investment and the generation of profit. In order to do so, every process involved will be thoroughly made as efficient as possible. Space activities will therefore become a massive economic generator and the launch costs will dramatically plummet, which will lead to an acceleration in the further development of this industry.
Space tourism will become an activity that will include a very large number of people (both operators, and beneficiaries) and will generate important commercial profits in the next few decades. It is imperative that we recognize and realize the fact that, in the near future, space tourism may become as common as other forms of tourism. However, since the reality of space tourism is still quite far away, it may be safely assumed that the current Covid pandemic will not influence this branch of niche tourism. Because of the sensational experiences offered to the consumer, space tourism will become a major sector of the entire tourism industry, transforming this niche branch of tourism into one of the most important tourism activities of humanity.
Cultural Tourism
Cultural tourism is the most dynamic contemporary form of tourism, being interested in the lifestyle and traditions of particular communities or regions, built or natural heritage, artistic performances and products, cultural hubs and landscapes.
The first appearance of cultural tourism as a research topic has its origins at the beginnings of the 20 th century, but only in 2002 did the International Council on Monuments and Sites publish a formal definition regarding this form of tourism: cultural and cognitive-cultural tourism is the form of tourism that is focused on the cultural environment and that includes historical and cultural landmarks within a destination, and the values, arts, crafts, traditions, habits and lifestyle of the local populace.
Cultural tourism is defined by the World Tourism Organization (WTO 2012 Report) as “journeys whose primary or secondary purpose is the visiting of sites and the participation in events that represent a cultural and historical component which is part of a communities’ cultural heritage”. There are serious cultural and heritage/historical tourists who are motivated by the inherent characteristics of cultural sites and, at the other end of the spectrum, there are people who accidentally visit such venues but are not truly interested in the sites’ inherent cultural and heritage assets (Morrison, 2013).
Cultural tourism includes, besides visiting historical sites, the opportunity to learn more about past human achievements. As a part of domestic tourism, these visits are a great source of admiration, national pride and learning about ancestors.
The complexity of cultural tourism is further generated by customer motivation diversity, induced by differences in education levels, tourism experience, quality of life and quality of the tourism products being offered (Davidson, 1993). Also, cultural tourism has been identified as one of the most rapidly growing areas of global tourism demand (Richards, 2005).
Cultural tourism is an important instrument for economic growth, generated by attracting visitors from outside the local host destinations. These visitors are partially or generally motivated by an interest in historical, artistic and scientific components, or by information regarding the lifestyle, the realities and the traditions of a particular community, region, group or institution. This kind of voyage focuses on the study of the cultural landscape, and this includes visual and theatrical arts, values, traditions, events and lifestyle. Cultural tourism is especially interesting for suppliers because, as a rule of thumb, people that focus strongly on cultural attractions spend more money than regular tourists. Also, they show a tendency toward staying longer at the destinations, which, in turn, brings even more revenue (Richards, 2007).
Because cultural tourism isprimarily focused on the visiting of cultural venues or museums and experiencing artistic products and performances, the current global pandemic has affected, to some extent, this important tourism sector. But people will always be interested in the lifestyles and traditions of different cultures, and as soon as the Covid pandemic loses momentum, we will definitely see a resurgence in cultural tourism demand.
Armchair Tourism
The one thing that history has taught us is that people are most innovative in difficult times. This also applies to the travel industry, where professionals and brands are doing their best to keep the interest in traveling at a high level, despite the current global Covid pandemic situation. This has resulted in the surprisingly successful overnight growth of armchair tourism. This adaptation happened because tourism is going through one of its darkest periods in a long time, and tourism specialists find themselves in the impossibility to change this situation. Indeed, this isn’t the greatest of times for classic travels, but, in the meantime, we can opt for virtual travel. If, until more recently, the trend of virtual tourism was relatively ignored, because people preferred real experiences, more and more people are now glad that the technology that enables this type of tourism has advanced so much that it can now facilitate easy and comfortable access for many willing tourists.
Because lately, due to the current global pandemic, tourism has been mostly relegated to rescheduling holiday plans or postponing them, the phenomena of armchair tourism is currently growing at a rapid pace, enabling us to travel all over the world, virtually.
If tourism is not seen as a physical change of the hereabouts but rather as a change of ones’ psychological state of recreation, education, adventure, or other purposes associated with tourism, armchair-tourism can also be included (Mazanec, et al., 2002).
Armchair-tourism has three main parts: books, television and the internet. Until the emergence of the internet, books were the armchair-tourism media because they were the best information source for life there. Nevertheless, new media has slowly overtaken the time spent on reading. Armchair-tourism such as travel magazines or cultural documentations are more focused on consumers aged 40 and older. Nevertheless, the younger generation should not be neglected since new developments will enhance the experience of watching TV, increasingly attracting younger viewers (Papathanassis, 2011).
Many tourist boards are nowadays using more and more virtual content in order to attract customers and to encourage future visits. These can come in the form of digital events, which provide enriching cultural content and livestreaming video talks using live content from experts, partners and notable individuals. Tourist boards will also use dedicated web pages on which they will promote virtual experiences. Museums, safaris, or other interesting venues can therefore be experienced while enjoying the comfort of your own home.
There are destinations and travel brands which can keep the magic and inspiration of traveling alive even if it is virtually, from the armchair. Many travel brands and destinations are working on the premise that if the travel consumer can’t come to us, we will go to the travel consumer. There are digital platforms where a plethora of extraordinary destinations can be accessed and visited by virtual means. Over 2500 museums all over the world are providing virtual tours for those who are interested. During these tours, tourists can enjoy rooms, shows and events, in which they can participate virtually.
Also, the exponential evolution of technology has another benefit. Even if virtual reality is, at present, only capable of recreating, to a limited degree, the destination that is being visited, we now have another tool at our disposal: augmented reality. This changes the way in which a visitor can explore a destination in real time. Augmented reality is the technology that gives the visitor information that can be superimposed over the real time landscapes or streets, using a digital device. This technology is being used in order to animate history and to bring back life into exhibits found in the most important museums and venues of the world. Having all these means at our disposal, we can therefore travel anywhere, anytime and we are no longer dependent on the caprices of weather or the uncertainty found in difficult times, such as the one we are experiencing nowadays.
Shopping Tourism
As studies have shown, shopping is one of the most sought out activities no matter where tourists go (Timothy, 2003). This activity gained traction with the development of theme parks, of malls and designer shops. Visiting a theme park or going shopping in another country and even inside the borders of your own country has become, for many tourists, a purpose in itself. Bill Bryson, an American travel and humor book author said that in the past, people used to build civilizations, but now they build shopping malls. Another American author, Erma Bombeck, affirms that the chances of entering into a store to buy a loaf of bread and exiting with just a loaf of bread are three billion to one. These aspects emphasize the worldwide consensus that, in our society, humans are unable to function without constantly going shopping.
When trying to define this special tourism sector, only one facet can be defined clearly, namely that this kind of tourism includes the purchase of goods, the most typical being clothes, shoes, leather goods and luxury foodstuff (Friedrich, 2006).
The main advantage a tour operator could enjoy is the fact that shopping tourism has a positive economic impact on the destinations and limited negative environmental and socio-cultural effects. Meaning local life, natural environment and cultural sites are not going to be disturbed nor destroyed since many traditional malls, factory outlets, and markets do already exist. To be more precise, economically, this implies: more secure jobs, as the malls will have a continuous number of visitors; tax income will increase due to the value-added tax (VAT) of more sales; shopping tourism does not seem as seasonal as other tourism products; in addition, foreign tourists will increase the balance of payments (Papathanassis, 2011). Also, the environmental impact is almost non-existent, this not being the usual norm with tourism activities. This happens because, neither accidentally nor by design, wildlife killing or vegetation being destroyed by tourists do not occur. There is also a socio-cultural impact: a shopping mall is visited by locals as well as national or international tourists, and as such, it is seen as a positive attraction since access is not limited to neither of the two groups (Swarbrooke, 2002).
The Covid situation has temporarily shifted this type of tourism to a more domestic focused approach. People are now more inclined to go shopping in local tourism destinations. But shopping has become a life-dictating activity for many people, and even in the current difficult pandemic context, everybody goes shopping and we have become dependent on it.
Wellness Tourism
In our fast-paced society, we tend to often forget about ourselves. Because of this, health issues can arise due to stress, exhaustion and living a sedentary life. All these problems can be fixed by escaping into wellness centers. For more and more people, wellness is no longer a trend or a necessity, but has become a lifestyle.
The wellness industry has grown substantially in the last years, at a global level. The numbers are continually growing and the market value of the wellness industry has reached 580 billion Euros. Lots of hotels, airports and corporations have understood the importance of wellness, and thus provide some kind of wellness services to both guests and staff.
The wellness world is a global economy made out of multiple components: beauty and care, fitness, nutrition and alternative medicine. A popular perception regarding the importance of healthy diets, fitness and other health practices has been developed into whole new business sectors. As the healthy lifestyle movement gains more and more traction, auxiliary markets, ranging from food and beverage to hospitality, start offering more products that reflect the values of the health-conscious consumers. This is another example of the multiplier effect of tourism. Additionally, the Covid situation is the perfect incentive for healthier lifestyle choices. Thus, people are becoming more aware of the importance of overall health management and are more readily willing to pay for these kinds of services.
Wellness tourism is defined in the specialty literature as traveling associated with the practice of maintaining or improving personal states of being.
From 2015 until 2017, the wellness tourism market has grown annually by a margin of 6,5 %. Until 2022, GWI anticipates that this market value will reach 919 billion dollars – representing 18% of global tourism – with over a billion wellness-oriented travels all over the globe (GWI, 2018).
Today, wellness tourism is much more than just the destination or the activities – it is an extension of the traveler’s lifestyle and values. The wellness tourism sector is a large spectrum one, and offers are divided between many categories: fitness, healthy nutrition, therapeutic treatments (massages, beauty procedures). But every one of them is centered around enhancing the tourist state of being and state of mind.
Further opportunities are given to current trends, such as the alternative forms of medical therapies from Asia. However, these trends have to be recognized early enough and then must be implemented through serious, high-quality products. Beside the competitive criteria, such as price, or the kind and quality of services provided, the importance of the attractiveness of the surrounding area as a choice criterion should not be underestimated (Papathanassis, 2011).
Specialists estimate that, if the consumers’ appetite for wellness services maintains its rate of growth, the wellness global tourism industry will reach one trillion dollars in the shortest of time.
Conclusions
There is enormous potential with all of the emerging niche tourism products presented in this paper. All of them arguably represent what one may designate as a megatrend, either at present or in the near future. Additionally, each of the selected products has incredible versatility because they don’t target a particular “special” group of consumers, but instead, they appeal to a larger proportion of the population. In other words, the niches examined are not mutually exclusive in terms of their target market. The phenomena of tourism globalization by developing infrastructure and thus new destinations, and the technological advances in human transportation, with the usage of the mega-ship or the implementation of large-scale commercial space travel, will transform these megatrends into tourism behemoths, and will result in the creation of new specialized holiday niches that will generate huge profits and further expansion. The examples presented show a promising outlook for each of the niches examined, as the current global pandemic cannot but temporarily slow the inevitable growth of these tourism sectors.
There are three main aspects of the tourism industry that can be synthesized from this paper. Firstly, the tourism sector is in a constant, ever-growing direction, with more and more people willing to spend money in tourism activities. Secondly, the mainstream holiday package isn’t as stable as it used to be, and it can be said that the current crisis in the world is a major influencing factor. Thirdly, there are some tourism niches that have great appeal and show incredible potential for the near future.
However, there are three more tour operating aspects that have to be taken into consideration when making assertions: the capacity risk, the consumers’ perceived risk and the unknown reaction of the large tourism groups.
Higher profits can be generated when entering and developing niche markets. Because of this, there are many mainstream companies that have already entered into a number of niche markets. The technological advancement can thus be utilized by specialists in order to benefit, in a sustainable way, from each particular niche selected. Moreover, tourists are more pleased because the holiday experiences are tailored to their needs and wants, making the product more individualized and consumer-oriented. For the tourism industry as a whole, the growing of niche markets can be seen as a “holiday” from the usual negative practices regularly associated with mainstream tourism, such as environmental irresponsibility and questionable ethics. This means that when niche tourism fully matures and inevitably integrates itself into mass tourism, becoming mainstream, it will carry its benefits into the new tourism industry.
- T., G., 2010. Niche market study. Cape Town: s.n.
- Crouch, G. I., Devinney, T. M., Louviere, J. J. & Islam, T., 2008. Modelling consumer choice behaviour in space tourism. Tourism Management, 30(3), pp. 441-454.
- Davidson, R., 1993. Tourism. London: Longman.
- Devinney, T., Crouch, G. I. & Louviere, J., 2006. Going Where No Tourist Has Gone Before: The Future Demand for Space Tourism, s.l.: Future Choice Initiative.
- Friedrich, W., 2006. Shopping tourism impulses for growth of tourism and retail in Germany. s.l.:s.n.
- Futron, 2002. Space Tourism Market Study – Orbital Space Travel & Destinations with Suborbital Space Travel, Wisconsin: Futron Corporation.
- Goehlich, R. A., 2005. A ticket pricing strategy for an oligopolistic space tourism market. Space Policy, Volume 21, pp. 293-306.
- GWI, 2018. Global Wellness Economy, s.l.: Global Wellness Institute.
- Hutchinson, G., 1957. Concluding Remarks. Cold Spring Harbor Symposia on Quantitative Biology, Volume 22, pp. 415-427.
- Lew, A. A., 2008. Long tail tourism: New geographies for marketing niche tourism products. Journal of Travel and Tourism Marketing, 25(3-4), pp. 409-419.
- Mazanec, J., Crouch, G., Brent Ritchie, J. & Woodside, A., 2002. Consumer psychology of Tourism, Hospitality and Leisure. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, 14(2).
- Morrison, A. M., 2013. Marketing and managing tourism destinations. New York: Routledge.
- Novelli, M., 2005. Niche Tourism: Contemporary issues, trends and cases. Oxford: Butterworth-Heinemann.
- Paapathanassis, A., 2011. The long tail of tourism. 1st ed. s.l.:Gabler.
- Richards, G., 2005. Cultural tourism in Europe, Wallingford: CABI.
- Richards, G., 2007. Cultural Tourism: Global and local perspectives. In: Binghampton: The Haworth Press Inc..
- Richards, G., 2011. Rethinking niche tourism in the network society. ATLAS.
- Smith, V., 2001. Space tourism. Annals of Tourism Research, Volume 28, pp. 238-240.
- Sugathan, P. & Ranjan, K. R., 2019. Co-creating the tourism experience. Journal of Business Research, Issue 100, pp. 207-2017.
- Swarbrooke, J., 2002. The development and management of visitor attractions. Oxford: Elsevier Butterworth-Heinemann.
- Timothy, D., 2003. Shopping tourism, retailing, and leisure. s.l.:Channel view publications.
- Weaver, D., 2008. Ecotourism. Australia: Wiley&Sons.
- Ziffer, K., 1989. Ecotourism: The Uneasy Alliance. Washington D.C.: Conservation International.
Conferences
Latest articles, latest coip articles, +general information, publication ethics, indexing and abstracting, international editorial board, open access, lifetime article preservation.

Niche Tourism is now recognized across the entire industry with many companies looking to differentiate their brand from others. Niche tourism has many synergies with the experience economy because niche tourists are constantly searching for engaging and unique experiences which match their interests.
In recent years, mainstream holiday providers have identified niche tourism as a potential growth area. Subsequently, niche tourism is no longer confined to small independent companies. Many large conglomerates such as Expedia, TUI and Booking Holdings have globalized the niche tourism industry through mergers and acquisitions and brand extensions, globalizing the sector.
However, the globalization of niche tourism has arguably reduced its authenticity. Many large travel intermediaries now market to mass tourists. Cruise operators are a prime example of this, where they can often carry thousands of tourists on an all-inclusive basis, serving food and drink which meets the demands of the typical mass tourist. All the while, many are advertising 'authentic' experiences such as walking tours, wine tasting, cookery classes and festivals - all of which are considered types of niche tourism.
COVID-19 has altered traveler demands which has created an opportunity for tourism businesses to innovate and develop their product. Many people have been confined to homeworking, lockdowns, and social distancing intermittently for the past two years, creating a desire to enjoy wider, 'greener' spaces while engaging with others.
As a result, there is a significant opportunity for niche tourism companies involved in rural and adventure tourism to grow their product. Research from the the publisher Ads database suggests that operators targeting these types of tourists will receive strong support from DMO's (Destination Marketing Organizations) as many are actively targeting this market.
Key Highlights
- Niche tourism within the travel industry can no longer be considered 'small'. With a growing global middle class and better-educated population, particularly in developing and densely populated countries in the APAC region, more tourists seek more wholesome, immersive, and fulfilling touristic experiences. The experience economy also plays a large part, with many travel products now commoditized due to the online travel boom and the emergence of price comparison sites. The future of travel is providing a more fulfilling experience. With many core travel and tourism companies such as hotels and airlines aiming to create more brand loyalty, changes to the 'traditional' travel product are likely.
- In recent years, the maturing tourism market has shifted tourists away from the annual 'sun and beach' getaway to develop an experience more aligned with holidaymakers' specific hobbies, interests, curiosities and needs. As the publisher shift to a world with increasingly more leisure time, there is a greater desire to maximize each experience. Leisure tourism is now a broad term for traveler motivations as niche tourism is a critical element to consider as consumer attitudes shift towards more special interest travel. Although this consumer behavior ripples across all age groups in tourism, it has become particularly relevant among younger adults such as Millennials and GenZ.
- The tastes of Gen Z and Millennials are helping to drive some forms of niche tourism to the next level. Over the past three years (2018 to 2021), the publisher has surveyed adults regarding their typical holiday across several generations. The publisher has discovered that a higher proportion of younger adults typically book niche holiday types such as adventure, sport, gastronomy, and LGBTQ within these surveys.
- Ecotourism saw the most significant increase of respondents within the the publisher consumer surveys, growing by 5% between 2018 and 2021 (14% to 19%). Sustainable travel has become a significant issue within the travel industry, and there is a growth in the 'responsible tourist'. Key public figures in popular culture such as David Attenborough have highlighted the impacts of human consumption on global warming. At the same time, activists such as Greta Thunberg have become a significant global influence, particularly on younger generations who are increasingly concerned about their future on the planet.
- This thematic report provides an overview of niche tourisms role within the travel sector today and how it will continue its involvement.
- The key trends within this theme are split between enterprise trends and tourist trends that are recognizable today.
- Several case studies are included to analyze the multiple ways travel companies such as tour operators, travel agencies, DMO's and cruise lines have tried to capitalize on niche tourism.
- Our unique thematic analysis then looks at recommendations for travel and tourism organizations and a deep dive into the leaders and laggards within the niche tourism spectrum, complete with industry examples and analysis.
Key Topics Covered:
- Executive Summary
- Thematic Briefing
- Consumer trends
- Enterprise trends
- Industry trends
- Industry Analysis
- Holidays are becoming more varied
- Case studies
- Impacts of niche tourism
- Tourists are searching for more immersive experiences
- Overtourism
- Social impacts on local communities
- Recommendations
- Mergers and acquisitions
- Value Chain
- Third-party suppliers
- Direct suppliers
- Ancillary suppliers
- Public companies
- Private companies
Companies Mentioned
- Alux Caverna Lounge
- Booking Holdings
- British Airways
- Carnival Corporation
- Celebrity Cruises
- Chernobyl Tour
- Comcast Corp
- Despagar.com Group
- Expedia Group
- Friendly Planet Travel
- GAdventures
- Genting Malaysia
- Gourmet on Tour
- Hays Travel
- Hemingway's Lounge
- Intrepid Travel
- Kimpton Hotels
- Merlin Entertainments
- Las Vegas Sands
- MGM Resorts International
- Miral Asset Group
- Norwegian Cruise Lines
- Makemytrip.com
- On the Beach
- Rainforest Cafe
- Responsible Travel
- Seaworld Parks and Entertainment
- SIM Holdings
- Soviet Tours
- The Northern Lights Bar
- Virgin Atlantic
- United Airlines
- Universal Studios
- Walt Disney
- Wynn Resorts
- Young Pioneer Tours
For more information about this report visit https://www.researchandmarkets.com/r/mgjit2
ResearchAndMarkets.com Laura Wood, Senior Press Manager [email protected] For E.S.T Office Hours Call 1-917-300-0470 For U.S./CAN Toll Free Call 1-800-526-8630 For GMT Office Hours Call +353-1-416-8900


- History & Milestones
Connecting the seemingly unconnected

- India Portfolio
- International Portfolio
- Travel Commerce
- Airline Management
- Advanced Pilot Training
- Aircraft Maintenance Engineering
InterGlobe and Assago launch AIonOS - an AI business venture

- Culture & Heritage
- Environment
- Contribute & Support
InterGlobe Foundation

- Life at InterGlobe
- Opportunities
#MyConnectionWithInterGlobe: Employee Stories

- In the News
- Press Releases

- InterGlobe Foundation: Restoring heritage sites
- IndiGo awarded Asia’s Best Low-Cost airline by TripAdvisor’s 2019 Travellers' Choice Airline Awards
Niche Tourism: Unlocking New Travel Experiences
With the world moving forward, the landscape of the tourism industry has evolved only to make it more specialized and convenient for travellers.
Niche Tourism introduces how a specific tourism aspect can be tailored to meet the needs of a market segment, which is interested in something particular or distinct. The concept focuses on how experiences of tourists can be customized to meet the needs and be more personalized for the different types of audience in the market.
The idea can be perceived as a response to an increase in the number of more modern tourists demanding tailored tourism products. Under this setup, the destinations can direct their offerings to distinguish their tourism products and compete in an increasingly competitive and cluttered industry environment.
Different Segments of Niche Tourism:
Varying from Gastronomy to Leisure and Recreational, and Adventure to Heritage, it's nearly impossible for anyone to fit all the aspects of niche tourism in just one list.
The ever-evolving interest of the audience has resulted in a specialised corner of the tourism market, primarily developed around a tailor-made experience for the visitors.
Here are a few examples of some popular interests groups in Niche Tourism -
Heritage and Cultural Tourism: Essentially directed towards history and culture, this type of tourism is more traditional and occurs typically in urban areas with a distinct area of interest, such as museums and theatres. This aspect of tourism also brings in light the diverse traditions of native communities through witnessing their rituals, customs, and their values and way of living. Owing to its diversity, India is symbolized by the plurality of its heritage value. All the captivating monuments and heritage sites in the country depict their story while keeping the visitors fascinated.
Sustainable Tourism: Not similar to eco-tourism or green tourism, which focuses on protection and environmental implications, Sustainable tourism, on the other hand, is a way of doing things to protect and ensure the future of the local tourism industry. This niche of tourism is mainly directed towards striving to make as profound an influence as possible on the environment and local culture while helping to generate income and employment for the local market.
Adventure Tourism: Travelling that involves exploration, and some amount of risk potentially come under Adventure Tourism. Under this segment, the audience is expected to possess specialized skills and the willingness to be under physical duress while undergoing, if not rigorous, at least the minimum required training to experience this multifaceted dimension of tourism.
Art Tourism: This niche of tourism can be observed when people travel to a destination to engage in activities related to art such as museums, special events related to art, dance and book festivals, etc. For some, art tourism is a subdivision under Cultural Tourism, but because of its growing vastness, it has become a niche aspect of travelling.
Wellness and Spiritual Tourism: Some tourists tend to select their destination to relax and indulge in reflexology and special massages. People visit destinations like Hawaii or Costa Rica for various reasons, but these countries owing to their islands or unique retreat centres, are the most preferred one for an unwinding getaway. For Spiritual Tourism, the travellers are looking to explore temples, meditation and yoga at different destinations, or some for pilgrimage. India, owing to its rich legacy and being the birthplace of Hinduism and Buddhism and home to thousands of monasteries and ancient temples, tops the list of such destinations.
Film Tourism: As a recently emerged niche in the tourism industry, Film Tourism is a thriving marvel worldwide. People have indeed started showing their interest in destinations which became famous due to their appearance in cinemas and television series.
Culinary Tourism: One of the most interesting and latest niches emerging in the tourism industry is around the gastronomical delights that the travellers are looking for.
For a "Foodie" to plan its journey, the culinary offerings have a considerable influence on their itinerary.
Apart from all the popular segments of niche tourism, there are a host of other categories that visitors like to experience. The visitors are definitely not limited to just one of the different forms of tourism, and the most memorable itinerary likely includes a mixture of adventure, sightseeing, culture and more.
The Role of Niche Tourism in Destination Development
With the rise of Niche tourism in the market, the concept of positioning is not entirely limited to brands but destinations as well. The positioning of a destination therefore involves categorizing the place in essence to the kind of experience it offers to the visitors - it is all unique and distinct for all the destinations. The destination image contains components that are holistic and based on attributes that help tourists identify them under segregated niches to plan accordingly.
This not only makes it easier for the tourist to find the right kind of place for them but also the destination to create a unique image for itself that attracts all the relevant visitors.
What does Niche Tourism have in store for India?
Owing to the rich culture with diverse topography and geopolitical heritage, India attracts tourists from various niches. Without any doubt, one can also predict that these niches can soon become the businesses of tomorrow, and many of them will be crucial for the growth of India's tourism industry.
Travel & Tourism sector plays a crucial role in the Indian Economic Development, and it has already been discovered that niche is where the money is. Visitors do not limit themselves to just one of the different forms of tourism in India, clubbing them all together results in the most memorable itinerary that's likely to include everything ranging from adventure to sightseeing, and culture to wildlife.
Keeping in mind the prospect of becoming a tourist hub for various niches and driving higher returns, it is imperative that the tourism industry is able to continuously evolve. While the authorities are working towards not just identifying new segments but also creating a ground-level infrastructure, the industry should utilize the systems to attract the right audience and better manage the burgeoning tourism.
https://www.nibusinessinfo.co.uk/content/niche-tourism-opportunities https://www.napier.ac.uk/~/media/worktribe/output-209366/fullthesispdf.pdf https://geographycasestudysite.wordpress.com/niche-tourism/ https://www.tourismtattler.com/articles/niche-tourism/30-niche-tourism-groups/12645 http://www.travelbizmonitor.com/Trend-Watch/niche-tourism--opportunities-for-india-14794

Niche Tourism and Types Of Tourism
The niche tourism.

Niche tourism refers to the numerous specialty forms of tourism that have emerged over the years, each with its own adjective. Many of these terms have come into common use by the tourism industry and academics. Others are emerging concepts that may or may not gain popular usage. Examples of the more common niche tourism markets are:
- Agritourism
- Birth tourism
- Culinary tourism
- Cultural tourism
- Dark tourism
- Eco tourism
- Extreme tourism
- Heritage tourism
- LGBT tourism
- Medical tourism
- Film tourism
- Nautical tourism
- Pop-culture tourism
- Niche Tourism
- Sex tourism
- Slum tourism
- Sports tourism
- Textile tourism
- Vaccine Tourism
- Virtual tourism
- War tourism
- Wellness tourism
- Wildlife tourism
Other terms used for niche or specialty travel forms include the term "destination" in the descriptions, such as destination weddings, and terms such as location vacation.
Discover More About Tourism
Tourism is travel for pleasure or business; also the theory and practice of touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tours. The World Tourism Organization defines tourism more generally, in terms which go "beyond the common perception of tourism as being limited to holiday activity only", as people "traveling to and staying in places outside their usual environment for not more than one consecutive year for leisure and not less than 24 hours, business and other purposes". Tourism can be domestic (within the traveller's own country) or international, and international tourism has both incoming and outgoing implications on a country's balance of payments.
Tourism numbers in 2000s recession
Tourism numbers declined as a result of a strong economic slowdown (the late-2000s recession) between the second half of 2008 and the end of 2009, and in consequence of the outbreak of the 2009 H1N1 influenza virus, but slowly recovered until the COVID-19 pandemic put an abrupt end to the growth. The United Nations World Tourism Organization estimated that global international tourist arrivals might decrease by 58% to 78% in 2020, leading to a potential loss of US$0.9–1.2 trillion in international tourism receipts..
International Tourism Affected in 2020
Globally, international tourism receipts (the travel item in balance of payments) grew to US$1.03 trillion (€740 billion) in 2005, corresponding to an increase in real terms of 3.8% from 2010. International tourist arrivals surpassed the milestone of 1 billion tourists globally for the first time in 2012, emerging source markets such as China, Russia, and Brazil had significantly increased their spending over the previous decade.
Global tourism 2020
Global tourism accounts for c. 8% of global greenhouse-gas emissions, as well as other significant environmental and social impacts that are not always beneficial to local communities and their economies. For this reason, many tourist development organizations are beginning to focus on sustainable tourism in order to mitigate negative effects caused by the growing impact of tourism. The United Nations World Tourism Organization emphasized these practices by promoting tourism as part of the Sustainable Development Goals, through programs like the International Year for Sustainable Tourism for Development in 2017, and programs like Tourism for SDGs focusing on how SDG 8, SDG 12 and SDG 14 implicate tourism in creating a sustainable economy.
- Airport Taxi
- Visa and eVisa
- Top Tourist Destinations
- Travel Restrictions
- Cars Rental
Reach us Support Netafri.com

Get in touch on


Special Interest Tourism: Find Your Niche

Special interest tourism (SIT) is on the rise, and for good reason. It provides travelers the chance to explore their passions and gives you the opportunity to curate a once-in-a-lifetime experience. Special interest tourism focuses on providing leisure and adventure activities that cater to the needs of a specific audience. Tapping into your special interest niche will connect you to a smaller, yet highly-devoted audience. Think quality over quantity.

In a sector that celebrates individuality and personalization, there is something for everyone. Special interest tourism examples range from spiritual, adventure, and food tourism to military, nostalgia, and lighthouse tourism. These are just a few examples from the long list of special interest tourism options – you just have to find the niche that works for you and your audience!
What does SIT look like in 2022? The COVID-19 pandemic has brought a shift in consciousness that has changed the way that travelers want to explore their destinations. In the summer of 2020, Booking.com conducted a global survey with 60 percent of respondents saying they would use an app or website that recommended itineraries where tours would have a positive impact on locals. Special interest tourism concepts and cases have shifted as travelers are increasingly concerned about the impact of their travels on the climate and local community.
Top Types of Special Interest Tourism
Environmental tourism:.
As sustainability remains a chief driver in SIT, environmental tourism has emerged as a dominant niche. Often referred to as ecotourism, sustainable tourism and responsible tourism, environmental tourism focuses on activities that don’t compromise the needs of future generations. Environmental tourism is at the forefront of special interest tourism trends and will continue to grow in demand.
In its 2025 Megatrends prediction report, Skift reveals how this is already influencing travel decisions. In a global survey, 51 percent of respondents claimed they would change their chosen travel destination and head instead to a less-popular one if that decision would have less of an adverse environmental impact.
Some online travel agencies and tour operators now offer guests the option of dedicating a day or two of their trip to activities like helping to construct a local water purification system or planting trees along shorelines devastated by hurricanes.
Adventure Tourism:

According to Future Market Insights , adventure tourism is resilient and supports local economies by attracting high-value customers. With an increasing number of Millennial and Gen-Z travelers who prefer adventure sports, adventure tourism is creating a lucrative scope for expansion in the activities segment. Adventure tourism activities vary in risk and difficulty and can include hiking, backpacking, climbing, mountain biking and snowshoeing.
Wellness Tourism:

Wellness tourism is a growing industry, supported by travelers actively seeking ways to enhance their well-being. Dating back to the ancient baths in Rome, traveling for the purpose of improving our well-being has always been a priority, and now there are seemingly endless ways to provide customers with a wellness-centered experience. Whether it’s nutrient-rich food, a trip to a natural hot spring, or meditation and yoga, wellness tourism is an attractive niche for travelers because the desire for self-improvement is part of being human.
Finding your special interest niche
What is unique about your tours that makes you stand out? What values do you share with your customers? These are things to consider when choosing your niche. For example, female-run Travel Insights offers “Wander Women” tours. These all-female trips are centered around local women’s businesses and achievements, focusing on those who work within their communities to sustain their culture, heritage and the planet’s future. This is brilliant for a number of reasons: it ties into the growing desire for sustainable tourism, while allowing female travelers to develop lasting relationships with other like-minded women. If the pandemic has taught us anything, it’s that we all need connection in our lives.

You know your audience better than anyone, so why not consider personalizing your tour packages? According to Think With Google , nearly 57% of travelers are in favor of personalizing their buying experiences based on their personal preferences. It might be wise to think of ways that you can offer flexible packages and tailor them to suit the traveler’s needs. There is a rising demand for personalization, and it will aid in the expansion of the market in the coming years.
We see this happening in Kenya, which is home to over 3000 tour operators offering safari excursions. This has led many operators to begin incorporating unique features to meet their customer’s needs. On top of seeing wildlife, a customer might be passionate about food, so they might consider pairing their tour with culinary lunches and dinners. Or perhaps they value wellness, so an operator might pair their tour with yoga classes. The possibilities are endless!

Another great way to find your niche is to focus on your local area. Consider the heritage sites , national parks, or landmarks in your region that make it special. Are there any sites in your area that have been formally recognized? A popular destination in adventure tourism is the hike across the Grand Canyon rim-to-rim trail, which was made even more popular in 2019 when it was declared an International Dark Sky Park by the International Dark-Sky Association.
Awards like this are worth noting because they increase tourist popularity and attract people based on the title alone. Chances are you’re already aware of how amazing your area is, and it’s already accessible to you, so think of the ways that you like to enjoy it, and build your niche around makes you passionate about where you live.
Reaching the right audience
With special interest tourism, you’re not providing an experience for the masses and your marketing should reflect that. You want your messaging to reach those who will appreciate what you have to offer and get excited to book with you. In order to target your audience, you need to know who they are. Consider factors like their budget, age, gender, values and interests. The great thing about having a niche is that it allows you to become an expert in that area, and with expertise comes credibility.
Once you have chosen your niche, you can focus your research to pinpoint exactly what your audience is looking for and market to them accordingly. If you are a smaller business, consider moving to an online booking system rather than booking over the phone or in person. Online analytics can give you the data you need to make a big impact even with a small marketing budget.

Social media is also a great way for small businesses to market to their audience. Not only is it relatively inexpensive, but content is also targeted towards users based on their tastes and preferences. There are a number of ways to promote your tour on social media . With the right strategy and audience information, you’ll attract business organically.
Making special interest tourism work for you
The beauty of special interest tourism is that you can focus all your attention on one thing and really excel in a specific area. Lasting relationships are formed with your customers because you understand their needs and interests. You’ll gain credibility by having a clear mission and executing it well. The importance of special interest tourism is that it gives travelers the chance to bond with like-minded people and form genuine connections, and in a disconnected world, that is invaluable.

Written By | Caitlyn McGee
Caitlyn is Vancouver-based freelance writer covering the tourism industry. With a Communication Studies degree, she specializes in digital and content marketing.
Previous Article Your Marketing Mix: the 7 Ps of Travel and Tourism Marketing
Next Article Thoughtful pricing strategies for tour operators
Related Posts

Articles , Increase Online Bookings , Tourism Trends
Set-jetting, forest bathing, and hush trips: 20 innovative tourism business ideas and trends for 2023.

Articles , Increase Online Bookings , Tourism Best Practices
Advantages and disadvantages of online travel agencies (otas).

Articles , Increase Online Bookings , Marketing Strategies
Your marketing mix: the 7 ps of travel and tourism marketing, search the blog.
- All Categories
- Marketing Strategies
- Tourism Trends
Most Popular Articles
- Set-jetting, Forest Bathing, and Hush Trips: 20 Innovative Tourism Business Ideas and Trends for 2023 142 views
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Online Travel Agencies (OTAs) 42 views
- Your Marketing Mix: the 7 Ps of Travel and Tourism Marketing 29 views
- How to Create a Business Plan for Your Tour or Travel Company 12 views
- How to Create and Promote Amazing Tour Packages 10 views
I have read and agree to the Rezgo Privacy Policy
GET STARTED
Sign-up for a free demo.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmo tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua.
Schedule A Demo

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In the context of tourism, niche is referring to products, services or interests that are shared by a small group of people. Niche tourism is the umbrella term covering a range of types of tourism. Niche tourism products and services serve a specialised segment of the tourism industry. Niche tourism is the antithesis of mass tourism.
Types of niche tourism like ecotourism, which focuses on environmental conservation and responsible travel, have seen a surge in popularity as a result. Changes in demographics and lifestyle are also playing a role. As populations in many parts of the world age, and as people become more health-conscious, sectors like wellness and medical ...
Tourism Tattler October 21, 2019. 48,429 6 minutes read. If you thought that Niche Tourism covers just a handful of interest groups, think again. In the 5th edition of his book ' Marketing Tourism in South Africa ', Richard George identified 20 distinct Special Interest or 'Niche' tourism groups, and we've added 11 more to this ...
Sustainable and eco-tourism is a rapidly growing niche in the travel industry, focusing on responsible travel practices. This niche promotes travelling in a way that respects local culture and environment, minimises impact on nature, and contributes to conserving natural and cultural heritage. Eco-tourism often involves visiting pristine ...
Special interest tourism (also known as specialist tourism or SIT), is a branch of niche tourism and alternative tourism. Essentially, special interest tourism is tourism which is tailored to a specific interest. There are many tour operators who focus their business on special interest tourism (and this number is growing).
The report found that niche tourism - travel that focuses on fulfilling the specific and personalized needs of a traveler, whether that be a yoga or wellness retreat, an active adventure tour structured around remote working or a vacation centered around a destination's gastronomy - was growing most rapidly among the younger generations, Gen Z ...
The Rise of Niche Tourism. By SnC. April 16, 2022. Niche tourism is a new work I recently came across. When looking more into it, it was difficult pinning down a specific definition. I later read that Niche Tourism is actually a collective term used to group a number of types of tourism - which explained why there's no one definition.
Niche Tourism An Introduction. Mike Robinson and Marina Novelli. The concept of niche tourism has emerged in recent years in counter-point to what is commonly referred to as mass tourism . It implies a more sophisticated set of practices that distinguish and differentiate tourists. In a globalising world of increasing sameness, niche tourism ...
and significance of niche tourism evolved quickly. Numerous studies emerged in a relatively short period of time, with Novelli (2005) providing evidence of its validity as an alternative to mainstream forms of mass tourism. Niche tourism has since become widely adopted in tourism studies, with growing industry application.
This Handbook provides a critical analysis of the evolution of the contemporary niche tourism phenomenon. By framing discussions around sustainable development thinking, concepts and practical applications, each chapter provides specific reflections on niche tourism trends, successes and/or failures, and the challenges and opportunities that destinations that pursue tourism as a vehicle for ...
In this post, I will list the major types of travels that I consider to be broad enough to deserve a mention as a travel niche. These tourism niches have big enough market demand to sustain as an independent category on their own. ... Adventure Travel - Adventure tourism is the fastest growing and biggest travel niche today; Nature and ...
Niche tourism is the future. In recent years we have seen many different types of niche tourism emerge, from golf tourism to dark tourism to rural tourism, a...
In order to better analyze the impact that certain types of niche tourism have over mass tourism, the classification made by Alex Papathanassis in his book, The Long Tail of Tourism, will be utilized (Paapathanassis, 2011). Tourism niches are built on persisting social trends such as: Sustainability (e.g. Eco-, Inclusive-, Agro-tourism)
Niche Tourism, also known as Special Interest Tourism, refers to specialized tourism. products offered to a small group of tourists. Regarded as the antidote to mass tourism, niche. tourism has ...
All the while, many are advertising 'authentic' experiences such as walking tours, wine tasting, cookery classes and festivals - all of which are considered types of niche tourism.
Niche Tourism examines one of the fastest growing areas within the tourism sector. This book provides an integrated picture of speciality/niche tourism as a whole looking at both the 'macro' and 'micro' niche area. It has a comprehensive theoretical framework, and discusses initiatives, policies and strategies adopted internationally. With an emphasis on linking theory to practice, it is ...
Niche Tourism introduces how a specific tourism aspect can be tailored to meet the needs of a market segment, which is interested in something particular or distinct. The concept focuses on how experiences of tourists can be customized to meet the needs and be more personalized for the different types of audience in the market. The idea can be ...
The Niche Tourism. Niche tourism refers to the numerous specialty forms of tourism that have emerged over the years, each with its own adjective. Many of these terms have come into common use by the tourism industry and academics. Others are emerging concepts that may or may not gain popular usage. Examples of the more common niche tourism ...
Based on the fulfilment of special interests, niche tourism is an important tool for destinations seeking to create, diversify or extend the market appeal of particular places. The continuum of niche forms of tourism is increasingly broad, ranging from the near mainstream (such as gastronomy, film, and television-induced and wellbeing tourism ...
Niche tourism is defined as speciality form of tourism. Niche tourism products have come a long way. Earlier they were considered to be expensive and were only meant for elite section of society.
Top Types of Special Interest Tourism Environmental Tourism: As sustainability remains a chief driver in SIT, environmental tourism has emerged as a dominant niche. Often referred to as ecotourism, sustainable tourism and responsible tourism, environmental tourism focuses on activities that don't compromise the needs of future generations. ...
Foreword (Robinson) Niche Tourism: An Introduction (Robinson & Novelli) Part one - Special Interest Tourism Photographic tourism (Palmer & Lester) Geotourism (Hose) Youth tourism (Richards & Wilson) Dark tourism (Tarlow) Genealogy tourism (Birtwistle) Gastronomic tourism (Hall & Mitchell) Transport tourism (Hall) Part two - Tradition and Culture Based Tourism Tribal tourism (Burns & Figurova ...
This tourism niche is a prominent emerging type of tourism and is expected to contribute to the digital transformation of the tourism industry in the near future. ...