- Story Writing Guides

12 Hero’s Journey Stages Explained (+ Free Templates)
From zero to hero, the hero’s journey is a popular character development arc used in many stories. In today’s post, we will explain the 12 hero’s journey stages, along with the simple example of Cinderella.
The Hero’s Journey was originally formulated by American writer Joseph Campbell to describe the typical character arc of many classic stories, particularly in the context of mythology and folklore. The original hero’s journey contained 17 steps. Although the hero’s journey has been adapted since then for use in modern fiction, the concept is not limited to literature. It can be applied to any story, video game, film or even music that features an archetypal hero who undergoes a transformation. Common examples of the hero’s journey in popular works include Star Wars, Lord of the Rings, The Hunger Games and Harry Potter and the Philosopher’s Stone.
- What is the hero's journey?
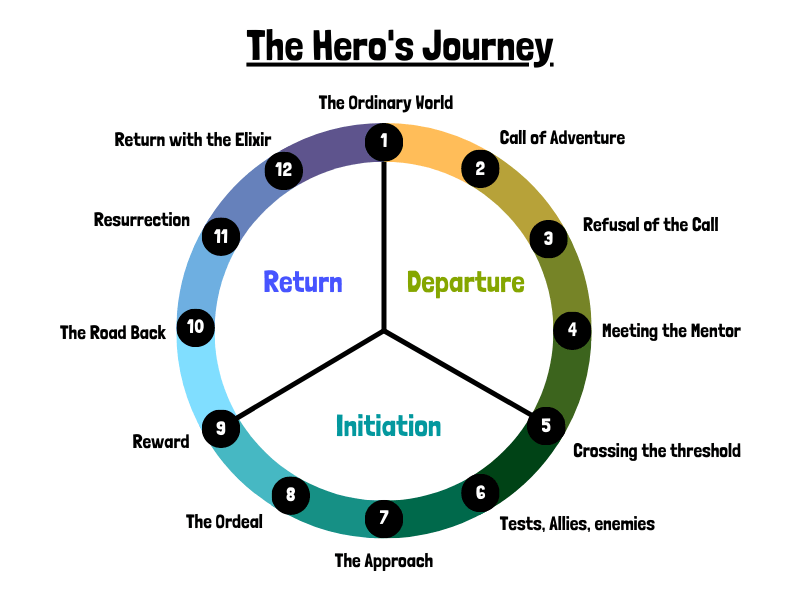
Stage 1: The Ordinary World
Stage 2: call of adventure, stage 3: refusal of the call, stage 4: meeting the mentor, stage 5: crossing the threshold, stage 6: tests, allies, enemies, stage 7: the approach, stage 8: the ordeal, stage 9: reward, stage 10: the road back, stage 11: resurrection, stage 12: return with the elixir, cinderella example, campbell’s 17-step journey, leeming’s 8-step journey, cousineau’s 8-step journey.
- Free Hero's Journey Templates
What is the hero’s journey?
The hero’s journey, also known as the monomyth, is a character arc used in many stories. The idea behind it is that heroes undergo a journey that leads them to find their true selves. This is often represented in a series of stages. There are typically 12 stages to the hero’s journey. Each stage represents a change in the hero’s mindset or attitude, which is triggered by an external or internal event. These events cause the hero to overcome a challenge, reach a threshold, and then return to a normal life.
The hero’s journey is a powerful tool for understanding your characters. It can help you decide who they are, what they want, where they came from, and how they will change over time. It can be used to
- Understand the challenges your characters will face
- Understand how your characters react to those challenges
- Help develop your characters’ traits and relationships
In this post, we will explain each stage of the hero’s journey, using the example of Cinderella.
You might also be interested in our post on the story mountain or this guide on how to outline a book .
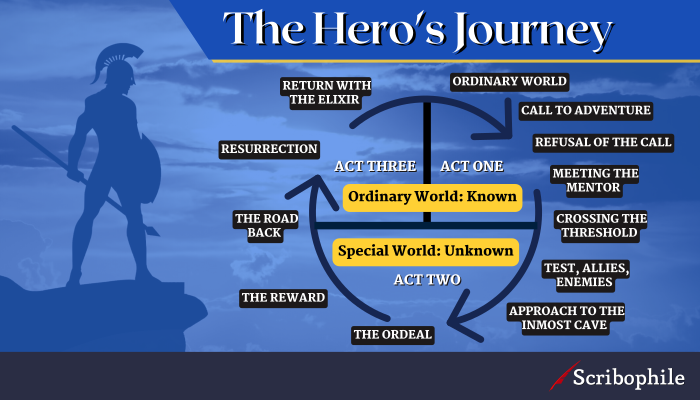
12 Hero’s Journey Stages
The archetypal hero’s journey contains 12 stages and was created by Christopher Vogler. These steps take your main character through an epic struggle that leads to their ultimate triumph or demise. While these steps may seem formulaic at first glance, they actually form a very flexible structure. The hero’s journey is about transformation, not perfection.
Your hero starts out in the ordinary world. He or she is just like every other person in their environment, doing things that are normal for them and experiencing the same struggles and challenges as everyone else. In the ordinary world, the hero feels stuck and confused, so he or she goes on a quest to find a way out of this predicament.
Example: Cinderella’s father passes away and she is now stuck doing chores and taking abuse from her stepsisters and stepmother.
The hero gets his or her first taste of adventure when the call comes. This could be in the form of an encounter with a stranger or someone they know who encourages them to take a leap of faith. This encounter is typically an accident, a series of coincidences that put the hero in the right place at the right time.
Example: An invite arrives inviting the family to a royal ball where the Prince will choose a wife.
Some people will refuse to leave their safe surroundings and live by their own rules. The hero has to overcome the negative influences in order to hear the call again. They also have to deal with any personal doubts that arise from thinking too much about the potential dangers involved in the quest. It is common for the hero to deny their own abilities in this stage and to lack confidence in themselves.
Example: Cinderella accepts the call by making her own dress for the ball. However, her stepmother refuses the call for her by not letting her go to the ball. And her step-sisters ruin her dress, so she can not go.
After hearing the call, the hero begins a relationship with a mentor who helps them learn about themselves and the world. In some cases, the mentor may be someone the hero already knows. The mentor is usually someone who is well-versed in the knowledge that the hero needs to acquire, but who does not judge the hero for their lack of experience.
Example: Cinderella meets her fairy godmother who equips her with everything she needs for the ball, including a dress and a carriage.
The hero leaves their old life behind and enters the unfamiliar new world. The crossing of the threshold symbolises leaving their old self behind and becoming a new person. Sometimes this can include learning a new skill or changing their physical appearance. It can also include a time of wandering, which is an essential part of the hero’s journey.
Example: Cinderella hops into the carriage and heads off to the ball. She has transformed from a servant into an elegant young lady.
As the hero goes on this journey, they will meet both allies (people who help the hero) and enemies (people who try to stop the hero). There will also be tests, where the hero is tempted to quit, turn back, or become discouraged. The hero must be persistent and resilient to overcome challenges.
Example: At the ball, Cinderella meets the prince, and even see’s her stepmother and stepsister. She dances with Prince all night long making her step-sisters extremely jealous.
The hero now reaches the destination of their journey, in some cases, this is a literal location, such as a cave or castle. It could also be metaphorical, such as the hero having an internal conflict or having to make a difficult decision. In either case, the hero has to confront their deepest fears in this stage with bravery. In some ways, this stage can mark the end of the hero’s journey because the hero must now face their darkest fears and bring them under control. If they do not do this, the hero could be defeated in the final battle and will fail the story.
Example: Cinderella is having a great time at the ball and nearly forgets about the midnight rule. As she runs away in a hurry, her glass slipper falls off outside the palace.
The hero has made it to the final challenge of their journey and now must face all odds and defeat their greatest adversary. Consider this the climax of the story. This could be in the form of a physical battle, a moral dilemma or even an emotional challenge. The hero will look to their allies or mentor for further support and guidance in this ordeal. Whatever happens in this stage could change the rest of the story, either for good or bad.
Example: Prince Charming looks all over the kingdom for the mysterious girl he met at the ball. He finally visits Cinderella’s house and tries the slippers on the step-sisters. The prince is about to leave and then he sees Cinderella in the corner cleaning.
When the hero has defeated the most powerful and dangerous of adversaries, they will receive their reward. This reward could be an object, a new relationship or even a new piece of knowledge. The reward, which typically comes as a result of the hero’s perseverance and hard work, signifies the end of their journey. Given that the hero has accomplished their goal and served their purpose, it is a time of great success and accomplishment.
Example: The prince tries the glass slipper on Cinderella. The glass slipper fits Cinderella perfectly, and they fall in love.
The journey is now complete, and the hero is now heading back home. As the hero considers their journey and reflects on the lessons they learned along the way, the road back is sometimes marked by a sense of nostalgia or even regret. As they must find their way back to the normal world and reintegrate into their former life, the hero may encounter additional difficulties or tests along the way. It is common for the hero to run into previous adversaries or challenges they believed they had overcome.
Example: Cinderella and Prince Charming head back to the Prince’s castle to get married.
The hero has one final battle to face. At this stage, the hero might have to fight to the death against a much more powerful foe. The hero might even be confronted with their own mortality or their greatest fear. This is usually when the hero’s true personality emerges. This stage is normally symbolised by the hero rising from the dark place and fighting back. This dark place could again be a physical location, such as the underground or a dark cave. It might even be a dark, mental state, such as depression. As the hero rises again, they might change physically or even experience an emotional transformation.
Example: Cinderella is reborn as a princess. She once again feels the love and happiness that she felt when she was a little girl living with her father.
At the end of the story, the hero returns to the ordinary world and shares the knowledge gained in their journey with their fellow man. This can be done by imparting some form of wisdom, an object of great value or by bringing about a social revolution. In all cases, the hero returns changed and often wiser.
Example: Cinderella and Prince Charming live happily ever after. She uses her new role to punish her stepmother and stepsisters and to revitalise the kingdom.
We have used the example of Cinderella in Vogler’s hero’s journey model below:

Below we have briefly explained the other variations of the hero’s journey arc.
The very first hero’s journey arc was created by Joseph Campbell in 1949. It contained the following 17 steps:
- The Call to Adventure: The hero receives a call or a reason to go on a journey.
- Refusal of the Call: The hero does not accept the quest. They worry about their own abilities or fear the journey itself.
- Supernatural Aid: Someone (the mentor) comes to help the hero and they have supernatural powers, which are usually magical.
- The Crossing of the First Threshold: A symbolic boundary is crossed by the hero, often after a test.
- Belly of the Whale: The point where the hero has the most difficulty making it through.
- The Road of Trials: In this step, the hero will be tempted and tested by the outside world, with a number of negative experiences.
- The Meeting with the Goddess: The hero meets someone who can give them the knowledge, power or even items for the journey ahead.
- Woman as the Temptress: The hero is tempted to go back home or return to their old ways.
- Atonement with the Father: The hero has to make amends for any wrongdoings they may have done in the past. They need to confront whatever holds them back.
- Apotheosis: The hero gains some powerful knowledge or grows to a higher level.
- The Ultimate Boon: The ultimate boon is the reward for completing all the trials of the quest. The hero achieves their ultimate goal and feels powerful.
- Refusal of the Return: After collecting their reward, the hero refuses to return to normal life. They want to continue living like gods.
- The Magic Flight: The hero escapes with the reward in hand.
- Rescue from Without: The hero has been hurt and needs help from their allies or guides.
- The Crossing of the Return Threshold: The hero must come back and learn to integrate with the ordinary world once again.
- Master of the Two Worlds: The hero shares their wisdom or gifts with the ordinary world. Learning to live in both worlds.
- Freedom to Live: The hero accepts the new version of themselves and lives happily without fear.
David Adams Leeming later adapted the hero’s journey based on his research of legendary heroes found in mythology. He noted the following steps as a pattern that all heroes in stories follow:
- Miraculous conception and birth: This is the first trauma that the hero has to deal with. The Hero is often an orphan or abandoned child and therefore faces many hardships early on in life.
- Initiation of the hero-child: The child faces their first major challenge. At this point, the challenge is normally won with assistance from someone else.
- Withdrawal from family or community: The hero runs away and is tempted by negative forces.
- Trial and quest: A quest finds the hero giving them an opportunity to prove themselves.
- Death: The hero fails and is left near death or actually does die.
- Descent into the underworld: The hero rises again from death or their near-death experience.
- Resurrection and rebirth: The hero learns from the errors of their way and is reborn into a better, wiser being.
- Ascension, apotheosis, and atonement: The hero gains some powerful knowledge or grows to a higher level (sometimes a god-like level).
In 1990, Phil Cousineau further adapted the hero’s journey by simplifying the steps from Campbell’s model and rearranging them slightly to suit his own findings of heroes in literature. Again Cousineau’s hero’s journey included 8 steps:
- The call to adventure: The hero must have a reason to go on an adventure.
- The road of trials: The hero undergoes a number of tests that help them to transform.
- The vision quest: Through the quest, the hero learns the errors of their ways and has a realisation of something.
- The meeting with the goddess: To help the hero someone helps them by giving them some knowledge, power or even items for the journey ahead.
- The boon: This is the reward for completing the journey.
- The magic flight: The hero must escape, as the reward is attached to something terrible.
- The return threshold: The hero must learn to live back in the ordinary world.
- The master of two worlds: The hero shares their knowledge with the ordinary world and learns to live in both worlds.
As you can see, every version of the hero’s journey is about the main character showing great levels of transformation. Their journey may start and end at the same location, but they have personally evolved as a character in your story. Once a weakling, they now possess the knowledge and skill set to protect their world if needed.
Free Hero’s Journey Templates
Use the free Hero’s journey templates below to practice the skills you learned in this guide! You can either draw or write notes in each of the scene boxes. Once the template is complete, you will have a better idea of how your main character or the hero of your story develops over time:
The storyboard template below is a great way to develop your main character and organise your story:

Did you find this guide on the hero’s journey stages useful? Let us know in the comments below.

Marty the wizard is the master of Imagine Forest. When he's not reading a ton of books or writing some of his own tales, he loves to be surrounded by the magical creatures that live in Imagine Forest. While living in his tree house he has devoted his time to helping children around the world with their writing skills and creativity.
Related Posts

Comments loading...
- Features for Creative Writers
- Features for Work
- Features for Higher Education
- Features for Teachers
- Features for Non-Native Speakers
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide
Hero's Journey 101: How to Use the Hero's Journey to Plot Your Story

Dan Schriever

How many times have you heard this story? A protagonist is suddenly whisked away from their ordinary life and embarks on a grand adventure. Along the way they make new friends, confront perils, and face tests of character. In the end, evil is defeated, and the hero returns home a changed person.
That’s the Hero’s Journey in a nutshell. It probably sounds very familiar—and rightly so: the Hero’s Journey aspires to be the universal story, or monomyth, a narrative pattern deeply ingrained in literature and culture. Whether in books, movies, television, or folklore, chances are you’ve encountered many examples of the Hero’s Journey in the wild.
In this post, we’ll walk through the elements of the Hero’s Journey step by step. We’ll also study an archetypal example from the movie The Matrix (1999). Once you have mastered the beats of this narrative template, you’ll be ready to put your very own spin on it.
Sound good? Then let’s cross the threshold and let the journey begin.
What Is the Hero’s Journey?
The 12 stages of the hero’s journey, writing your own hero’s journey.
The Hero’s Journey is a common story structure for modeling both plot points and character development. A protagonist embarks on an adventure into the unknown. They learn lessons, overcome adversity, defeat evil, and return home transformed.

Joseph Campbell , a scholar of literature, popularized the monomyth in his influential work The Hero With a Thousand Faces (1949). Looking for common patterns in mythological narratives, Campbell described a character arc with 17 total stages, overlaid on a more traditional three-act structure. Not all need be present in every myth or in the same order.
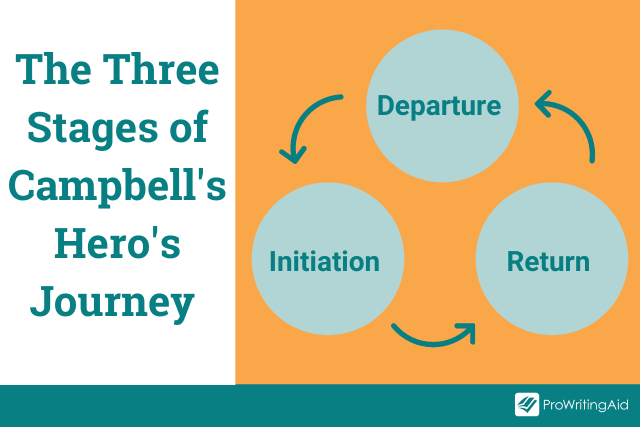
The three stages, or acts, of Campbell’s Hero’s Journey are as follows:
1. Departure. The hero leaves the ordinary world behind.
2. Initiation. The hero ventures into the unknown ("the Special World") and overcomes various obstacles and challenges.
3. Return. The hero returns in triumph to the familiar world.
Hollywood has embraced Campbell’s structure, most famously in George Lucas’s Star Wars movies. There are countless examples in books, music, and video games, from fantasy epics and Disney films to sports movies.
In The Writer’s Journey: Mythic Structure for Writers (1992), screenwriter Christopher Vogler adapted Campbell’s three phases into the "12 Stages of the Hero’s Journey." This is the version we’ll analyze in the next section.
For writers, the purpose of the Hero’s Journey is to act as a template and guide. It’s not a rigid formula that your plot must follow beat by beat. Indeed, there are good reasons to deviate—not least of which is that this structure has become so ubiquitous.
Still, it’s helpful to master the rules before deciding when and how to break them. The 12 steps of the Hero's Journey are as follows :
- The Ordinary World
- The Call of Adventure
- Refusal of the Call
- Meeting the Mentor
- Crossing the First Threshold
- Tests, Allies, and Enemies
- Approach to the Inmost Cave
- Reward (Seizing the Sword)
- The Road Back
- Resurrection
- Return with the Elixir
Let’s take a look at each stage in more detail. To show you how the Hero’s Journey works in practice, we’ll also consider an example from the movie The Matrix (1999). After all, what blog has not been improved by a little Keanu Reeves?

#1: The Ordinary World
This is where we meet our hero, although the journey has not yet begun: first, we need to establish the status quo by showing the hero living their ordinary, mundane life.
It’s important to lay the groundwork in this opening stage, before the journey begins. It lets readers identify with the hero as just a regular person, “normal” like the rest of us. Yes, there may be a big problem somewhere out there, but the hero at this stage has very limited awareness of it.
The Ordinary World in The Matrix :
We are introduced to Thomas A. Anderson, aka Neo, programmer by day, hacker by night. While Neo runs a side operation selling illicit software, Thomas Anderson lives the most mundane life imaginable: he works at his cubicle, pays his taxes, and helps the landlady carry out her garbage.
#2: The Call to Adventure
The journey proper begins with a call to adventure—something that disrupts the hero’s ordinary life and confronts them with a problem or challenge they can’t ignore. This can take many different forms.
While readers may already understand the stakes, the hero is realizing them for the first time. They must make a choice: will they shrink from the call, or rise to the challenge?
The Call to Adventure in The Matrix :
A mysterious message arrives in Neo’s computer, warning him that things are not as they seem. He is urged to “follow the white rabbit.” At a nightclub, he meets Trinity, who tells him to seek Morpheus.
#3: Refusal of the Call
Oops! The hero chooses option A and attempts to refuse the call to adventure. This could be for any number of reasons: fear, disbelief, a sense of inadequacy, or plain unwillingness to make the sacrifices that are required.
A little reluctance here is understandable. If you were asked to trade the comforts of home for a life-and-death journey fraught with peril, wouldn’t you give pause?
Refusal of the Call in The Matrix :
Agents arrive at Neo’s office to arrest him. Morpheus urges Neo to escape by climbing out a skyscraper window. “I can’t do this… This is crazy!” Neo protests as he backs off the ledge.

#4: Meeting the Mentor
Okay, so the hero got cold feet. Nothing a little pep talk can’t fix! The mentor figure appears at this point to give the hero some much needed counsel, coaching, and perhaps a kick out the door.
After all, the hero is very inexperienced at this point. They’re going to need help to avoid disaster or, worse, death. The mentor’s role is to overcome the hero’s reluctance and prepare them for what lies ahead.
Meeting the Mentor in The Matrix :
Neo meets with Morpheus, who reveals a terrifying truth: that the ordinary world as we know it is a computer simulation designed to enslave humanity to machines.
#5: Crossing the First Threshold
At this juncture, the hero is ready to leave their ordinary world for the first time. With the mentor’s help, they are committed to the journey and ready to step across the threshold into the special world . This marks the end of the departure act and the beginning of the adventure in earnest.
This may seem inevitable, but for the hero it represents an important choice. Once the threshold is crossed, there’s no going back. Bilbo Baggins put it nicely: “It’s a dangerous business, Frodo, going out your door. You step onto the road, and if you don't keep your feet, there's no knowing where you might be swept off to.”
Crossing the First Threshold in The Matrix :
Neo is offered a stark choice: take the blue pill and return to his ordinary life none the wiser, or take the red pill and “see how deep the rabbit hole goes.” Neo takes the red pill and is extracted from the Matrix, entering the real world .
#6: Tests, Allies, and Enemies
Now we are getting into the meat of the adventure. The hero steps into the special world and must learn the new rules of an unfamiliar setting while navigating trials, tribulations, and tests of will. New characters are often introduced here, and the hero must navigate their relationships with them. Will they be friend, foe, or something in between?
Broadly speaking, this is a time of experimentation and growth. It is also one of the longest stages of the journey, as the hero learns the lay of the land and defines their relationship to other characters.
Wondering how to create captivating characters? Read our guide , which explains how to shape characters that readers will love—or hate.
Tests, Allies, and Enemies in The Matrix :
Neo is introduced to the vagabond crew of the Nebuchadnezzar . Morpheus informs Neo that he is The One , a savior destined to liberate humanity. He learns jiu jitsu and other useful skills.
#7: Approach to the Inmost Cave

Time to get a little metaphorical. The inmost cave isn’t a physical cave, but rather a place of great danger—indeed, the most dangerous place in the special world . It could be a villain’s lair, an impending battle, or even a mental barrier. No spelunking required.
Broadly speaking, the approach is marked by a setback in the quest. It becomes a lesson in persistence, where the hero must reckon with failure, change their mindset, or try new ideas.
Note that the hero hasn’t entered the cave just yet. This stage is about the approach itself, which the hero must navigate to get closer to their ultimate goal. The stakes are rising, and failure is no longer an option.
Approach to the Inmost Cave in The Matrix :
Neo pays a visit to The Oracle. She challenges Neo to “know thyself”—does he believe, deep down, that he is The One ? Or does he fear that he is “just another guy”? She warns him that the fate of humanity hangs in the balance.
#8: The Ordeal
The ordeal marks the hero’s greatest test thus far. This is a dark time for them: indeed, Campbell refers to it as the “belly of the whale.” The hero experiences a major hurdle or obstacle, which causes them to hit rock bottom.
This is a pivotal moment in the story, the main event of the second act. It is time for the hero to come face to face with their greatest fear. It will take all their skills to survive this life-or-death crisis. Should they succeed, they will emerge from the ordeal transformed.
Keep in mind: the story isn’t over yet! Rather, the ordeal is the moment when the protagonist overcomes their weaknesses and truly steps into the title of hero .
The Ordeal in The Matrix :
When Cipher betrays the crew to the agents, Morpheus sacrifices himself to protect Neo. In turn, Neo makes his own choice: to risk his life in a daring rescue attempt.
#9: Reward (Seizing the Sword)
The ordeal was a major level-up moment for the hero. Now that it's been overcome, the hero can reap the reward of success. This reward could be an object, a skill, or knowledge—whatever it is that the hero has been struggling toward. At last, the sword is within their grasp.
From this moment on, the hero is a changed person. They are now equipped for the final conflict, even if they don’t fully realize it yet.
Reward (Seizing the Sword) in The Matrix :
Neo’s reward is helpfully narrated by Morpheus during the rescue effort: “He is beginning to believe.” Neo has gained confidence that he can fight the machines, and he won’t back down from his destiny.

#10: The Road Back
We’re now at the beginning of act three, the return . With the reward in hand, it’s time to exit the inmost cave and head home. But the story isn’t over yet.
In this stage, the hero reckons with the consequences of act two. The ordeal was a success, but things have changed now. Perhaps the dragon, robbed of his treasure, sets off for revenge. Perhaps there are more enemies to fight. Whatever the obstacle, the hero must face them before their journey is complete.
The Road Back in The Matrix :
The rescue of Morpheus has enraged Agent Smith, who intercepts Neo before he can return to the Nebuchadnezzar . The two foes battle in a subway station, where Neo’s skills are pushed to their limit.
#11: Resurrection
Now comes the true climax of the story. This is the hero’s final test, when everything is at stake: the battle for the soul of Gotham, the final chance for evil to triumph. The hero is also at the peak of their powers. A happy ending is within sight, should they succeed.
Vogler calls the resurrection stage the hero’s “final exam.” They must draw on everything they have learned and prove again that they have really internalized the lessons of the ordeal . Near-death escapes are not uncommon here, or even literal deaths and resurrections.
Resurrection in The Matrix :
Despite fighting valiantly, Neo is defeated by Agent Smith and killed. But with Trinity’s help, he is resurrected, activating his full powers as The One . Isn’t it wonderful how literal The Matrix can be?
#12: Return with the Elixir
Hooray! Evil has been defeated and the hero is transformed. It’s time for the protagonist to return home in triumph, and share their hard-won prize with the ordinary world . This prize is the elixir —the object, skill, or insight that was the hero’s true reward for their journey and transformation.
Return with the Elixir in The Matrix :
Neo has defeated the agents and embraced his destiny. He returns to the simulated world of the Matrix, this time armed with god-like powers and a resolve to open humanity’s eyes to the truth.
If you’re writing your own adventure, you may be wondering: should I follow the Hero’s Journey structure?
The good news is, it’s totally up to you. Joseph Campbell conceived of the monomyth as a way to understand universal story structure, but there are many ways to outline a novel. Feel free to play around within its confines, adapt it across different media, and disrupt reader expectations. It’s like Morpheus says: “Some of these rules can be bent. Others can be broken.”
Think of the Hero’s Journey as a tool. If you’re not sure where your story should go next, it can help to refer back to the basics. From there, you’re free to choose your own adventure.
Are you prepared to write your novel? Download this free book now:

The Novel-Writing Training Plan
So you are ready to write your novel. excellent. but are you prepared the last thing you want when you sit down to write your first draft is to lose momentum., this guide helps you work out your narrative arc, plan out your key plot points, flesh out your characters, and begin to build your world..
Be confident about grammar
Check every email, essay, or story for grammar mistakes. Fix them before you press send.
Dan holds a PhD from Yale University and CEO of FaithlessMTG
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :
Improve your writing in one of the largest and most successful writing groups online
Join our writing group!
The Hero’s Journey Ultimate Writing Guide with Examples

by Alex Cabal
What do Star Wars , The Hobbit , and Harry Potter have in common? They’re all examples of a story archetype as old as time. You’ll see this universal narrative structure in books, films, and even video games.
This ultimate Hero’s Journey writing guide will define and explore all quintessential elements of the Hero’s Journey—character archetypes, themes, symbolism, the three act structure, as well as 12 stages of the Hero’s Journey. We’ll even provide a downloadable plot template, tips for writing the Hero’s Journey, and writing prompts to get the creative juices flowing.
What is the Hero’s Journey?
The Hero’s Journey is a universal story structure that follows the personal metamorphosis and psychological development of a protagonist on a heroic adventure. The protagonist goes through a series of stages to overcome adversity and complete a quest to attain an ultimate reward—whether that’s something tangible, like the holy grail, or something internal, like self confidence.
In the process of self-discovery, the archetypal Hero’s Journey is typically cyclical; it begins and ends in the same place (Think Frodo leaving and then returning to the Shire). After the epic quest or adventure has been completed by overcoming adversity and conflict—both physical and mental—the hero arrives where they once began, changed in some as they rose to meet the ultimate conflict or ordeal of the quest.
Joseph Campbell and Christopher Vogler
The Hero’s Journey has a long history of conversation around the form and its uses, with notable contributors including Joseph Campbell and the screenwriter Christopher Vogler , who later revised the steps of the Hero’s Journey.
Joseph Campbell’s “monomyth” framework is the traditional story structure of the Hero’s Journey archetype. Campbell developed it through analysis of ancient myths, folktales, and religious stories. It generally follows three acts in a cyclical, rather than a linear, way: a hero embarks on a journey, faces a crisis, and then returns home transformed and victorious.
Campbell’s ideation of the monomyth in his book The Hero With a Thousand Faces was influenced by Carl Jung’s perspective of psychology and models of self-transformation , where the Hero’s Journey is a path of transformation to a higher self, psychological healing, and spiritual growth.
While Campbell’s original take on the monomyth included 17 steps within the three acts, Christopher Vogler, in his book The Writer’s Journey , refined those 17 steps into 12 stages—the common formula for the modern structure many writers use today.
It’s also worth checking out Maureen Murdock’s work on the archetype, “The Heroine’s Journey.” This takes a look at the female Hero’s Journey, which examines the traditionally masculine journey through a feminist lens.
Hero’s Journey diagram: acts, steps, and stages
Below, you can see the way Volger’s Hero’s Journey is broken into twelve story beats across three acts.
Why is the Hero’s Journey so popular?
The structure of the Hero’s Journey appears in many of our most beloved classic stories, and it continues to resonate over time because it explores the concept of personal transformation and growth through both physical and mental trials and tribulations. In some sense, every individual in this mythic structure experiences rites of passage, the search for home and the true authentic self, which is mirrored in a protagonist’s journey of overcoming obstacles while seeking to fulfill a goal.
Additionally, the Hero’s Journey typically includes commonly shared symbols and aspects of the human psyche—the trickster, the mother, the child, etc. These archetypes play a role in creating a story that the reader can recognize from similar dynamics in their own relationships, experiences, and familiar world. Archetypes allow the writer to use these “metaphorical truths”—a playful deceiver, a maternal bond, a person of innocence and purity—to deeply and empathetically connect with the reader through symbolism. That’s why they continue to appear in countless stories all around the world.
Hero’s Journey character archetypes
Character archetypes are literary devices based on a set of qualities that are easy for a reader to identify, empathize with, and understand, as these qualities and traits are common to the human experience.
It should be noted that character archetypes are not stereotypes . While stereotypes are oversimplifications of demographics or personality traits, an archetype is a symbol of a universal type of character that can be recognized either in one’s self or in others in real life.
The following archetypes are commonly used in a Hero’s Journey:
The hero is typically the protagonist or principal point-of-view character within a story. The hero transforms—internally, externally, often both—while on their journey as they experience tests and trials and are aided or hindered by the other archetypes they encounter. In general, the hero must rise to the challenge and at some point make an act of sacrifice for the ultimate greater good. In this way, the Hero’s Journey represents the reader’s own everyday battles and their power to overcome them.
Heroes may be willing or unwilling. Some can be downright unheroic to begin with. Antiheroes are notably flawed characters that must grow significantly before they achieve the status of true hero.
The mentor often possesses divine wisdom or direct experience with the special world, and has faith in the hero. They often give the hero a gift or supernatural aid, which is usually something important for the quest: either a weapon to destroy a monster, or a talisman to enlighten the hero. The mentor may also directly aid the hero or present challenges to them that force internal or external growth. After their meeting, the hero leaves stronger and better prepared for the road ahead.
The herald is the “call to adventure.” They announce the coming of significant change and become the reason the hero ventures out onto a mysterious adventure. The herald is a catalyst that enters the story and makes it impossible for the hero to remain in status quo. Existing in the form of a person or an event, or sometimes just as information, they shift the hero’s balance and change their world.
The Threshold Guardian
This archetype guards the first threshold—the major turning point of the story where the hero must make the true commitment of the journey and embark on their quest to achieve their destiny. Threshold guardians spice up the story by providing obstacles the hero must overcome, but they’re usually not the main antagonist.
The role of the threshold guardian is to help round out the hero along their journey. The threshold guardian will test the hero’s determination and commitment and will drive them forward as the hero enters the next stage of their journey, assisting the development of the hero’s character arc within the plot. The threshold guardian can be a friend who doesn’t believe in the hero’s quest, or a foe that makes the hero question themselves, their desires, or motives in an attempt to deter the hero from their journey. Ultimately, the role of the threshold guardian is to test the hero’s resolve on their quest.
The Shape Shifter
The shape shifter adds dramatic tension to the story and provides the hero with a puzzle to solve. They can seem to be one thing, but in fact be something else. They bring doubt and suspense to the story and test the hero’s ability to discern their path. The shape shifter may be a lover, friend, ally, or enemy that somehow reveals their true self from the hero’s preconceived notion. This often causes the hero internal turmoil, or creates additional challenges and tests to overcome.
The shadow is the “monster under the bed,” and could be repressed feelings, deep trauma, or festering guilt. These all possess the dark energy of the shadow. It is the dark force of the unexpressed, unrealized, rejected, feared aspects of the hero and is often, but not necessarily, represented by the main antagonist or villain.
However, other characters may take the form of the shadow at different stages of the story as “foil characters” that contrast against the hero. They might also represent what could happen if the hero fails to learn, transform, and grow to complete their quest. At times, a hero may even succumb to the shadow, from which they will need to make sacrifices to be redeemed to continue on their overall quest.
The Trickster
The trickster is the jester or fool of the story that not only provides comic relief, but may also act as a commentator as the events of the plot unfold. Tricksters are typically witty, clever, spontaneous, and sometimes even ridiculous. The trickster within a story can bring a light-hearted element to a challenge, or find a clever way to overcome an obstacle.

Hero’s Journey themes and symbols
Alongside character archetypes, there are also archetypes for settings, situations, and symbolic items that can offer meaning to the world within the story or support your story’s theme.
Archetypes of themes, symbols, and situations represent shared patterns of human existence. This familiarity can provide the reader insight into the deeper meaning of a story without the writer needing to explicitly tell them. There are a great number of archetypes and symbols that can be used to reinforce a theme. Some that are common to the Hero’s Journey include:
Situational archetypes
Light vs. dark and the battle of good vs. evil
Death, rebirth, and transformation in the cycle of life
Nature vs. technology, and the evolution of humanity
Rags to riches or vice versa, as commentary on the material world and social status
Wisdom vs. knowledge and innocence vs. experience, in the understanding of intuition and learned experience
Setting archetypes
Gardens may represent the taming of nature, or living in harmony with nature.
Forests may represent reconnection with nature or wildness, or the fear of the unknown.
Cities or small towns may represent humanity at its best and at its worst. A small town may offer comfort and rest, while simultaneously offering judgment; a city may represent danger while simultaneously championing diversity of ideas, beings, and cultures.
Water and fire within a landscape may represent danger, change, purification, and cleansing.
Symbolic items
Items of the past self. These items are generally tokens from home that remind the hero of where they came from and who or what they’re fighting for.
Gifts to the hero. These items may be given to the hero from a mentor, ally, or even a minor character they meet along the way. These items are typically hero talismans, and may or may not be magical, but will aid the hero on their journey.
Found items. These items are typically found along the journey and represent some sort of growth or change within the hero. After all, the hero would never have found the item had they not left their everyday life behind. These items may immediately seem unimportant, but often carry great significance.
Earned rewards. These items are generally earned by overcoming a test or trial, and often represent growth, or give aid in future trials, tests, and conflicts.
The three act structure of the Hero’s Journey
The structure of the Hero’s Journey, including all 12 steps, can be grouped into three stages that encompass each phase of the journey. These acts follow the the external and internal arc of the hero—the beginning, the initiation and transformation, and the return home.
Act One: Departure (Steps 1—5)
The first act introduces the hero within the ordinary world, as they are—original and untransformed. The first act will typically include the first five steps of the Hero’s Journey.
This section allows the writer to set the stage with details that show who the hero is before their metamorphosis—what is the environment of the ordinary world? What’s important to the hero? Why do they first refuse the call, and then, why do they ultimately accept and embark on the journey to meet with the conflict?
This stage introduces the first major plot point of the story, explores the conflict the hero confronts, and provides the opportunity for characterization for the hero and their companions.
The end of the first act generally occurs when the hero has fully committed to the journey and crossed the threshold of the ordinary world—where there is no turning back.
Act Two: Initiation (Steps 6—9)
Once the hero begins their journey, the second act marks the beginning of their true initiation into the unfamiliar world—they have crossed the threshold, and through this choice, have undergone their first transformation.
The second act is generally the longest of the three and includes steps six through nine.
In this act, the hero meets most of the characters that will be pivotal to the plot, including friends, enemies, and allies. It offers the rising action and other minor plot points related to the overarching conflict. The hero will overcome various trials, grow and transform, and navigate subplots—the additional and unforeseen complexity of the conflict.
This act generally ends when the hero has risen to the challenge to overcome the ordeal and receives their reward. At the end of this act, it’s common for the theme and moral of the story to be fully unveiled.
Act Three: Return (Steps 10—12)
The final stage typically includes steps 10—12, generally beginning with the road back—the point in the story where the hero must recommit to the journey and use all of the growth, transformation, gifts and tools acquired along the journey to bring a decisive victory against their final conflict.
From this event, the hero will also be “reborn,” either literally or metaphorically, and then beginning anew as a self-actualized being, equipped with internal knowledge about themselves, external knowledge about the world, and experience.
At the end of the third act, the hero returns home to the ordinary world, bringing back the gifts they earned on their journey. In the final passages, both the hero and their perception of the ordinary world are compared with what they once were.
The 12 steps of the Hero’s Journey
The following guide outlines the 12 steps of the Hero’s Journey and represents a framework for the creation of a Hero’s Journey story template. You don’t necessarily need to follow the explicit cadence of these steps in your own writing, but they should act as checkpoints to the overall story.
We’ll also use JRR Tolkien’s The Hobbit as a literary example for each of these steps. The Hobbit does an exemplary job of following the Hero’s Journey, and it’s also an example of how checkpoints can exist in more than one place in a story, or how they may deviate from the typical 12-step process of the Hero’s Journey.

1. The Ordinary World
This stage in the Hero’s Journey is all about exposition. This introduces the hero’s backstory—who the hero is, where they come from, their worldview, culture, and so on. This offers the reader a chance to relate to the character in their untransformed form.
As the story and character arc develop, the reader is brought along the journey of transformation. By starting at the beginning, a reader has a basic understanding of what drives the hero, so they can understand why the hero makes the choices they do. The ordinary world shows the protagonist in their comfort zone, with their worldview being limited to the perspective of their everyday life.
Characters in the ordinary world may or may not be fully comfortable or satisfied, but they don’t have a point of reference to compare—they have yet to leave the ordinary world to gain the knowledge to do so.
Step One example
The Hobbit begins by introducing Bilbo in the Shire as a respectable and well-to-do member of the community. His ordinary world is utopian and comfortable. Yet, even within a village that is largely uninterested in the concerns of the world outside, the reader is provided a backstory: even though Bilbo buys into the comforts and normalcy of the Shire, he still yearns for adventure—something his neighbors frown upon. This ordinary world of the Shire is disrupted with the introduction of Gandalf—the “mentor”—who is somewhat uncomfortably invited to tea.
2. Call to Adventure
The call to adventure in the Hero’s Journey structure is the initial internal conflict that the protagonist hero faces, that drives them to the true conflict that they must overcome by the end of their journey.
The call occurs within the known world of the character. Here the writer can build on the characterization of the protagonist by detailing how they respond to the initial call. Are they hesitant, eager, excited, refusing, or willing to take a risk?
Step Two example
Bilbo’s call to adventure takes place at tea as the dwarves leisurely enter his home, followed by Gandalf, who identifies Bilbo as the group’s missing element—the burglar, and the lucky 14th member.
Bilbo and his ordinary world are emphasized by his discomfort with his rambunctious and careless guests. Yet as the dwarves sing stories of old adventures, caverns, and lineages, which introduce and foreshadow the conflict to come, a yearning for adventure is stirred. Though he still clings to his ordinary world and his life in the Shire, he’s conflicted. Should he leave the shire and experience the world, or stay in his comfortable home? Bilbo continues to refuse the call, but with mixed feelings.

3. Refusal of the Call
The refusal of the call in the Hero’s Journey showcases a “clinging” to one’s original self or world view. The initial refusal of the call represents a fear of change, as well as a resistance to the internal transformation that will occur after the adventure has begun.
The refusal reveals the risks that the protagonist faces if they were to answer the call, and shows what they’ll leave behind in the ordinary world once they accept.
The refusal of the call creates tension in the story, and should show the personal reasons why the hero is refusing—inner conflict, fear of change, hesitation, insecurity, etc. This helps make their character clearer for the reader.
These are all emotions a reader can relate to, and in presenting them through the hero, the writer deepens the reader’s relationship with them and helps the reader sympathize with the hero’s internal plight as they take the first step of transformation.
Step Three example
Bilbo refuses the call in his first encounter with Gandalf, and in his reaction to the dwarves during tea. Even though Bilbo’s “Tookish” tendencies make him yearn for adventure, he goes to bed that night still refusing the call. The next morning, as Bilbo awakes to an empty and almost fully clean hobbit home, he feels a slight disappointment for not joining the party, but quickly soothes his concerns by enjoying the comfort of his home—i.e. the ordinary world. Bilbo explores his hesitation to disembark from the ordinary world, questioning why a hobbit would become mixed up in the adventures of others, and choosing not to meet the dwarves at the designated location.
4. Meeting the Mentor
Meeting the mentor in the Hero’s Journey is the stage that provides the hero protagonist with a guide, relationship, and/or informational asset that has experience outside the ordinary world. The mentor offers confidence, advice, wisdom, training, insight, tools, items, or gifts of supernatural wonder that the hero will use along the journey and in overcoming the ultimate conflict.
The mentor often represents someone who has attempted to overcome, or actually has overcome, an obstacle, and encourages the hero to pursue their calling, regardless of the hero’s weaknesses or insecurities. The mentor may also explicitly point out the hero’s weaknesses, forcing them to reckon with and accept them, which is the first step to their personal transformation.
Note that not all mentors need to be a character . They can also be objects or knowledge that has been instilled in the hero somehow—cultural ethics, spiritual guidance, training of a particular skill, a map, book, diary, or object that illuminates the path forward, etc. In essence, the mentor character or object has a role in offering the protagonist outside help and guidance along the Hero’s Journey, and plays a key role in the protagonist’s transition from normalcy to heroism.
The mentor figure also offers the writer the opportunity to incorporate new information by expanding upon the story, plot, or backstory in unique ways. They do this by giving the hero information that would otherwise be difficult for the writer to convey naturally.
The mentor may accompany the hero throughout most of the story, or they may only periodically be included to facilitate changes and transformation within them.
Step Four example
The mentor, Gandalf, is introduced almost immediately. Gandalf is shown to be the mentor, firstly through his arrival from—and wisdom of—the outside world; and secondly, through his selection of Bilbo for the dwarven party by identifying the unique characteristics Bilbo has that are essential to overcoming the challenges in the journey. Gandalf doesn’t accompany Bilbo and the company through all of the trials and tribulations of the plot, but he does play a key role in offering guidance and assistance, and saves the group in times of dire peril.

5. Crossing the Threshold
As the hero crosses the first threshold, they begin their personal quest toward self-transformation. Crossing the threshold means that the character has committed to the journey, and has stepped outside of the ordinary world in the pursuit of their goal. This typically marks the conclusion of the first act.
The threshold lies between the ordinary world and the special world, and marks the point of the story where the hero fully commits to the road ahead. It’s a crucial stage in the Hero’s Journey, as the hero wouldn’t be able to grow and transform by staying in the ordinary world where they’re comfortable and their world view can’t change.
The threshold isn’t necessarily a specific place within the world of the story, though a place can symbolize the threshold—for example a border, gateway, or crossroads that separate what is safe and “known” from what is potentially dangerous. It can also be a moment or experience that causes the hero to recognize that the comforts and routine of their world no longer apply—like the loss of someone or something close to the hero, for example. The purpose of the threshold is to take the hero out of their element and force them, and the reader, to adapt from the known to the unknown.
This moment is crucial to the story’s tension. It marks the first true shift in the character arc and the moment the adventure has truly begun. The threshold commonly forces the hero into a situation where there’s no turning back. This is sometimes called the initiation stage or the departure stage.
Step Five example
The threshold moment in The Hobbit occurs when the party experiences true danger as a group for the first time. Bilbo, voted as scout by the party and eager to prove his burglar abilities, sneaks upon a lone fire in the forest where he finds three large trolls. Rather than turn back empty-handed—as he initially wants to—Bilbo chooses to prove himself, plucking up the courage to pickpocket the trolls—but is caught in the process. The dwarves are also captured and fortunately, Gandalf, the mentor, comes to save the party.
Bilbo’s character arc is solidified in this threshold moment. He experiences his first transformation when he casts aside fear and seeks to prove himself as a burglar, and as an official member of the party. This moment also provides further characterization of the party as a whole, proving the loyalty of the group in seeking out their captured member.
Gandalf’s position as the mentor is also firmly established as he returns to ultimately save all of the members of the party from being eaten by trolls. The chapter ends with Bilbo taking ownership of his first hero talisman—the sword that will accompany him through the rest of the adventure.
6. Tests, Allies, Enemies
Once the hero has crossed the threshold, they must now encounter tests of courage, make allies, and inevitably confront enemies. All these elements force the hero to learn the new ways of the special world and how it differs from the hero’s ordinary world—i.e. how the rules have changed, the conditions of the special world vs. the ordinary world, and the various beings and places within it.
All these elements spark stages of transformation within the hero—learning who they can trust and who they can’t, learning new skills, seeking training from the mentor, and overcoming challenges that force and drive them to grow and transform.
The hero may both succeed and fail at various points of this stage, which will test their commitment to the journey. The writer can create tension by making it clear that the hero may or may not succeed at the critical moment of crisis. These crises can be external or internal.
External conflicts are issues that the character must face and overcome within the plot—e.g. the enemy has a sword drawn and the hero must fight to survive.
Internal conflicts occur inside the hero. For example, the hero has reached safety, but their ally is in peril; will they step outside their comfort zone and rise to the occasion and save their friend? Or will they return home to their old life and the safety of the ordinary world?
Tests are conflicts and threats that the hero must face before they reach the true conflict, or ordeal, of the story. These tests set the stage and prime the hero to meet and achieve the ultimate goal. They provide the writer the opportunity to further the character development of the hero through their actions, inactions, and reactions to what they encounter. The various challenges they face will teach them valuable lessons, as well as keep the story compelling and the reader engaged.
Allies represent the characters that offer support to the protagonist along the journey. Some allies may be introduced from the beginning, while others may be gained along the journey. Secondary characters and allies provide additional nuance for the hero, through interactions, events, and relationships that further show who the hero is at heart, what they believe in, and what they’re willing to fight for. The role of the allies is to bring hope, inspiration, and further drive the hero to do what needs to be done.
Enemies represent a foil to the allies. While allies bring hope and inspiration, enemies will provide challenges, conflicts, tests, and challenges. Both allies and enemies may instigate transformative growth, but enemies do so in a way that fosters conflict and struggle.
Characterization of enemies can also enhance the development of the hero through how they interact and the lessons learned through those interactions. Is the hero easily duped, forgiving, empathetic, merciful? Do they hold a grudge and seek revenge? Who is the hero now that they have been harmed, faced an enemy, and lost pieces of their innocent worldview? To answer that, the hero is still transforming and gestating with every lesson, test, and enemy faced along the way.
Step Six example
As the plot of The Hobbit carries on, Bilbo encounters many tests, allies, and enemies that all drive complexity in the story. A few examples include:
The first major obstacle that Bilbo faces occurs within the dark and damp cave hidden in the goblin town. All alone, Bilbo must pluck up the wit and courage to outriddle a creature named Gollum. In doing so, Bilbo discovers the secret power of a golden ring (another hero talisman) that will aid him and the party through the rest of the journey.
The elves encountered after Bilbo “crosses the threshold” are presented as allies in the story. The hero receives gifts of food, a safe place to rest, and insight and guidance that allows the party to continue on their journey. While the party doesn’t dwell long with the elves, the elves also provide further character development for the party at large: the serious dwarf personalities are juxtaposed against the playful elvish ones, and the elves offer valuable historical insight with backstory to the weapons the party gathered from the troll encounter.
Goblins are a recurring enemy within the story that the hero and party must continue to face, fight, and run from. The goblins present consistent challenges that force Bilbo to face fear and learn and adapt, not only to survive but to save his friends.

7. Approach to the Inmost Cave
The approach to the inmost cave of the Hero’s Journey is the tense quiet before the storm; it’s the part of the story right before the hero faces their greatest fear, and it can be positioned in a few different ways. By now, the hero has overcome obstacles, setbacks, and tests, gained and lost allies and enemies, and has transformed in some way from the original protagonist first introduced in the ordinary world.
The moment when the hero approaches the inmost cave can be a moment of reflection, reorganization, and rekindling of morale. It presents an opportunity for the main characters of the story to come together in a moment of empathy for losses along the journey; a moment of planning and plotting next steps; an opportunity for the mentor to teach a final lesson to the hero; or a moment for the hero to sit quietly and reflect upon surmounting the challenge they have been journeying toward for the length of their adventure.
The “cave” may or may not be a physical place where the ultimate ordeal and conflict will occur. The approach represents the momentary period where the hero assumes their final preparation for the overall challenge that must be overcome. It’s a time for the hero and their allies, as well as the reader, to pause and reflect on the events of the story that have already occurred, and to consider the internal and external growth and transformation of the hero.
Having gained physical and/or emotional strength and fortitude through their trials and tests, learned more rules about the special world, found and lost allies and friends, is the hero prepared to face danger and their ultimate foe? Reflection, tension, and anticipation are the key elements of crafting the approach to the cave.
Step Seven example
The approach to the cave in The Hobbit occurs as the party enters the tunnel of the Lonely Mountain. The tunnel is the access point to the ultimate goal—Thorin’s familial treasure, as well as the ultimate test—the formidable dragon Smaug. During this part of the story, the party must hide, plot, and plan their approach to the final conflict. It’s at this time that Bilbo realizes he must go alone to scout out and face the dragon.
8. The Ordeal
The ordeal is the foreshadowed conflict that the hero must face, and represents the midpoint of the story. While the ordeal is the ultimate conflict that the hero knows they must overcome, it’s a false climax to the complete story—there’s still much ground to cover in the journey, and the hero will still be tested after completing this, the greatest challenge. In writing the ordeal phase of the Hero’s Journey, the writer should craft this as if it actually were the climax to the tale, even though it isn’t.
The first act, and the beginning of the second act, have built up to the ordeal with characterization and the transformation of the hero through their overcoming tests and trials. This growth—both internal and external—has all occurred to set the hero up to handle this major ordeal.
As this stage commences, the hero is typically faced with fresh challenges to make the ordeal even more difficult than they previously conceived. This may include additional setbacks for the hero, the hero’s realization that they were misinformed about the gravity of the situation, or additional conflicts that make the ordeal seem insurmountable.
These setbacks cause the hero to confront their greatest fears and build tension for both the hero and the reader, as they both question if the hero will ultimately succeed or fail. In an epic fantasy tale, this may mean a life-or-death moment for the hero, or experiencing death through the loss of an important ally or the mentor. In a romance, it may be the moment of crisis where a relationship ends or a partner reveals their dark side or true self, causing the hero great strife.
This is the rock-bottom moment for the hero, where they lose hope, courage, and faith. At this point, even though the hero has already crossed the threshold, this part of the story shows how the hero has changed in such a way that they can never return to their original self: even if they return to the ordinary world, they’ll never be the same; their perception of the world has been modified forever.
Choosing to endure against all odds and costs to face the ordeal represents the loss of the hero’s original self from the ordinary world, and a huge internal transformation occurs within the hero as they must rise and continue forth to complete their journey and do what they set out to do from the beginning.
The ordeal may also be positioned as an introduction to the greater villain through a trial with a shadow villain, where the hero realizes that the greatest conflict is unveiled as something else, still yet to come. In these instances, the hero may fail, or barely succeed, but must learn a crucial lesson and be metaphorically resurrected through their failure to rise again and overcome the greater challenge.
Step Eight example
Bilbo must now face his ultimate challenge: burgle the treasure from the dragon. This is the challenge that was set forth from the beginning, as it’s his purpose as the party’s 14th member, the burglar, anointed by Gandalf, the mentor. Additional conflicts arise as Bilbo realizes that he must face the dragon alone, and in doing so, must rely on all of the skills and gifts in the form of talismans and tokens he has gained throughout the adventure.
During the ordeal, Bilbo uses the courage he has gained by surmounting the story’s previous trials; he’s bolstered by his loyalty to the group and relies upon the skills and tools he has earned in previous trials. Much as he outwitted Gollum in the cave, Bilbo now uses his wit as well as his magical ring to defeat Smaug in a game of riddles, which ultimately leads Smaug out of the lair so that Bilbo can complete what he was set out to do—steal the treasure.

The reward of the Hero’s Journey is a moment of triumph, celebration, or change as the hero achieves their first major victory. This is a moment of reflection for both the reader and the hero, to take a breath to contemplate and acknowledge the growth, development, and transformation that has occurred so far.
The reward is the boon that the hero learns, is granted, or steals, that will be crucial to facing the true climax of the story that is yet to come. The reward may be a physical object, special knowledge, or reconciliation of some sort, but it’s always a thing that allows for some form of celebration or replenishment and provides the drive to succeed before the journey continues.
Note that the reward may not always be overtly positive—it may also be a double-edged sword that could harm them physically or spiritually. This type of reward typically triggers yet another internal transformation within the hero, one that grants them the knowledge and personal drive to complete the journey and face their remaining challenges.
From the reward, the hero is no longer externally driven to complete the journey, but has evolved to take on the onus of doing so.
Examples of rewards may include:
A weapon, elixir, or object that will be necessary to complete the quest.
Special knowledge, or a personal transformation to use against a foe.
An eye-opening experience that provides deep insight and fundamentally changes the hero and their position within the story and world.
Reconciliation with another character, or with themselves.
No matter what the reward is, the hero should experience some emotional or spiritual revelation and a semblance of inner peace or personal resolve to continue the journey. Even if the reward is not overtly positive, the hero and the reader deserve a moment of celebration for facing the great challenge they set out to overcome.
Step Nine example
Bilbo defeats the dragon at a battle of wits and riddles, and now receives his reward. He keeps the gifts he has earned, both the dagger and the gold ring. He is also granted his slice of the treasure, and the Lonely Mountain is returned to Thorin. The party at large is rewarded for completing the quest and challenge they set out to do.
However, Tolkien writes the reward to be more complex than it first appears. The party remains trapped and hungry within the Mountain as events unfold outside of it. Laketown has been attacked by Smaug, and the defenders will want compensation for the damage to their homes and for their having to kill the dragon. Bilbo discovers, and then hides, the Arkenstone (a symbolic double edged reward) to protect it from Thorin’s selfishness and greed.

10. The Road Back
The road back in the Hero’s Journey is the beginning of the third act, and represents a turning point within the story. The hero must recommit to the journey, alongside the new stakes and challenges that have arisen from the completion of the original goal.
The road back presents roadblocks—new and unforeseen challenges to the hero that they must now face on their journey back to the ordinary world. The trials aren’t over yet, and the stakes are raised just enough to keep the story compelling before the final and ultimate conflict—the hero’s resurrection—is revealed in the middle of the third act.
The hero has overcome their greatest challenge in the Ordeal and they aren’t the same person they were when they started. This stage of the story often sees the hero making a choice, or reflecting on their transformed state compared to their state at the start of the journey.
The writer’s purpose in the third act is not to eclipse the upcoming and final conflict, but to up the stakes, show the true risk of the final climax, and to reflect on what it will take for the hero to ultimately prevail. The road back should offer a glimmer of hope—the light at the end of the tunnel—and should let the reader know the dramatic finale is about to arrive.
Step Ten example
What was once a journey to steal treasure and slay a dragon has developed new complications. Our hero, Bilbo, must now use all of the powers granted in his personal transformation, as well as the gifts and rewards he earned on the quest, to complete the final stages of the journey.
This is the crisis moment of The Hobbit ; the armies of Laketown are prepared for battle to claim their reward for killing Smaug; the fearless leader of their party, Thorin, has lost reason and succumbed to greed; and Bilbo makes a crucial choice based his personal growth: he gives the Arkenstone to the king as a bargaining chip for peace. Bilbo also briefly reconnects with the mentor, Gandalf, who warns him of the unpleasant times ahead, but comforts Bilbo by saying that things may yet turn out for the best. Bilbo then loyally returns to his friends, the party of dwarves, to stand alongside them in the final battle.
11. Resurrection
The resurrection stage of the Hero’s Journey is the final climax of the story, and the heart of the third act. By now the hero has experienced internal and external transformation and a loss of innocence, coming out with newfound knowledge. They’re fully rooted in the special world, know its rules, and have made choices that underline this new understanding.
The hero must now overcome the final crisis of their external quest. In an epic fantasy tale, this may be the last battle of light versus darkness, good versus evil, a cumulation of fabulous forces. In a thriller, the hero might ultimately face their own morality as they approach the killer. In a drama or romance, the final and pivotal encounter in a relationship occurs and the hero puts their morality ahead of their immediate desires.
The stakes are the highest they’ve ever been, and the hero must often choose to make a sacrifice. The sacrifice may occur as a metaphoric or symbolic death of the self in some way; letting go of a relationship, title, or mental/emotional image of the self that a hero once used as a critical aspect of their identity, or perhaps even a metaphoric physical death—getting knocked out or incapacitated, losing a limb, etc.
Through whatever the great sacrifice is, be it loss or a metaphoric death, the hero will experience a form of resurrection, purification, or internal cleansing that is their final internal transformation.
In this stage, the hero’s character arc comes to an end, and balance is restored to the world. The theme of the story is fully fleshed out and the hero, having reached some form of self-actualization, is forever changed. Both the reader and the hero experience catharsis—the relief, insight, peace, closure, and purging of fear that had once held the hero back from their final transformation.
Step Eleven example
All the armies have gathered, and the final battle takes place. Just before the battle commences, Bilbo tells Thorin that it was he who gave the Arkenstone to the city of men and offers to sacrifice his reward of gold for taking the stone. Gandalf, the mentor, arrives, standing beside Bilbo and his decision. Bilbo is shunned by Thorin and is asked to leave the party for his betrayal.
Bilbo experiences a symbolic death when he’s knocked out by a stone. Upon awakening, Bilbo is brought to a dying Thorin, who forgives him of his betrayal, and acknowledges that Bilbo’s actions were truly the right thing to do. The theme of the story is fully unveiled: that bravery and courage comes in all sizes and forms, and that greed and gold are less worthy than a life rich in experiences and relationships.

12. Return with the Elixir
The elixir in the Hero’s Journey is the final reward the hero brings with them on their return, bridging their two worlds. It’s a reward hard earned through the various relationships, tests, and growth the hero has experienced along their journey. The “elixir” can be a magical potion, treasure, or object, but it can also be intangible—love, wisdom, knowledge, or experience.
The return is key to the circular nature of the Hero’s Journey. It offers a resolution to both the reader and the hero, and a comparison of their growth from when the journey began.
Without the return, the story would have a linear nature, a beginning and an end. In bringing the self-actualized hero home to the ordinary world, the character arc is completed, and the changes they’ve undergone through the journey are solidified. They’ve overcome the unknown, and though they’re returning home, they can no longer resume their old life because of their new insight and experiences.
Step Twelve example
The small yet mighty hero Bilbo is accompanied on his journey home by his mentor Gandalf, as well as the allies he gathered along his journey. He returns with many rewards—his dagger, his golden ring, and his 1/14th split of the treasure—yet his greatest rewards are his experience and the friends he has made along the way. Upon entering the Shire Bilbo sings a song of adventure, and the mentor Gandalf remarks, “My dear Bilbo! Something is the matter with you, you are not the hobbit you were.”
The final pages of The Hobbit explore Bilbo’s new self in the Shire, and how the community now sees him as a changed hobbit—no longer quite as respectable as he once was, with odd guests who visit from time to time. Bilbo also composes his story “There and Back Again,” a tale of his experiences, underlining his greatest reward—stepping outside of the Shire and into the unknown, then returning home, a changed hobbit.
Books that follow the Hero’s Journey
One of the best ways to become familiar with the plot structure of the Hero’s Journey is to read stories and books that successfully use it to tell a powerful tale. Maybe they’ll inspire you to use the hero’s journey in your own writing!
The Lord of the Rings trilogy by J. R. R. Tolkien.
The Harry Potter series by J. K. Rowling.
The Earthsea series by Ursula K. Le Guin.
The Odyssey by Homer.
Siddhartha by Herman Hesse.
Pride and Prejudice by Jane Austen.
Writing tips for the Hero’s Journey
Writing a Hero’s Journey story often requires planning beforehand to organize the plot, structure, and events of the story. Here are some tips to use the hero’s journey archetype in a story:
Use a template or note cards to organize and store your ideas. This can assist in ensuring that you tie up any loose ends in the plot, and that the cadence of your story is already outlined before you begin writing.
Use word count goals for writing different sections of your story. This can help you keep pace while you plan and write the first draft. You can always revise, edit, and add in detail at later stages of development, but getting the ideas written without bogging them down with details can assist in preparing your outline, and may perhaps provide additional inspiration and guidance along the way.
Lean into creativity and be flexible with the 12 steps. They don’t need to occur in the exact order we’ve listed above, but that ordering can offer great checkpoint moments for your story.
Invest in characterization and ensure that your main character is balanced with credible strengths and weaknesses. A perfect, pure hero has no room to grow. A one-dimensional villain who relies on the trope of “pure evil” without any motivations for their actions is boring and predictable.
Ensure tension and urgency is woven into the story. An epic tale to the grocery store for baby formula may still be fraught with danger, and the price of failure is a hungry child. Without urgency, tension, and risk, a Hero’s Journey will fall flat.
Be hard on your characters. Give them deep conflicts that truly test their nature, and their mental, physical, and spiritual selves. An easy journey isn’t a memorable one.
Have a balance of scenes that play on both positive and negative emotions and outcomes for the hero to create a compelling plot line that continues to engage your reader. A story that’s relentlessly positive doesn’t provide a pathway for the hero to transform. Likewise, a story that’s nothing but doom, strife, and turmoil, without a light at the end of the tunnel or an opportunity for growth, can make a story feel stagnant and unengaging.
Reward your characters and your reader. Personal transformation and the road to the authentic self may be grueling, but there’s peace or joy at the end of the tunnel. Even if your character doesn’t fully saved the world, they—and the reader—should be rewarded with catharsis, a new perspective, or personal insight at the end of the tale.
Hero’s Journey templates
Download these free templates to help you plan out your Hero’s Journey:
Download the Hero’s Journey template template (docx) Download the Hero’s Journey template template (pdf)
Prompts and practices to help you write your own Hero’s Journey
Use the downloadable template listed below for the following exercises:
Read a book or watch a movie that follows the Hero’s Journey. Use the template to fill in when each step occurs or is completed. Make note of themes and symbols, character arcs, the main plot, and the subplots that drive complexity in the story.
When writing, use a timer set to 2—5 minutes per section to facilitate bursts of creativity. Brainstorm ideas for cadence, plot, and characters within the story. The outline you create can always be modified, but the timer ensures you can get ideas on paper without a commitment; you’re simply jotting down ideas as quickly as you can.
Use the downloadable template above to generate outlines based on the following prompts.
A woman’s estranged mother has died. A friend of the mother arrives at the woman’s home to tell her that her mother has left all her belongings to her daughter, and hands her a letter. The letter details the mother’s life, and the daughter must visit certain places and people to find her mother’s house and all the belongings in it—learning more about her mother’s life, and herself, along the way.
The last tree on earth has fallen, and technology can no longer sustain human life on Earth. An engineer, having long ago received alien radio signals from a tower in their backyard, has dedicated their life to building a spaceship in their garage. The time has come to launch, and the engineer must select a group of allies to bring with them to the stars, on a search for a new life, a new home, and “the others” out there in the universe.
A detective is given a new case: to find a much-talked-about murderer. The twist is, the murderer has sent a letter to the detective agency, quietly outing a homicidal politician who is up for re-election and is a major financial contributor to the police. In the letter, the murderer states that if the politician doesn’t come clean about their crimes, the murderer will kill the politician on the night of the election. The detective must solve the case before the election, and come to terms with their own feelings of justice and morality.
Get feedback on your writing today!
Scribophile is a community of hundreds of thousands of writers from all over the world. Meet beta readers, get feedback on your writing, and become a better writer!
Join now for free

Related articles

Worldbuilding: The Ultimate Guide (Plus a Template!)

What You Need to Know as a Writer About Narrative Tenses

Writing the Rebel Archetype: Fictional Characters Who Make Their Own Rules (with Examples)

Story Archetypes: 50+ Plot Archetypes to Craft Your Narrative

Low Fantasy vs. High Fantasy: What’s the Difference?

The Five-Act Structure: The Foundation of an Engaging Story
Looking to publish? Meet your dream editor, designer and marketer on Reedsy.
Find the perfect editor for your next book
1 million authors trust the professionals on Reedsy. Come meet them.
Last updated on Aug 10, 2023
The Hero's Journey: 12 Steps to a Classic Story Structure
The Hero's Journey is a timeless story structure which follows a protagonist on an unforeseen quest, where they face challenges, gain insights, and return home transformed. From Theseus and the Minotaur to The Lion King , so many narratives follow this pattern that it’s become ingrained into our cultural DNA.
In this post, we'll show you how to make this classic plot structure work for you — and if you’re pressed for time, download our cheat sheet below for everything you need to know.

FREE RESOURCE
Hero's Journey Template
Plot your character's journey with our step-by-step template.
What is the Hero’s Journey?
The Hero's Journey, also known as the monomyth, is a story structure where a hero goes on a quest or adventure to achieve a goal, and has to overcome obstacles and fears, before ultimately returning home transformed.
This narrative arc has been present in various forms across cultures for centuries, if not longer, but gained popularity through Joseph Campbell's mythology book, The Hero with a Thousand Faces . While Campbell identified 17 story beats in his monomyth definition, this post will concentrate on a 12-step framework popularized in 2007 by screenwriter Christopher Vogler in his book The Writer’s Journey .
The 12 Steps of the Hero’s Journey
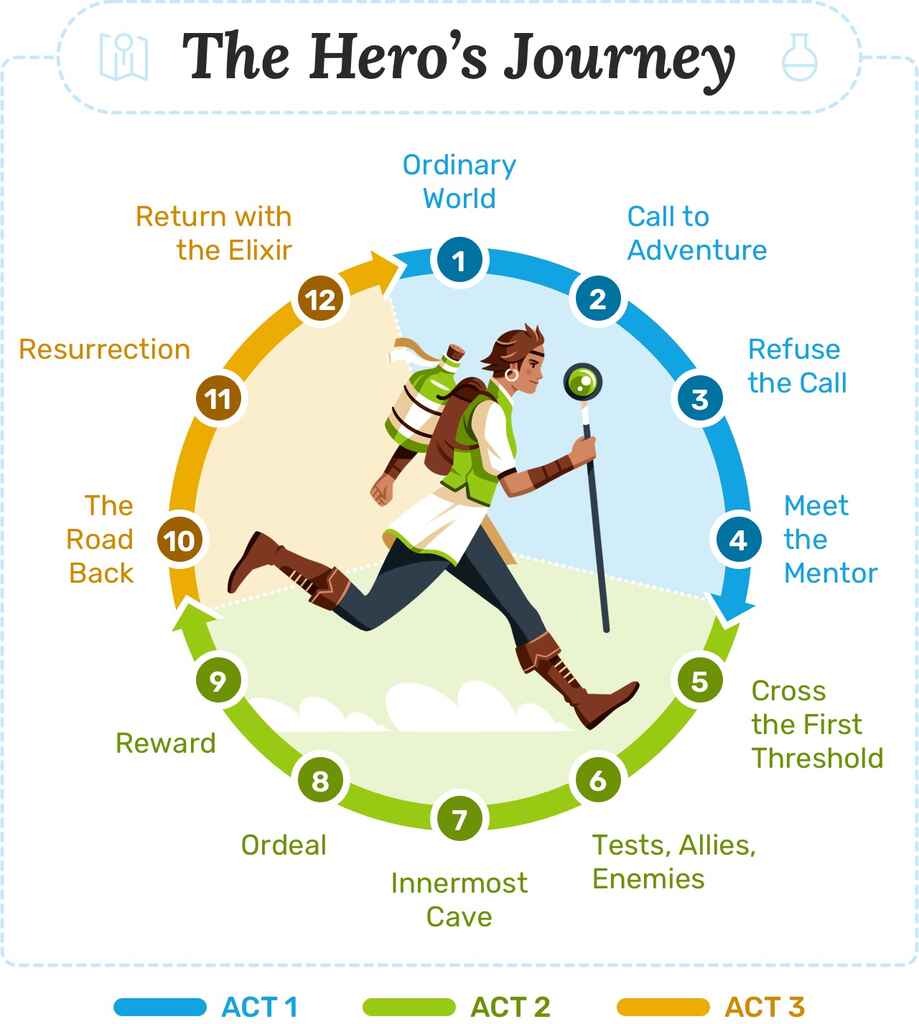
The Hero's Journey is a model for both plot points and character development : as the Hero traverses the world, they'll undergo inner and outer transformation at each stage of the journey. The 12 steps of the hero's journey are:
- The Ordinary World. We meet our hero.
- Call to Adventure. Will they meet the challenge?
- Refusal of the Call. They resist the adventure.
- Meeting the Mentor. A teacher arrives.
- Crossing the First Threshold. The hero leaves their comfort zone.
- Tests, Allies, Enemies. Making friends and facing roadblocks.
- Approach to the Inmost Cave. Getting closer to our goal.
- Ordeal. The hero’s biggest test yet!
- Reward (Seizing the Sword). Light at the end of the tunnel
- The Road Back. We aren’t safe yet.
- Resurrection. The final hurdle is reached.
- Return with the Elixir. The hero heads home, triumphant.
Believe it or not, this story structure also applies across mediums and genres (and also works when your protagonist is an anti-hero! ). Let's dive into it.
1. Ordinary World
In which we meet our Hero.
The journey has yet to start. Before our Hero discovers a strange new world, we must first understand the status quo: their ordinary, mundane reality.
It’s up to this opening leg to set the stage, introducing the Hero to readers. Importantly, it lets readers identify with the Hero as a “normal” person in a “normal” setting, before the journey begins.
2. Call to Adventure
In which an adventure starts.
The call to adventure is all about booting the Hero out of their comfort zone. In this stage, they are generally confronted with a problem or challenge they can't ignore. This catalyst can take many forms, as Campbell points out in Hero with a Thousand Faces . The Hero can, for instance:
- Decide to go forth of their own volition;
- Theseus upon arriving in Athens.
- Be sent abroad by a benign or malignant agent;
- Odysseus setting off on his ship in The Odyssey .
- Stumble upon the adventure as a result of a mere blunder;
- Dorothy when she’s swept up in a tornado in The Wizard of Oz .
- Be casually strolling when some passing phenomenon catches the wandering eye and lures one away from the frequented paths of man.
- Elliot in E.T. upon discovering a lost alien in the tool shed.
The stakes of the adventure and the Hero's goals become clear. The only question: will he rise to the challenge?

3. Refusal of the Call
In which the Hero digs in their feet.
Great, so the Hero’s received their summons. Now they’re all set to be whisked off to defeat evil, right?
Not so fast. The Hero might first refuse the call to action. It’s risky and there are perils — like spiders, trolls, or perhaps a creepy uncle waiting back at Pride Rock . It’s enough to give anyone pause.
In Star Wars , for instance, Luke Skywalker initially refuses to join Obi-Wan on his mission to rescue the princess. It’s only when he discovers that his aunt and uncle have been killed by stormtroopers that he changes his mind.
4. Meeting the Mentor
In which the Hero acquires a personal trainer.
The Hero's decided to go on the adventure — but they’re not ready to spread their wings yet. They're much too inexperienced at this point and we don't want them to do a fabulous belly-flop off the cliff.
Enter the mentor: someone who helps the Hero, so that they don't make a total fool of themselves (or get themselves killed). The mentor provides practical training, profound wisdom, a kick up the posterior, or something abstract like grit and self-confidence.

Wise old wizards seem to like being mentors. But mentors take many forms, from witches to hermits and suburban karate instructors. They might literally give weapons to prepare for the trials ahead, like Q in the James Bond series. Or perhaps the mentor is an object, such as a map. In all cases, they prepare the Hero for the next step.

GET ACCOUNTABILITY
Meet writing coaches on Reedsy
Industry insiders can help you hone your craft, finish your draft, and get published.
5. Crossing the First Threshold
In which the Hero enters the other world in earnest.
Now the Hero is ready — and committed — to the journey. This marks the end of the Departure stage and is when the adventure really kicks into the next gear. As Vogler writes: “This is the moment that the balloon goes up, the ship sails, the romance begins, the wagon gets rolling.”
From this point on, there’s no turning back.
Like our Hero, you should think of this stage as a checkpoint for your story. Pause and re-assess your bearings before you continue into unfamiliar territory. Have you:
- Launched the central conflict? If not, here’s a post on types of conflict to help you out.
- Established the theme of your book? If not, check out this post that’s all about creating theme and motifs .
- Made headway into your character development? If not, this character profile template may be useful:

Reedsy’s Character Profile Template
A story is only as strong as its characters. Fill this out to develop yours.
6. Tests, Allies, Enemies
In which the Hero faces new challenges and gets a squad.
When we step into the Special World, we notice a definite shift. The Hero might be discombobulated by this unfamiliar reality and its new rules. This is generally one of the longest stages in the story , as our protagonist gets to grips with this new world.
This makes a prime hunting ground for the series of tests to pass! Luckily, there are many ways for the Hero to get into trouble:
- In Jumanji: Welcome to the Jungle , Spencer, Bethany, “Fridge,” and Martha get off to a bad start when they bump into a herd of bloodthirsty hippos.
- In his first few months at Hogwarts, Harry Potter manages to fight a troll, almost fall from a broomstick and die, and get horribly lost in the Forbidden Forest.
- Marlin and Dory encounter three “reformed” sharks, get shocked by jellyfish, and are swallowed by a blue whale en route to finding Nemo.

This stage often expands the cast of characters. Once the protagonist is in the Special World, he will meet allies and enemies — or foes that turn out to be friends and vice versa. He will learn a new set of rules from them. Saloons and seedy bars are popular places for these transactions, as Vogler points out (so long as the Hero survives them).
7. Approach to the Inmost Cave
In which the Hero gets closer to his goal.
This isn’t a physical cave. Instead, the “inmost cave” refers to the most dangerous spot in the other realm — whether that’s the villain’s chambers, the lair of the fearsome dragon, or the Death Star. Almost always, it is where the ultimate goal of the quest is located.
Note that the protagonist hasn’t entered the Inmost Cave just yet. This stage is all about the approach to it. It covers all the prep work that's needed in order to defeat the villain.
In which the Hero faces his biggest test of all thus far.
Of all the tests the Hero has faced, none have made them hit rock bottom — until now. Vogler describes this phase as a “black moment.” Campbell refers to it as the “belly of the whale.” Both indicate some grim news for the Hero.
The protagonist must now confront their greatest fear. If they survive it, they will emerge transformed. This is a critical moment in the story, as Vogler explains that it will “inform every decision that the Hero makes from this point forward.”
The Ordeal is sometimes not the climax of the story. There’s more to come. But you can think of it as the main event of the second act — the one in which the Hero actually earns the title of “Hero.”
9. Reward (Seizing the Sword)
In which the Hero sees light at the end of the tunnel.
Our Hero’s been through a lot. However, the fruits of their labor are now at hand — if they can just reach out and grab them! The “reward” is the object or knowledge the Hero has fought throughout the entire journey to hold.
Once the protagonist has it in their possession, it generally has greater ramifications for the story. Vogler offers a few examples of it in action:
- Luke rescues Princess Leia and captures the plans of the Death Star — keys to defeating Darth Vader.
- Dorothy escapes from the Wicked Witch’s castle with the broomstick and the ruby slippers — keys to getting back home.

10. The Road Back
In which the light at the end of the tunnel might be a little further than the Hero thought.
The story's not over just yet, as this phase marks the beginning of Act Three. Now that he's seized the reward, the Hero tries to return to the Ordinary World, but more dangers (inconveniently) arise on the road back from the Inmost Cave.
More precisely, the Hero must deal with the consequences and aftermath of the previous act: the dragon, enraged by the Hero who’s just stolen a treasure from under his nose, starts the hunt. Or perhaps the opposing army gathers to pursue the Hero across a crowded battlefield. All further obstacles for the Hero, who must face them down before they can return home.
11. Resurrection
In which the last test is met.
Here is the true climax of the story. Everything that happened prior to this stage culminates in a crowning test for the Hero, as the Dark Side gets one last chance to triumph over the Hero.
Vogler refers to this as a “final exam” for the Hero — they must be “tested once more to see if they have really learned the lessons of the Ordeal.” It’s in this Final Battle that the protagonist goes through one more “resurrection.” As a result, this is where you’ll get most of your miraculous near-death escapes, à la James Bond's dashing deliverances. If the Hero survives, they can start looking forward to a sweet ending.
12. Return with the Elixir
In which our Hero has a triumphant homecoming.
Finally, the Hero gets to return home. However, they go back a different person than when they started out: they’ve grown and matured as a result of the journey they’ve taken.
But we’ve got to see them bring home the bacon, right? That’s why the protagonist must return with the “Elixir,” or the prize won during the journey, whether that’s an object or knowledge and insight gained.
Of course, it’s possible for a story to end on an Elixir-less note — but then the Hero would be doomed to repeat the entire adventure.
Examples of The Hero’s Journey in Action
To better understand this story template beyond the typical sword-and-sorcery genre, let's analyze three examples, from both screenplay and literature, and examine how they implement each of the twelve steps.
The 1976 film Rocky is acclaimed as one of the most iconic sports films because of Stallone’s performance and the heroic journey his character embarks on.

- Ordinary World. Rocky Balboa is a mediocre boxer and loan collector — just doing his best to live day-to-day in a poor part of Philadelphia.
- Call to Adventure. Heavyweight champ Apollo Creed decides to make a big fight interesting by giving a no-name loser a chance to challenge him. That loser: Rocky Balboa.
- Refusal of the Call. Rocky says, “Thanks, but no thanks,” given that he has no trainer and is incredibly out of shape.
- Meeting the Mentor. In steps former boxer Mickey “Mighty Mick” Goldmill, who sees potential in Rocky and starts training him physically and mentally for the fight.
- Crossing the First Threshold. Rocky crosses the threshold of no return when he accepts the fight on live TV, and 一 in parallel 一 when he crosses the threshold into his love interest Adrian’s house and asks her out on a date.
- Tests, Allies, Enemies. Rocky continues to try and win Adrian over and maintains a dubious friendship with her brother, Paulie, who provides him with raw meat to train with.
- Approach to the Inmost Cave. The Inmost Cave in Rocky is Rocky’s own mind. He fears that he’ll never amount to anything — something that he reveals when he butts heads with his trainer, Mickey, in his apartment.
- Ordeal. The start of the training montage marks the beginning of Rocky’s Ordeal. He pushes through it until he glimpses hope ahead while running up the museum steps.
- Reward (Seizing the Sword). Rocky's reward is the restoration of his self-belief, as he recognizes he can try to “go the distance” with Apollo Creed and prove he's more than "just another bum from the neighborhood."
- The Road Back. On New Year's Day, the fight takes place. Rocky capitalizes on Creed's overconfidence to start strong, yet Apollo makes a comeback, resulting in a balanced match.
- Resurrection. The fight inflicts multiple injuries and pushes both men to the brink of exhaustion, with Rocky being knocked down numerous times. But he consistently rises to his feet, enduring through 15 grueling rounds.
- Return with the Elixir. Rocky loses the fight — but it doesn’t matter. He’s won back his confidence and he’s got Adrian, who tells him that she loves him.
Moving outside of the ring, let’s see how this story structure holds on a completely different planet and with a character in complete isolation.
The Martian
In Andy Weir’s self-published bestseller (better known for its big screen adaptation) we follow astronaut Mark Watney as he endures the challenges of surviving on Mars and working out a way to get back home.

- The Ordinary World. Botanist Mark and other astronauts are on a mission on Mars to study the planet and gather samples. They live harmoniously in a structure known as "the Hab.”
- Call to Adventure. The mission is scrapped due to a violent dust storm. As they rush to launch, Mark is flung out of sight and the team believes him to be dead. He is, however, very much alive — stranded on Mars with no way of communicating with anyone back home.
- Refusal of the Call. With limited supplies and grim odds of survival, Mark concludes that he will likely perish on the desolate planet.
- Meeting the Mentor. Thanks to his resourcefulness and scientific knowledge he starts to figure out how to survive until the next Mars mission arrives.
- Crossing the First Threshold. Mark crosses the mental threshold of even trying to survive 一 he successfully creates a greenhouse to cultivate a potato crop, creating a food supply that will last long enough.
- Tests, Allies, Enemies. Loneliness and other difficulties test his spirit, pushing him to establish contact with Earth and the people at NASA, who devise a plan to help.
- Approach to the Inmost Cave. Mark faces starvation once again after an explosion destroys his potato crop.
- Ordeal. A NASA rocket destined to deliver supplies to Mark disintegrates after liftoff and all hope seems lost.
- Reward (Seizing the Sword). Mark’s efforts to survive are rewarded with a new possibility to leave the planet. His team 一 now aware that he’s alive 一 defies orders from NASA and heads back to Mars to rescue their comrade.
- The Road Back. Executing the new plan is immensely difficult 一 Mark has to travel far to locate the spaceship for his escape, and almost dies along the way.
- Resurrection. Mark is unable to get close enough to his teammates' ship but finds a way to propel himself in empty space towards them, and gets aboard safely.
- Return with the Elixir. Now a survival instructor for aspiring astronauts, Mark teaches students that space is indifferent and that survival hinges on solving one problem after another, as well as the importance of other people’s help.
Coming back to Earth, let’s now examine a heroine’s journey through the wilderness of the Pacific Crest Trail and her… humanity.
The memoir Wild narrates the three-month-long hiking adventure of Cheryl Strayed across the Pacific coast, as she grapples with her turbulent past and rediscovers her inner strength.

- The Ordinary World. Cheryl shares her strong bond with her mother who was her strength during a tough childhood with an abusive father.
- Call to Adventure. As her mother succumbs to lung cancer, Cheryl faces the heart-wrenching reality to confront life's challenges on her own.
- Refusal of the Call. Cheryl spirals down into a destructive path of substance abuse and infidelity, which leads to hit rock bottom with a divorce and unwanted pregnancy.
- Meeting the Mentor. Her best friend Lisa supports her during her darkest time. One day she notices the Pacific Trail guidebook, which gives her hope to find her way back to her inner strength.
- Crossing the First Threshold. She quits her job, sells her belongings, and visits her mother’s grave before traveling to Mojave, where the trek begins.
- Tests, Allies, Enemies. Cheryl is tested by her heavy bag, blisters, rattlesnakes, and exhaustion, but many strangers help her along the trail with a warm meal or hiking tips.
- Approach to the Inmost Cave. As Cheryl goes through particularly tough and snowy parts of the trail her emotional baggage starts to catch up with her.
- Ordeal. She inadvertently drops one of her shoes off a cliff, and the incident unearths the helplessness she's been evading since her mother's passing.
- Reward (Seizing the Sword). Cheryl soldiers on, trekking an impressive 50 miles in duct-taped sandals before finally securing a new pair of shoes. This small victory amplifies her self-confidence.
- The Road Back. On the last stretch, she battles thirst, sketchy hunters, and a storm, but more importantly, she revisits her most poignant and painful memories.
- Resurrection. Cheryl forgives herself for damaging her marriage and her sense of worth, owning up to her mistakes. A pivotal moment happens at Crater Lake, where she lets go of her frustration at her mother for passing away.
- Return with the Elixir. Cheryl reaches the Bridge of the Gods and completes the trail. She has found her inner strength and determination for life's next steps.
There are countless other stories that could align with this template, but it's not always the perfect fit. So, let's look into when authors should consider it or not.
When should writers use The Hero’s Journey?

The Hero’s Journey is just one way to outline a novel and dissect a plot. For more longstanding theories on the topic, you can go this way to read about the ever-popular Three-Act Structure or here to discover Dan Harmon's Story Circle and three more prevalent structures .
So when is it best to use the Hero’s Journey? There are a couple of circumstances which might make this a good choice.
When you need more specific story guidance than simple structures can offer
Simply put, the Hero’s Journey structure is far more detailed and closely defined than other story structure theories. If you want a fairly specific framework for your work than a thee-act structure, the Hero’s Journey can be a great place to start.
Of course, rules are made to be broken . There’s plenty of room to play within the confines of the Hero’s Journey, despite it appearing fairly prescriptive at first glance. Do you want to experiment with an abbreviated “Resurrection” stage, as J.K. Rowling did in Harry Potter and the Sorcerer’s Stone? Are you more interested in exploring the journey of an anti-hero? It’s all possible.
Once you understand the basics of this universal story structure, you can use and bend it in ways that disrupt reader expectations.
Need more help developing your book? Try this template on for size:

Get our Book Development Template
Use this template to go from a vague idea to a solid plan for a first draft.
When your focus is on a single protagonist
No matter how sprawling or epic the world you’re writing is, if your story is, at its core, focused on a single character’s journey, then this is a good story structure for you. It’s kind of in the name! If you’re dealing with an entire ensemble, the Hero’s Journey may not give you the scope to explore all of your characters’ plots and subplot — a broader three-act structure may give you more freedom to weave a greater number story threads.
Which story structure is right for you?
Take this quiz and we'll match your story to a structure in minutes!
Whether you're a reader or writer, we hope our guide has helped you understand this universal story arc. Want to know more about story structure? We explain 6 more in our guide — read on!
6 responses
PJ Reece says:
25/07/2018 – 19:41
Nice vid, good intro to story structure. Typically, though, the 'hero's journey' misses the all-important point of the Act II crisis. There, where the hero faces his/her/its existential crisis, they must DIE. The old character is largely destroyed -- which is the absolute pre-condition to 'waking up' to what must be done. It's not more clever thinking; it's not thinking at all. Its SEEING. So many writing texts miss this point. It's tantamount to a religions experience, and nobody grows up without it. STORY STRUCTURE TO DIE FOR examines this dramatic necessity.
↪️ C.T. Cheek replied:
13/11/2019 – 21:01
Okay, but wouldn't the Act II crisis find itself in the Ordeal? The Hero is tested and arguably looses his/her/its past-self for the new one. Typically, the Hero is not fully "reborn" until the Resurrection, in which they defeat the hypothetical dragon and overcome the conflict of the story. It's kind of this process of rebirth beginning in the earlier sections of the Hero's Journey and ending in the Resurrection and affirmed in the Return with the Elixir.
Lexi Mize says:
25/07/2018 – 22:33
Great article. Odd how one can take nearly every story and somewhat plug it into such a pattern.
Bailey Koch says:
11/06/2019 – 02:16
This was totally lit fam!!!!
↪️ Bailey Koch replied:
11/09/2019 – 03:46
where is my dad?
Frank says:
12/04/2020 – 12:40
Great article, thanks! :) But Vogler didn't expand Campbell's theory. Campbell had seventeen stages, not twelve.
Comments are currently closed.
Join a community of over 1 million authors
Reedsy is more than just a blog. Become a member today to discover how we can help you publish a beautiful book.
Bring your stories to life
Our free writing app lets you set writing goals and track your progress, so you can finally write that book!

1 million authors trust the professionals on Reedsy. Come meet them.
Enter your email or get started with a social account:
7 Hero’s Journey Examples In Real Life
If you’re looking for hero’s journey examples in real life, here are the books and movies to seek out – plus, get tips on applying the template to your story!
The hero’s journey is one we all know well: it has formed the structure of our stories, myths, and legends since humans first began to weave tales and remains part of our collective subconscious today. Joseph Campbell detailed the tropes of the hero’s journey in his seminal book, The Hero with a Thousand Faces , setting out the key stages that a main character typically progresses through: Odysseus and Katniss Everdeen , though thousands of years apart in their creation, must navigate these same phases of their journeys.
So, we know the hero’s journey in movies and stories is a popular storytelling framework, but what about real life?
Below, we take a look at how this template can translate into real-world tales of heroism and adventure and how the story structure of the hero’s journey can inform our understanding of them. Plus, we give you a getting-started guide on applying the hero’s journey template to recount your own real-life experiences.
Here Are Best Hero’s Journey Examples In Real Life
1. jarhead by anthony swofford, 2. the pursuit of happyness by chris gardner, 3. gorillas in the mist by dian fossey, 4. apollo 13 by jim lovell and jeffrey klugar, 5. a beautiful mind by sylvia nasar, 6. girl waits with gun by amy stewart, 7. annapurna by maurice herzog, how to craft your hero’s journey, finding each stage, becoming your own mythologist.

As the narrator of his own story, Swofford offers up to the reader his experiences as a young Marine rifle sniper in the first Gulf War . Although the book is based on real events, its structure perfectly reflects the steps of the hero’s journey as they appear in stories through the ages.
Beginning in the ordinary world of his childhood, the narrator details his desire to join the military (specifically, the Marine Corps) from a young age. On the surface, our hero’s journey may look very different from that of Odysseus or Frodo Baggins, but dig a little deeper, and it mirrors the quests that these characters undertake. Leaving his known world behind to join the military, the narrator soon fears he has made a terrible error.
This narrator appears to be The Warrior archetypal hero – but herein lies the rub. The protagonist aligns with an entirely different archetype (possibly that of The Researcher), which causes much of the psychological conflict within the book.
After the Crossing the Threshold section, where the narrator begins his military training and endures the various privations of boot camp, he must face many trials and tribulations, from mental breakdown to dealing with the inadequate kit that puts the life of himself and his comrades at risk, and the daily discomfort of living in the desert.
The book is a disturbing insight into the psychological impact of being trained to kill, and war. The Return with the Elixir is powerful: it’s only many years after leaving the Marines, and much time spent reflecting that the narrator can dissect his experiences and recognize the lessons inherent within them – the book that he wrote, as a result, is the manifestation of the elixir.
“Every war is different. Every war is the same.” Anthony Swofford
- Orders are despatched from our UK warehouse next working day.
- Swofford, Anthony (Author)
- English (Publication Language)
- 272 Pages - 04/05/2024 (Publication Date) - Scribner Book Company (Publisher)
Perfectly embodying all the stages of the hero’s journey, this book tells the true story of a man who’d just landed a promising role in the world of finance before getting caught up in a terrible, unexpected spiral of life events that result in him and his young son finding themselves on the streets, homeless.
The road of trials is a bitter and brutal one. The narrator spends nearly a year in shelters, waiting in soup lines and sleeping rough. But, despite the terrible tribulations he faces, Gardner does not give in, determined never to be parted from his son but to seek the Road Back – just as the heroes in Campbell’s monomyths successfully do. Eventually, the circle closes, and the narrator and his son return home as Campbell transitions from the invisible homeless to an influential, powerful, highly visible figure in the world of high finance.
Critics have likened The Pursuit of Happyness to a myth for its resonance, power, and timelessness. This means that when the hero returns, we’re all on our feet, having rooted for his triumph throughout. Because his victory becomes our collective redemption.
“Still a dream, yet more a realist than ever before, I knew this was my time to sail.” Chris Gardner
- Chris Gardner (Author)
- 320 Pages - 10/24/2006 (Publication Date) - Amistad (Publisher)
Widely cited as one of the most important books ever written about the connection of humans to the natural world, Gorillas in the Mist follows Fossey as she leaves behind her everyday life to enter a special world deep within the rainforests of the Virunga Mountains in Africa. Fossey subsequently spent thirteen years studying and living with a family of mountain gorillas , enduring the daily challenges of loneliness, constant rain, and the threat of poachers.
Fossey’s work was highly influential in convincing people of primates’ innate sentience, and she was fiercely determined in her conversation efforts and opposition to poaching. Tragically, Fossey was murdered in her remote cabin in Rwanda in 1985. But her legacy was powerful: her research and work in the field helped reduce the downward trend of the mountain gorilla population.
The book is a personal adventure story and a quest for enlightenment, with Fossey detailing her attempts at securing the future of the mountain apes that she spends so many years studying. The publication itself serves as her Return with the Elixir (a key stage in the hero’s journey): designed to pass on knowledge of our closest primate relatives, the specialness of these animals, and what must be done to safeguard their survival.
“There are times when one cannot accept facts for fear of shattering one’s being.” Dian Fossey
- Mint Condition
- Dispatch same day for order received before 12 noon
- Guaranteed packaging
- No quibbles returns
Used as the basis of the Apollo 13 movie, this is the real-life account of the lunar shot that nearly ended in total catastrophe. As well as spawning the Hollywood blockbuster film of the same name, the book is told using the classic hero’s journey template – evidence of how ingrained this storytelling is in our collective subconscious.
This story literally starts in the known world, Earth, before the Crossing of the Threshold stage, where Jim and his crew are recruited for the daring mission. Next comes The Ordeal. An explosion shortly after launch forces the astronauts to abandon the main ship, seeking refuge in the lunar capsule – which was designed to keep two men alive for just two days. The Return Home stage is fraught with danger, and the narrative shifts focus to what’s going on at mission control to ensure the men’s safe return.
The Return with the Elixer is the last of the steps of the hero’s journey. In the case of this story, it is represented both by the astronauts’ changed sense of self in the wake of the events they’ve endured and in the vital information that NASA has gained from the experience and the rescue, which will inform future space missions.
“From now on, we live in a world where man has walked on the moon. And it’s not a miracle, we just decided to go.” Jim Lovell
- James Lovell (Author)
- 400 Pages - 08/17/1995 (Publication Date) - Coronet (Publisher)
This biography of the Nobel prize-winning mathematician and economist John Forbes Nash Jr. was nominated for the Pulitzer prize upon its release. It was later adapted into a film directed by Russell Howard. It features an unlikely hero – but a hero nonetheless – in its subject, Nash, a brilliant mathematician whose descent into serious mental illness derailed his career and had devastating effects on his personal life.
The Road of Trials was a harrowing one for Nash. Schizophrenia meant he missed out on a Nobel Prize, despite his game-changing work on game theory – which, by the 1980s, was underpinning much of economics. The Nobel committee decided they weren’t prepared to give the award to him due to his mental illness.
Step-by-step Nash recovered, and in 1994 his work finally received the credit it deserved. He shared the Nobel Prize for Economics with two others. In the subsequent critically-praised film, the movie’s screenwriter perfectly captured the impact of this journey on Nash and those around him.
Nash’s subsequent invitation from Princeton to join the faculty as a professor is his apotheosis moment: this is a key stage of the hero’s journey, as described by Joseph Campbell. It’s the point where, after defeating the enemy, the hero travels toward and meets their destiny.
Linked to this stage is the receiving of the Ultimate Boon: in A Beautiful Mind, this is represented by Nash’s re-connection with his old life. He rebuilds relationships with friends and family members that had been lost during his trials. And, most powerfully of all, connecting once more with his ex-wife, the pair remarried in 2001 and lived – of course – happily ever after.
“People look to the order of numbers when the world falls apart.” Sylvia Nasar
- Sylvia Nasar (Author)
- 461 Pages - 04/04/1999 (Publication Date) - Faber and Faber (Publisher)

Based on the true story of one of the US’ first female sheriffs, Girls Waits with Gun tells the story of Constance Kopp and her two sisters. It’s a hero’s journey story that, like Kopp herself, breaks the mold of the genre. The tale, as a whole, is about finding your place in a world that sees you as a misfit: Kopp isn’t interested in getting married and has no time for a quiet domestic routine. Instead, she yearns for adventure and independence.
The Call to Action announces itself loud and clear: when a drunk driver, Henry Kaufman (owner of the local silk factory), crashes into the sisters’ buggy, Kopp demands the man pay for the damages. When he refuses, she begins plotting how to obtain justice. The First Threshold is crossed when, turning up at the silk factory, Kopp meets an employee in a state of high distress: her baby has gone missing.
A campaign of intimidation against the sisters unfolds, which results in the sheriff arming the women for them to defend themselves. But neither Kopp nor her sisters are prepared to back down, and Constance can’t get the missing baby out of her mind…
As a direct result of successfully navigating her trials and tribulations, Kaufman ends up in court, and the judge finds against him. There’s a buzz around Kopp, who’s now famed for her bravery and tenacity – so much so that the sheriff offers her the Ultimate Boon: the position of undersheriff – a role in which no woman had ever served before.
“We have to be a part of the world in which we live. We don’t scurry away when we’re in trouble, or if someone else is. We don’t run and hide.” Amy Stewart
- 416 Pages - 03/10/2016 (Publication Date) - Scribe Publications (Publisher)
A survival story is a perfect vehicle in which to deploy the hero’s journey structure. Annapurna recounts Herzog’s attempt in 1950 (along with his climbing partner Louis Lachenel) to scale the notorious, treacherous Himalayan mountain, after which the book is named.
The trials and tribulations that follow are brutal: frostbite and snow blindness nearly resulted in the death of the two climbers, but ultimately, they were successful in their quest. The Road Back is not just a spiritual one: it’s represented by the very real climb back down the mountain. And the Ultimate Boon? Having passed through The Ordeal, Herzog and Lachenel were recognized as the first expedition in history to have reached the summit of an 8,000-plus meter mountain…and return alive.
The book has enjoyed enduring appeal since its first publication in 1951, which turned Herzog into the world’s first mountaineering celebrity! National Geographic ranked Annapurna at number six in its list of 100 Greatest Adventure and Exploration Books, claiming it to be one of the most influential books on mountaineering of all time.
“Annapurna, to which we had gone empty-handed, was a treasure on which we should live the rest of our days. With this realization we turn the page: a new life begins.” Maurice Herezog
- Herzog, Maurice; Joe Simpson (new introduction) (Author)
- 288 Pages - 04/04/1997 (Publication Date) - Pimlico (Publisher)
Applying the Hero’s Journey Template to Your Own Life Story
The monomyth template is a powerful tool for fictional and real-life stories. The same steps can be discerned in Frodo’s journey to Mordor in The Lord of the Rings, in Harry Potter’s quest to discover his wizarding destiny, and in Luke Skywalker’s adventure that takes him from moisture farm worker to Jedi in Star Wars can be deployed to create a compelling true-life tale.
Begin by identifying some of the key stages in the hero’s journey to add structure and dynamism to your story. Start the tale in the Ordinary World. Write about your subject’s life before the Call to Adventure. Next is a Refusal of the Call moment. Perhaps the individual unexpectedly got awarded a scholarship or was presented with an opportunity to travel abroad? If they were initially reluctant to cross this First Threshold, then this marks the important Refusal stage. For inspiration, read our article profile common essays about heroes .
Work through the story you want to tell, using Campbell’s hero outline to find those milestones in the tale that can act as both strong organizing and structural devices. While there may not be the presence of supernatural aids as mentors, look to your narrator’s key allies with a view to how they fulfill this role. Consider a moment that marked the Return Threshold and how your narrator and those around them reacted to it.
You may be surprised at just how natural the hero’s journey template fits when crafting a real life story – whether your own or someone else’s. The power of myth is so potent, after all, because it captures the kernel of our collective human experience, across borders and time.
Try using this story structure when creating a piece of creative writing or crafting a documentary or video content. The hero’s journey structure can even be used to assemble and edit a wedding video to create a powerful narrative that stirs emotions!

Melanie Smith is a freelance content and creative writer from Gloucestershire, UK, where she lives with her daughter, long-suffering partner, and cat, The Magical Mr. Bobo. Her blog posts and articles feature regularly in magazines and websites around the world.
View all posts
- Book Category Tool
- Gadgets and Gizmos
- All About Me
The Hero’s Journey: The 12 (or 17) Steps for Writers
- by Sam Howard
In this article, you will learn all about the hero’s journey – the common template seen in many myths, legends, and stories across cultures that involves a hero going on an adventure, overcoming challenges, and returning home transformed. Specifically, we will cover:
- What the hero’s journey is and why it’s so prevalent in storytelling
- The origins of the hero’s journey concept by Joseph Campbell
- The 12 main stages of the journey outlined by Christopher Vogler
- Examples of the hero’s journey in famous myths, films, novels, and stories
- Tips for using the hero’s journey structure in your own writing
When I first learned about the hero’s journey, I was fascinated by how this template seems to capture the essence of storytelling and the universal human experience. In this article, I’ll share my own excitement and perspectives on this captivating concept as we explore what makes the hero’s journey such a timeless and powerful narrative structure. Let’s begin our own adventure into the world of the monomyth!
What Is the Hero’s Journey And Why Do People Talk About it All The Time?
The hero’s journey, also referred to as the monomyth, is essentially the common template of stories that involve a hero who goes on an adventure, faces various challenges, comes through a crisis or major ordeal, and returns home transformed in some fundamental way.
This basic narrative arc can be traced back centuries and is found in myths, legends, folklore, and religious tales across vastly different cultures. For example, the epic of Gilgamesh from ancient Mesopotamia, the Odyssey by Homer, the legend of the Buddha’s enlightenment, the Bible stories of Moses and Jesus, and medieval Arthurian legends, all follow this fundamental template.
The hero’s journey was popularized in the 20th century by American mythologist Joseph Campbell. In his seminal 1949 book The Hero with a Thousand Faces, Campbell analyzed myths across cultures and found this common throughline structure he called the monomyth. He summarized the journey in this way:
“A hero ventures forth from the world of common day into a region of supernatural wonder: fabulous forces are there encountered and a decisive victory is won: the hero comes back from this mysterious adventure with the power to bestow boons on his fellow man.”
Ever since Campbell published his work, the hero’s journey concept has been applied extensively in understanding myths, legends, films, novels, plays, video games, and all types of stories. Writers, directors, storytellers, and artists have latched onto this idea because it seems to resonate with universal themes about human experience.
We all face trials and challenges in life. We go on both physical and emotional journeys to overcome obstacles and grow. In stories, we get to live vicariously through the heroic protagonist. The hero’s journey allows us to relate to them and be inspired by their perseverance. At its core, this monomythic cycle ties into concepts like love, sacrifice, courage, transformation, and fulfilling one’s destiny. These timeless themes and character arcs continue to captivate audiences and new generations.
The 12 Stages of the Hero’s Journey (as outlined by Christopher Vogler)
While Joseph Campbell originally outlined 17 stages of the monomyth in his book, screenwriter Christopher Vogler simplified it into 12 stages in a popular guidebook for writers. Known as the hero’s journey model, these 12 steps are:
- Ordinary World
- Call to Adventure
- Refusal of the Call
- Meeting the Mentor
- Crossing the Threshold
- Tests, Allies, Enemies
- Approach to the Inmost Cave
- The Road Back
- Resurrection
- Return with the Elixir
Let’s look at each of these 12 stages in more detail:
1. Ordinary World
The hero exists in the ordinary world, their normal environment, when we first meet them. This allows us to see what their daily life is like before the adventure begins. In The Matrix, we see Neo living an ordinary life as a computer programmer before he is called to his destiny. In Harry Potter, we witness Harry’s difficult life with the Dursleys until he’s summoned to Hogwarts.
The ordinary world establishes the status quo that will eventually be disrupted as the journey unfolds. It lets us relate to the hero as an everyday person like us before they embark on something extraordinary.
2. Call to Adventure
The hero receives a call to go on an adventure that disrupts their ordinary world. It may come in the form of a threat to the hero or their community. This call could come from a herald like Gandalf summoning Frodo in Lord of the Rings. Or it may be adventure itself that calls to the hero, spurring them to seize new opportunities.
However it arrives, the call ignites the hero’s journey as they are drawn into a new world of possibilities. But hearing the call is just the beginning of their transformation.
3. Refusal of the Call
When presented with the call to adventure, the hero may initially refuse or express reluctance to embark on the journey. Refusing the call hints at their fears or shortcomings that must be overcome.
At this stage, heroes might believe they are unfit for the journey ahead. Bilbo Baggins tries refusing Gandalf’s request for him to join the dwarves in reclaiming their home. Other times, refusal comes from a sense of duty preventing the hero from leaving home.
4. Meeting the Mentor
The hero needs guidance to answer the call, which comes in the form of a mentor figure. The mentor prepares the hero for the journey ahead by training, advising, and empowering them.
The mentor can appear as a wise old wizard like Merlin or Dumbledore. Or they may impart wisdom in less obvious ways. In The Karate Kid, the unassuming maintenance man Mr. Miyagi mentors Daniel through karate lessons and life advice that transform him. Whatever form they take, the mentor molds the hero toward being ready to face their destiny.
5. Crossing the Threshold
The hero commits wholeheartedly to the adventure by crossing the threshold into the special world beyond their ordinary one. There is often an actual threshold representing the boundary between worlds.
Dorothy leaves Kansas behind by squinting through the door of her tornado-blown house into the colorful Land of Oz. By committing to the journey, the hero enters Act Two, facing tests in the special world. The threshold marks the point of no return.
6. Tests, Allies, Enemies
In the special world of Act Two, the hero faces a series of tests that allow them to gather allies and enemies. The tests are part of the training the hero must undergo to prepare for the bigger ordeals yet to come.
The hero discovers new abilities, but also weaknesses that they seek to overcome. Allies join the hero on the journey and work with them to pass tests. Enemies create obstacles and complications for the hero. Through these trials and relationships, we see the hero change and grow.
7. Approach to the Inmost Cave
The inmost cave may be an actual location in the special world, but really represents the innermost darkness of the hero’s psyche, their deepest fear they must face. As they approach this critical juncture, they prepare themselves for facing this ultimate ordeal.
On the approach, the hero may appear to be reaching their goal or think the journey is coming to an end, only to find this is yet another prelude to a more difficult confrontation with death ahead.
8. The Ordeal
Here, the hero undergoes the supreme ordeal of facing their greatest fear in the hope of being rewarded or resurrected anew. This is the climactic central confrontation often representing facing death and rebirth both metaphorically and literally.
The ordeal allows the hero to conquer their enemies or shadowy aspects of themselves once and for all. By dying to their old self, they can be reborn as their true heroic self.
After surviving death in the ordeal, the hero gains the reward they’ve sought like the holy grail or some elixir to save their people. It may come in the form of new knowledge or insight. This rest period lets us see the hero enjoy the fruits of their labor and sacrifice.
10. The Road Back
Carrying the reward, the hero begins their return journey home to the ordinary world. But the adventure isn’t over yet. New dangerous obstacles arise that imperil the hero’s journey home.
The stakes are raised once more as the hero must stay resilient on the road back, holding onto the reward and wisdom gained from their difficult trials. The journey is about mastery of two worlds.
11. Resurrection
As the hero nears the threshold home, they must endure one last test where everything learned so far is put to the ultimate test. Facing mortal danger, they may need rescue from without. This final trial leads to the hero’s resurrection and ascension as a superior being.

12. Return with the Elixir
This brings the hero full circle as they return to the ordinary world, but able to bestow gifts on that world as a powerful guide ready to lead others. Their elixir is the wisdom gained from the ordeal. The hero comes back from death transformed and enlightened.
By mastering and balancing both worlds, the hero is a carrier of boons to help renew their community. They return wiser and more enlightened than when they started.
The Original 17 Stages of the Hero’s Journey (as outlined by Joseph Campbell)
Joseph Campbell’s original 1949 outline of the monomyth actually had more stages – 17 steps versus the simplified version’s 12 steps. Campbell’s 17 stages, grouped into a three act structure, are:
Act I – Departure
- The Call to Adventure
- Supernatural Aid
- Crossing the First Threshold
- Belly of the Whale
Act II – Initiation
- The Road of Trials
- Meeting with the Goddess
- Woman as Temptress
- Atonement with the Father
- The Ultimate Boon
Act III – Return
- Refusal of the Return
- Magic Flight
- Rescue from Without
- Crossing the Return Threshold
- Master of Two Worlds
- Freedom to Live
While containing more steps, Campbell’s outline aligns with Vogler’s simplified version covering departure, initiation, and return. The expanded 17 stages provide more details about certain phases of the journey. Both models offer a guide to crafting an archetypal heroic story.
My Favorite Examples of the Hero’s Journey
The hero’s journey monomyth structure has been analyzed in many myths, legends, films and stories. Here are some of my personal favorites:
- The Odyssey – This classic epic by Homer shaped much of the hero’s journey template through Odysseus’s long difficult voyage home after the Trojan War.
- Star Wars – Luke Skywalker’s journey follows the hero template faithfully, one reason the film resonates so powerfully.
- The Matrix – Neo’s journey from hacker to hero/savior closely aligns with the monomyth. Facing Agent Smith is akin to an ordeal and resurrection.
- Harry Potter – Harry progresses through each stage, mentored by Dumbledore, gaining allies like Hermione and Ron, facing enemies like Voldemort, dying and returning to defeat evil.
- The Lion King – Simba’s epic quest contains numerous stages like crossing a threshold into the elephant graveyard, undergoing an ordeal facing his evil uncle, and returning to restore the kingdom.
Each example above takes the universal monomyth template and makes it singular and unforgettable by creating iconic heroes, mentors, allies and villains. The hero’s journey is infinitely malleable.
How to Use the Hero’s Journey in a Novel
If you want to employ the hero’s journey structure in your own novel or screenplay, here are some tips:
- Have a clear vision of your hero and their ordinary world before disrupting it with the call to adventure.
- Make your mentor, allies and enemies dimensional, memorable characters that impact the hero.
- Structure key events like the ordeal, the climax, and the hero’s resurrection around the middle and end to shape the emotional arc.
- Customize the template to fit your unique story needs. Not all 17 stages must be included.
- Outline the stages before writing, but also allow some to emerge organically from story and characters.
- Include symbolic thresholds like crossroads, gates, bridges, or actual magical portals marking transitions into new worlds.
- Use tests in the special world to allow your hero to grow incrementally through small wins and losses.
- Consider how bringing back the “elixir” transforms not just the hero but also their community.
In essence, incorporating a monomyth structure provides a time-tested narrative arc while leaving plenty of room for your own imaginative embellishment. Allow the template to guide, not limit, your creativity.
That concludes my personal guide to the hero’s journey draws from myths, films and literature! I hope relaying my own perspectives and enthusiasm brought this monomyth template to life. Now that you’ve completed your own vicarious adventure through the world of the hero’s journey, you have all the tools to craft an epic tale full of memorable characters, riveting ordeals and triumphant returns. Wishing you the best as you set forth on your own writing journey ahead!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Hero’s Journey: 12 Steps, Examples, Use Cases
- Post author By Punit Thakkar
- Post date January 7, 2024
Once you’ve decided that you need to Outline your story before you start writing the screenplay, you will need to choose between the various storytelling structures out there. The three-act structure as a narrative breakdown can be applied to almost any story. But to further breakdown your story in beats, certain storytelling frameworks can be quite useful. One such framework is the Hero’s Journey by Joseph Campbell.
Who is Joseph Campbell?
Joseph Campbell (1904–1987) was an American mythologist, writer, and lecturer best known for his work in comparative mythology and his exploration of the hero’s journey. Campbell’s most influential work is the concept of the monomyth or the hero’s journey. This was the result of his examination of common patterns and themes found in the myths and legends of various cultures throughout history.
What is the Hero’s Journey?
In 1949, Campbell published his book “ The Hero with a Thousand Faces “. In this seminal work, he examined common patterns and themes found in the myths and legends of various cultures throughout history. The phrase “Hero’s Journey” suggests that myths and stories from different cultures often follow a similar narrative structure. The hero typically embarks on an adventure, faces challenges and trials, undergoes a transformation, and returns home changed. It was later popularized by screenwriter, Christopher Vogler, in his book “ The Writer’s Journey “. Vogler condensed the principles into a 12-step framework.
12 Steps of The Hero’s Journey
Let’s take a look at each of the 12 steps that you can use to outline your story. To illustrate the same, we’ll be using the application of this concept with a movie where the filmmaker was famously inspired by the Hero’s Journey template while writing his film ie. Star Wars (1977).
1. Ordinary World
The hero begins in their familiar environment, often characterized by routine and unawareness of the larger journey. This setting establishes the baseline for the hero’s growth.
Application : Luke Skywalker resides on the desert planet Tatooine, leading a mundane life as a farm boy.
2. Call to Adventure
An external event or internal desire disrupts the hero’s ordinary life, presenting an opportunity or challenge that sets the journey in motion. The call often introduces a quest or a significant change.
Application : Obi-Wan Kenobi invites Luke to join him in the quest to deliver the Death Star plans to the Rebel Alliance.
3. Refusal of the Call
Faced with uncertainty, fear, or a sense of duty to the familiar world, the hero hesitates or rejects the call initially. This reluctance adds depth to the hero’s internal conflict.
Application : Luke hesitates to leave Tatooine, citing responsibilities and family ties.
4. Meeting the Mentor
A mentor figure appears, providing guidance, wisdom, or supernatural aid. The mentor equips the hero with the tools or knowledge necessary for the journey.
Application : Obi-Wan becomes Luke’s mentor, introducing him to the Force and encouraging his journey.
5. Crossing the Threshold
The hero decides to leave the ordinary world, venturing into the unknown or a special world. This crossing represents a commitment to change and growth.
Application : Luke, with Obi-Wan, departs Tatooine and enters the larger galaxy.
6. Tests, Allies, Enemies
The hero encounters challenges, forms alliances with companions, and faces adversaries. These experiences shape the hero’s character and prepare them for more significant trials.
Application : Luke, Han Solo, and Princess Leia face various trials, forming alliances and encountering Imperial forces.
7. Approach to the Inmost Cave
The hero approaches a central challenge or a crucial location that holds the key to their quest. This stage builds anticipation and sets the stage for the ordeal.
Application : The Rebel Alliance plans to attack the Death Star, a critical mission.
The hero undergoes a severe trial, facing the most significant danger or fear. This moment tests the hero’s resolve and marks a pivotal point in the journey.
Application : Luke participates in the Battle of Yavin, aiming to destroy the Death Star amidst intense opposition.
Following the ordeal, the hero reaps a reward, gains new insight, or achieves success. This stage highlights the hero’s growth and the tangible or intangible benefits of the journey.
Application : Luke successfully destroys the Death Star, earning recognition and hero status.
10. The Road Back
The hero begins the journey back to the ordinary world, often encountering new challenges or facing the consequences of their actions. This stage introduces the final hurdles.
Application : The Rebels regroup and plan their next moves after the Death Star’s destruction.
11. Resurrection
The hero faces a final, life-altering test, representing a symbolic death and rebirth. This transformative experience solidifies the hero’s evolution.
Application : Luke confronts Darth Vader and the Death Star’s destruction leads to a symbolic rebirth.
12. Return with the Elixir
The hero returns to the ordinary world, bringing back the elixir—a tangible or metaphorical boon gained during the journey. This stage showcases the hero’s ability to contribute positively to the ordinary world.
Application : Luke returns to Tatooine, having become a skilled pilot and a key figure in the Rebel Alliance.
As we saw, Star Wars follows the Hero’s Journey with Luke Skywalker as the protagonist. From his ordinary life on Tatooine to the battles against the Empire and the ultimate confrontation with Darth Vader, the film adheres to the monomyth structure.
Use Cases: Stories Tailored for Hero’s Journey
One of the common beliefs around this template is that it typically applies to fantasy and adventure genres. While those genres are more naturally suited, the Hero’s Journey is equally applicable to different kinds of movies. It is particularly useful for stories that fall within the following genres or themes:
Fantasy and Adventure
The Hero’s Journey is frequently employed in fantasy tales where characters embark on epic quests. Examples include “The Lord of the Rings,” “Harry Potter,” and “The Chronicles of Narnia.”
Coming-of-Age Stories
Many coming-of-age narratives use the Hero’s Journey to depict a character’s maturation and self-discovery. Films like “The Karate Kid” and “Stand by Me” exemplify this application.
Science Fiction Epics
Stories set in futuristic or otherworldly settings often utilize the Hero’s Journey. “Star Wars” and “The Matrix” showcase how this structure can be applied in the science fiction genre.
Mythology and Legends
The Hero’s Journey is deeply rooted in mythology and is thus well-suited for stories inspired by ancient myths and legends. Examples include adaptations of Greek myths or Arthurian legends.
Quest Narratives
Any story that involves a quest, whether it’s a literal journey or a metaphorical one, can benefit from the Hero’s Journey structure. “Indiana Jones” and “The Odyssey” are classic examples.
Superhero Origin Stories
Many superhero origin stories align with the Hero’s Journey as characters discover their powers, face adversaries, and undergo personal growth. Examples include “Spider-Man,” “Wonder Woman,” and “Black Panther.”
Historical and Period Dramas
Even in stories set in historical or period settings, the Hero’s Journey can be applied. Films like “Braveheart” and “Gladiator” showcase protagonists facing significant challenges and transformation.
Character-Driven Dramas
While traditionally associated with more fantastical genres, the Hero’s Journey can also be adapted for character-driven dramas. Movies like “Forrest Gump” and “The Pursuit of Happyness” demonstrate this versatility.
Let’s take a look at one such example using the poignant, “non-heroic” drama written by Greta Gerwig ie. Ladybird.
Ladybird – Hero’s Journey
1. The Ordinary World : Christine “Lady Bird” McPherson navigates her senior year in high school in Sacramento, California. Dissatisfied with her surroundings and yearning for something more, she grapples with the challenges of adolescence.
2. Call to Adventure : Lady Bird desires to escape Sacramento and attend college on the East Coast, envisioning it as the key to a more fulfilling life beyond her current circumstances.
3. Refusal of the Cal l: Lady Bird’s family faces financial struggles, and her dream of attending an expensive East Coast college seems unattainable. She initially grapples with the reality of her family’s limitations.
4. Meeting the Mentor : Sister Sarah Joan, Lady Bird’s school principal, becomes a mentor figure, encouraging her to pursue her dreams and offering guidance.
5. Crossing the Threshold : Lady Bird applies to colleges in New York, symbolizing her venture into a world beyond Sacramento and her family’s constraints.
6. Tests, Allies, Enemies : Lady Bird navigates friendships, romance, and conflicts with her family, forming alliances with friends like Julie and facing challenges that shape her character.
7. Approach to the Inmost Cave : Lady Bird’s relationships face challenges as she experiences heartbreak, and she confronts the reality of her family’s financial struggles.
8. Ordeal : Lady Bird’s relationship with her mother reaches a breaking point, leading to a confrontation that forces both to confront their feelings and expectations.
9. Reward : Lady Bird gains insight into her identity and aspirations, realizing the value of her family and the impact of her choices.
10. The Road Back : Lady Bird leaves Sacramento for college, symbolizing her journey back into the world with newfound wisdom and self-discovery.
11. Resurrection : Lady Bird’s return home prompts reconciliation and understanding with her family, particularly her mother, as they navigate the complexities of love and acceptance.
12. Return with the Elixir : Lady Bird’s return home marks a resolution, bringing a sense of acceptance and understanding, not only for herself but also for her family.
In Lady Bird, the Hero’s Journey is elegantly woven into the fabric of a coming-of-age story. It captures her challenges, growth, and self-discovery inherent in the journey from adolescence to adulthood, offering a nuanced exploration of identity, family dynamics, and the pursuit of dreams.
Exceptions: Not Every Plot Fits the Hero’s Journey
Whilst the Hero’s Journey is a flexible template and can be adapted to various genres and themes, it might not be the best fit for certain stories; especially the ones that intentionally subvert traditional narrative structures, focus solely on ensemble casts without a clear central protagonist, or explore experimental storytelling methods. Here are a few examples:
Experimental Films
Experimental films often prioritize unconventional storytelling methods, abstract concepts, and non-linear narratives. In such cases, the traditional stages of the Hero’s Journey may not be evident, as these films may prioritize artistic expression over a structured plot.
Example: Koyaanisqatsi (1982) Directed by Godfrey Reggio, “Koyaanisqatsi” is an experimental documentary film that uses time-lapse photography and innovative editing techniques to depict the relationship between humans, nature, and technology. The film doesn’t follow a traditional narrative structure or a hero’s journey but rather offers a visual and auditory exploration of its themes.
Documentaries
Some documentaries aim to capture real-life events, explore social issues, or provide informative content. The Hero’s Journey, with its focus on fictional characters and their transformative arcs, may not align with the goals of documentary filmmaking.
Example: Grizzly Man (2005) Directed by Werner Herzog, this documentary explores the life and death of Timothy Treadwell, who lived among grizzly bears in Alaska. The film is a character study and examination of nature, presenting real-life events without following a fictional hero’s journey.
Slice-of-Life Dramas
Movies that focus on depicting everyday life without a central conflict or clear protagonist’s journey might not adhere strictly to the Hero’s Journey structure. The emphasis is often on realism and capturing ordinary moments rather than a hero’s transformative adventure.
Example : Boyhood (2014) Directed by Richard Linklater, “Boyhood” is a coming-of-age film that spans over 12 years, following the life of a boy named Mason. The film captures ordinary moments in Mason’s life without a traditional central conflict, showcasing the challenges and joys of growing up.
Art House Cinema
Art house films often prioritize artistic expression, symbolism, and unique narrative structures. These films may not follow a traditional hero’s arc, as the focus might be on creating an emotional or intellectual experience rather than a clear, linear narrative.
Example: Mulholland Drive (2001) Directed by David Lynch, this enigmatic film is known for its surreal and dreamlike narrative. Lynch weaves a complex story with multiple layers, challenging conventional storytelling structures and incorporating elements of psychological horror and mystery.
Episodic or Anthology Films
Films with episodic or anthology formats, where multiple stories or vignettes are presented, might not follow a single hero’s journey across the entire film. Each segment may have its own thematic or narrative structure.
Example: Pulp Fiction (1994) Directed by Quentin Tarantino, “Pulp Fiction” is famously known for its non-linear narrative and multiple interconnected storylines. Each segment features different characters and situations, creating an anthology structure rather than following a single hero’s journey.
Certain Comedy Films
While many comedies incorporate elements of the Hero’s Journey, certain slapstick or purely situational comedies may prioritize humor over a structured hero’s arc. The primary goal is to generate laughs rather than guide the protagonist through a transformative journey.
Example: Monty Python and the Holy Grail (1975) Directed by Terry Gilliam and Terry Jones, this comedy classic is a parody of the Arthurian legend. The film is known for its absurd humor, satirical elements, and episodic structure, deviating from a traditional hero’s journey while delivering comedic brilliance.
Non-Narrative or Abstract Films
Films that lean heavily on visual aesthetics, abstract concepts, or non-narrative structures may not adhere to the Hero’s Journey. The focus is on evoking emotions or exploring themes through visuals rather than following a traditional story arc.
Example: Samsara (2011) Directed by Ron Fricke, this non-narrative documentary is a visual and musical journey through various cultures and landscapes. The film emphasizes stunning imagery and thematic exploration without a conventional plot or character-driven narrative.
These examples showcase the diversity of writing styles and genres that deviate from the traditional hero’s journey. There’s no one-size-fits-all. It’s important to know the technique that suits your style, be it Hero’s Journey or alternative frameworks like Save The Cat , Dan Harmon’s Story Circle , or any other. If none of those particularly suit you and you would still like to outline, you can create your custom template . Scrite allows you to use existing templates or create or own. You can download the app to get started for free.
- Tags 12 steps heros journey , chris vogler , heros journey , joseph campbell , ladybird , ladybird story structure , storytelling structure , writers journey
- Screenwriting \e607
- Cinematography & Cameras \e605
- Directing \e606
- Editing & Post-Production \e602
- Documentary \e603
- Movies & TV \e60a
- Producing \e608
- Distribution & Marketing \e604
- Fundraising & Crowdfunding \e60f
- Festivals & Events \e611
- Sound & Music \e601
- Games & Transmedia \e60e
- Grants, Contests, & Awards \e60d
- Film School \e610
- Marketplace & Deals \e60b
- Off Topic \e609
- This Site \e600
Unraveling The Concept of The Hero’s Journey in Filmmaking
This podcast featuring christopher vogler opens up a lot of storytelling ideas..

Many great stories, whether told through the written word or on the silver screen, share a common thread—a hero's journey. The Hero's Journey is a narrative structure that has been a fundamental part of storytelling for centuries, and it continues to be a powerful tool in filmmaking.
One of my favorite screenwriting books is ' The Writer’s Journey ', which details Joseph Campbell's journey through storytelling and takes the writer's POV.
This was the first book I read on screenwriting and one of the best.
Christopher Vogler wrote the book, and he was recently on the Film Crux podcast talking about these concepts. So check out the podcast and we'll talk after.
What is the Hero's Journey?
'Star Wars'
I figured that after the podcast you may need a refresher on Joseph Campbell and his concept of The Hero's Journey. This not a new concept; it dates back to ancient mythology and has been used by countless cultures throughout history.
Campbell was a scholar of comparative mythology and wrote a book called "The Hero with a Thousand Faces." He identified a common pattern in myths and stories from around the world, a pattern he called the monomyth or the Hero's Journey .
The Hero's Journey is a template that outlines the stages a hero typically goes through in a story. While there may be variations and adaptations, the core structure remains consistent.
It begins with the hero's ordinary world, followed by a call to adventure, a journey into the unknown, encounters with allies and enemies, a transformation or revelation, and finally, a return to the ordinary world with newfound wisdom or gifts.
A Diagram of The Hero's Journey
The Hero's Journey Diagram
Wikipedia Commons
The Hero's Journey is often depicted as a circular diagram, with each stage connected to the next in a cycle. there are many different names for the story beats in the circle.
The image above is from Wikipedia.
Here's a linear representation of Campbell's idea with beats I use when writing.
- Ordinary World : The hero's normal life before the adventure begins.
- Call to Adventure : The hero receives a call to leave their ordinary world and embark on a journey.
- Refusal of the Call : The hero hesitates or resists the call initially.
- Meeting the Mentor: The hero encounters a mentor or guide who provides advice or assistance.
- Crossing the Threshold : The hero commits to leaving the ordinary world and entering the unknown.
- Tests, Allies, and Enemies : The hero faces challenges, makes allies, and encounters adversaries.
- Approaching the Cave : The hero gets closer to the central challenge or conflict.
- Ordeal : The hero faces a major test, often their most significant challenge.
- Reward : The hero overcomes the ordeal and gains a reward or insight.
- The Road Back: The hero begins the journey back to the ordinary world.
- Resurrection : The hero faces one final, climactic challenge.
- Return with the Elixir: The hero returns to the ordinary world, transformed, and brings something valuable back.
Examples of The Hero's Journey in Film
'The Matrix'
Warner Bros.
Many iconic films have embraced the Hero's Journey structure to great effect. Here are a few examples:
- Star Wars : George Lucas drew heavily from Joseph Campbell's work when creating the Star Wars saga. Luke Skywalker's journey from a farm boy on Tatooine to a Jedi Knight follows the Hero's Journey pattern closely.
- The Lord of the Rings : J.R.R. Tolkien's epic fantasy trilogy, adapted into films by Peter Jackson, showcases the Hero's Journey through Frodo's quest to destroy the One Ring.
- The Matrix: The Wachowskis used the Hero's Journey to guide Neo's transformation from a computer hacker to "The One" who can save humanity.
- The Wizard of Oz: Dorothy's adventure in the Land of Oz is a classic Hero's Journey, complete with a call to adventure, allies, adversaries, and a return home with newfound wisdom.
How Filmmakers Utilize the Hero's Journey
- Creating Relatable Characters: One of the most significant advantages of the Hero's Journey in filmmaking is its ability to create relatable characters. Audiences connect with heroes who face challenges, make sacrifices, and experience personal growth. By following this narrative structure, filmmakers can craft characters that resonate with viewers on a deep emotional level.
- Building Tension and Conflict: The Hero's Journey provides a built-in framework for tension and conflict. As the hero progresses through the various stages, they encounter obstacles, adversaries, and setbacks, keeping the audience engaged and invested in the story's outcome.
- Engaging Audiences on an Emotional Level: The Hero's Journey is not just about physical challenges; it's also about the hero's internal journey. Filmmakers can use this structure to explore the hero's emotions, fears, and desires, allowing the audience to connect with the character on an emotional level.
- Crafting Memorable Endings: The return of the hero to the ordinary world at the end of their journey often leaves a lasting impact on the audience. Filmmakers can use this moment to deliver powerful messages, resolutions, or open-ended conclusions that leave viewers thinking long after the credits roll.
More Reading on The Hero's Journey
The Lion King (2019)
This is No Film School, of course we've written about this concept many times before. so here are some articles for you to peruse as well...
- What Are the Fundamentals of the Hero's Journey?
- What Is the 'Call to Adventure' in Storytelling?
- Joseph Campbell's Monomyth: A Brief History and Introduction
- Puppets Reenact Your Favorite Movie Moments to Explain Joseph Campbell’s ‘Hero’s Journey’
- The Other Hero's Journey: The Emotional Struggle of Screenwriting
- Over 48 Hours of Joseph Campbell Lectures Released for Free on Spotify
- This Supercut Takes You Through the Hero's Journey of over 50 Iconic Films
The Hero's Journey is a storytelling archetype deeply embedded in our collective consciousness. It provides filmmakers with a powerful tool to engage and captivate audiences.
By understanding and utilizing this narrative structure, filmmakers can create compelling stories with relatable characters, tension, and emotional depth.
Whether you're crafting a space opera or an intimate drama, the Hero's Journey remains a timeless blueprint for successful storytelling in filmmaking.
Let me know what you think in the comments.
- The Other Hero's Journey: The Emotional Struggle of Screenwriting ›
- This Supercut Takes You Through the Hero's Journey of over 50 Iconic Films ›
- What Are the Fundamentals of the Hero's Journey? ›
- Writing 101: What Is the Hero's Journey? 2 Hero's Journey ... ›
- The Hero's Journey: Joseph Campbell on His Life and Work (The ... ›
- Hero's journey - Wikipedia ›
The New Atomos Ninja Phone Kicks Butt
The device masters iphone monitoring & recording..
Fresh out of NAB 2024, we have a pretty cool new phone accessory. The Atomos Ninja Phone bridges the gap between your professional camera and your iPhone 15 Pro or Pro Max.
It takes your camera's HDMI output and enables you to monitor, record, and share high-quality ProRes or H.265 video directly on your phone. The Ninja Phone app offers complete filmmaking control with just a few taps.
Let's dive in.
Atomos Ninja Phone Details
The Atomos Ninja Phone turns your smartphone or tablet into a powerful filmmaking tool. Connect your professional camera via HDMI and record stunning 10-bit video in ProRes or H.265 formats, taking full advantage of the iPhone 15 Pro and Pro Max's vibrant OLED display.
Harness the power of your iPhone's A17 SoC processor to monitor footage with incredible detail, including 11 stops of dynamic range, 1600 nits peak brightness, and support for Dolby Vision, HDR10, and HLG. Store your ProRes videos directly on your iPhone, or leverage its 5G and Wi-Fi 6E connectivity for seamless cloud-based workflows and live streaming.
The Ninja Phone ensures you're never out of power. It works with NP series batteries, a battery eliminator, or USB-C input and charges your iPhone and connected accessories for extended shoots. Plus, its dedicated USB-C port lets you easily connect microphones and other essential tools.
Finally, the free Ninja Phone app simplifies control over your entire setup and caters to social media creators with both horizontal (16:9) and portrait (9:16) shooting modes. It's available for iOS and iPadOS.
Key Features
- 10-Bit Video Co-Processor
- Record from Professional HDMI Cameras
- Monitor Video On Your iPhone's Display
- Encode to ProRes or H.265
- HDMI Input | USB-C Video Output
- USB-C Accessory Port | USB-C Power Port
- Works with a Battery/Battery Eliminator
- Capture Footage 16:9 or 9:16
- Ninja Phone iPhone App
- Ninja iPhone Case Required for Use
Atomos Ninja Phone Video Co-Processor cots $399.
No Film School's coverage of NAB 2024 is brought to you by Blackmagic Design .
What Are The Best Western Movies of All Time?
What are the best thriller movies of all time, a comprehensive list of 50+ plot devices, how did an episode of 'the sopranos' change tv forever, why is the fujifilm x100vi struggling to stay in stock, the all new blackmagic cloud store max has a whopping 48tb capacity, new davinci resolve micro color panel comes with cinematic superpowers, blackmagic davinci resolve 19 adds neural engine ai tools and color grading improvements, shoot ef, pl, or l-mount with the box-style blackmagic pyxis 6k, these no film school listeners won slamdance and then some.


- Scriptwriting
Joseph Campbell’s Hero’s Journey: A Better Screenplay in 17 Steps
- What is a Scene
- What is The Three Act Structure
- What is Story Structure
- What is a Story Beat
- What Is a Plot
- Plot vs Story
- What is a Non-Linear Plot
- What is a Plot Device
- What is Freytag’s Pyramid
- Screenplay Structure Examples
- What is a Story Mountain
- Joseph Campbell’s Hero’s Journey
- What is Save the Cat
- Dan Harmon’s Story Circle
- What is Aristotle’s Poetics
- What is Exposition
- What is an Inciting Incident
- What is Rising Action
- What is the Climax of a Story
- What is the Falling Action
- What is Denouement
- How to Write the First Ten Pages of a Screenplay
- Plot Structure Tools
- The Ultimate Film Beat Sheet
- Secrets to Great Exposition in Screenwriting
- Writing Exposition in Film
- Best Inciting Incident Examples
- Examples of Midpoint In Movies
- Write Your Script For Free
dds are that if you’ve had any interest in writing a script within the past fifty years you’ve heard of the Hero’s Journey. A writer you got drinks with swore by it, a film professor suggested you read about it. Or you overheard the barista at your local coffee shop talking about how Die Hard is a picture-perfect template for it. But… what is it? I’ll explain all of the Hero’s Journey’s 17 steps and provide examples in the modern canon. Then you can kick writer’s block and get a strong script into the hands of agents and producers.
Watch: The Hero's Journey Explained
Subscribe for more filmmaking videos like this.
- Call to Action
- Refusal of Call
- Supernatural Aid
- Crossing The Threshold
- Belly of the Whale
- The Road of Trials
- Meeting the Goddess
- Atonement With the Father
- The Ultimate Boon
- Refusal of Return
- Magic Flight
- Rescue from Without
- Crossing the Return Threshold
- Master of Two Worlds
- Freedom to Live
Hero’s Journey Examples

The monomyth featuring three of your favorite franchises!
The hero's journey begins, 1. call to action.
Adventure is calling. Will your hero pick up?
The initial step in the first act of the Hero’s Journey - known as the departure - is the “call to action." The Hero is beckoned to go on a journey. Think Frodo Baggins meeting Gandalf. Or the Owl inviting Harry Potter to Hogwarts.
If having a tall wizard extend a hand may be a little too on the nose for you, don't worry. This comes in all forms. In Citizen Kane , the mystery surrounding Charles Foster Kane’s final words is the call to action for the reporter, Jerry Thompson, to get to work.
The Hero Hesitates
2. refusal of call.
Next is the Hero’s “refusal of call.” The Hero initially balks at the idea of leaving their lives. The Shire is beautiful, after all, who wants to embark on a dangerous journey across the world?
This refusal is typically because of a duty or obligation they have at home. Be it family, or work, it’s something our Hero cares deeply about. But, as pressure mounts, they eventually succumb and decide to leave with the help of “supernatural aid.”
The Hero Receives Assistance
3. supernatural aid.
Once the Hero has committed themselves to embarking on whatever that quest may be (keep in mind, a Hero’s Journey can apply to a modern, emotional story, as well), they receive “supernatural aid.”
Individuals give the Hero information or tools at the start of their journey to help their chances of completing the task. Rome wasn’t built in a day, and it definitely wasn’t built alone. Every hero has a set of allies helping them get the job done. From Luke, Han, and Chewie to Harry, Ron, and Hermoine, these teams are iconic and nearly inseparable.
The tools provided come in handy as the Hero begins…
The Hero Commits
4. crossing the threshold.
Now the hero ventures into a new, unfamiliar world where the rules and dangers are unknown. They’re not in Kansas anymore, Toto, and that becomes evidently clear when monkeys start flying.
This stage often requires a few examples to crystalize the change in environment from familiar to dangerous. The contrast is key to play up how ill-prepared they initially are.
The Hero is Challenged
5. belly of the whale.
Next thing you know, we're in “the belly of the whale.” The first point of real danger in the Hero’s Journey. Taken from the Biblical story of Jonah entering a literal whale’s belly, it’s here that the dangers we’ve been warned about are manifested into tangible characters. Like hungry Orcs with swords.

This is Jonah moments before actually being in the belly of the whale.
Now our Hero must make a decision to continue and, in turn, undergo a personal metamorphosis in the process.
They will not be the same individual at the end of this tale as they were in the beginning. This must be made clear while in the belly of the whale, as we enter Initiation, or act two. Which is the longest slice of the Hero’s Journey pie.
This part is filled with the most failure and risk, and ends with the climax. But first, it starts with...
The Hero is Tested
6. the road of trials.
“Road of trials” is a set of three tests that the Hero must take. Usually they will fail at least one of these tests. This could be a montage. It could also be a series of obstacles leading to a smaller goal in the journey.
Here is where the Hero learns to use his or her tools and allies while on their way to a...
The Great Advisor
7. meeting the goddess.
At this point in the monomyth, our Hero needs a break to adjust perspective and digest the ways they've changed. It’s here that they meet with an advisor, or a trusted individual, who will help them gain a better insight into the next steps of the journey. Frodo met with Galadriel, an elf who enlightened him with visions of potential futures.

This is Frodo meeting with the goddess
Luke met Leia, and the two formed of a bond of kinship, motivating them to commit more to their cause. This individual doesn’t have to be a woman, but whoever it is our hero will gain something from the wisdom they impart.
But no good deed goes unpunished, and as we reward our Heroes in storytelling, we must also tempt them to failure.
The Hero is Torn
8. temptation.
Much like “road of trials,” “temptation” is a test in the Hero’s Journey. It presents a set of, well… temptations... that our Hero must either overcome or avoid. These temptations pick and pull at the insecurities of the Hero. A microcosm can be found in our own everyday lives with the simple act of getting out of bed.
The temptation to stay in the cozy confines of our comforters (and comfort zones) can be strong and sometimes overwhelming. This must be manifested in our story with some type of a cheap way out. Or an opportunity to throw in the towel. Our Hero must decline and press forward, nobly facing danger.
A Moment of Catharsis
9. atonement with the father.
Once they’ve thrown away their temptations, the Hero enters the “atonement with the father.” This is always an emotional part of the Hero’s Journey. It's a point in the monomyth where our protagonist must confront an aspect of their character from act one that has been slowing them down.
Something that could be fatal to their journey in the coming climactic stages. While this is actuated as a confrontation with a male entity, it doesn’t have to be.
The point here is that the Hero finds within themselves a change from who they were into someone more capable. Harry has to reconcile with the loss of his father figure, Dumbledore. Now take on Voldemort alone, using the lessons he’s learned on the way. Just like Luke...and every other hero ever. This is the emotional climax of the story.
"Tell your sister... you were riiiiiiiiiight..."
Death of the hero, 10. apotheosis.
With a new sense of confidence and clarity we must then make our Hero deal with “apotheosis.” This is the stage of the Hero’s Journey where a greater perspective is achieved. Often embodied by a death of the Hero’s former self; where the old Frodo has died and the new one is born.
But this is sometimes interpreted as a more “a-ha!” moment — a breakthrough that leads to the narrative’s climax. This, too, can be tied to the death of Dumbledore and Harry’s reconciliation with the loss. This step is usually the final motivator for the Hero, driving the story into...
THe Hero Victorious
11. the ultimate boon.
This monomyth step is the physical climax of the story. This is often considered the MacGuffin of a film — the physical object that drives our Hero’s motivation. But it's a MacGuffin, to use Hitchcock's famous term, because ultimately... it doesn't matter.
In Pulp Fiction , we never find out what’s in the briefcase, but it’s the briefcase that led them on the wild journey. When we find out what “Rosebud” actually means, it simply forms a lynchpin to help us understand who Charles Foster Kane was. The mission is accomplished and the world can rest easy knowing that it is safe from evil.
The Hero's Journey Home
12. refusal of return.
Upon a successful completion of the Hero’s Journey, and a transformation into a different person, the Hero has a “refusal to return.” The Shire seems so boring now and the last thing Harry wants is to go back to that drawer under the stairs.
And, oftentimes, the return can be just as dangerous. This is the beginning of the third act of Campbell’s Hero’s Journey (known as the Return) and, while shorter, should still contain conflict. Our next step is an opportunity for that...
The Hero Transported
13. magic flight.
This is the point in the Hero’s Journey where they must get out alive, often requiring the help of individuals they met along the way. Dorothy still has to get back to Kansas, the solution to which may seem like a leap of faith.

The eagles rescue from without with a magic flight to Frodo and friends
The hero's rescue, 14. rescue from without.
Bringing us to the “rescuers from without” point in the monomyth. Just because Frodo destroyed the one ring to rule them all doesn’t mean he gets a free ride back to the Shire. Remember those giant eagles we met a while back in act two? Well their back just in time!
Homeward Bound
15. crossing the return threshold.
Once the Hero is back home, it’s time to acknowledge their change in character. “Crossing the return threshold” is the stage in the monomyth where the hero has left the chaos of the outer world and return home.
But it's hard to adjust to the old world. Remember that scene where Frodo tried to enjoy a beer back at the shire? Hard to go back to normal when you essentially live with Dark Lord PTSD.
A Triumphant Return
16. master of two worlds.
The hero survived an adventure in the chaos realm, and now survives in the normal order realm. This makes him or her the master of two worlds. Not many people come back and live to tell the tale.

Frodo and Gandalf wandering off into the sunset post accomplishing their mission
Plus which, throughout the story, they’ve become someone much more capable and resilient than they were in act one. They've learned lessons, and brought what they learned home with them.
Whatever issues they may have had before embarking on this chaotic tale (often the ones preventing from taking the call to action) now pale in comparison with what they’ve been through.
It’s easier to deal with your annoying cousin, Dudley, after you’ve defeated Voldemort. This, in turn, leads to...
The New Status Quo
17. freedom to live.
In many ways the Hero's Journey is about death and rebirth. The story may manifest as the death of an aspect of character, and the birth of some new way of life. But the metaphor behind any story is one about mortality.
Change is constant. Hero's living through the Hero's Journey are models for us. Models that we can travers the constant change of existence, face our mortality, and continue. In a religious sense, and religions are all part of the monomyth, this is about the eternal spirit.
Look no farther than the prayer of St. Francis to understand this final step in the Hero's quest. "It is in dying that we are born to eternal life."
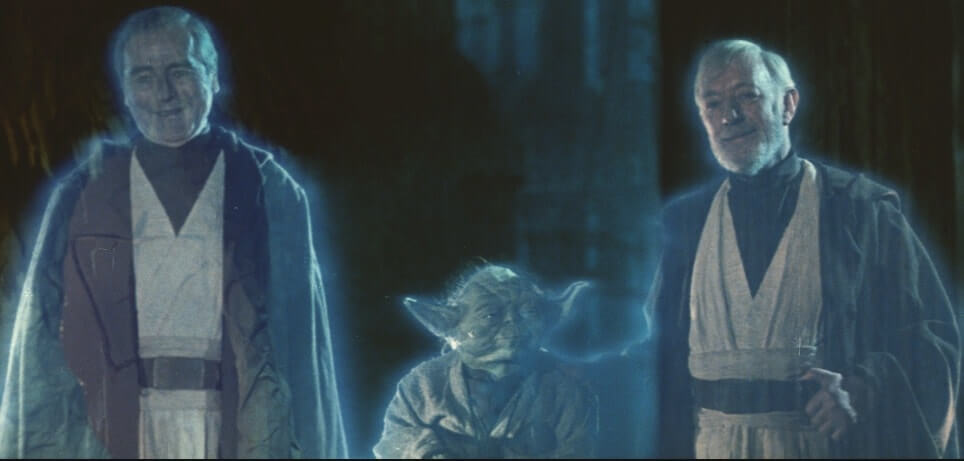

The Hero’s Journey Concludes
Cinematic heroes.
The monomyth is practically ubiquitous in Hollywood. As you’ve read earlier, Harry Potter , Star Wars , Lord of the Rings , and Citizen Kane all follow the Hero’s Journey. But, because this concept was built upon the foundations of major mythologies, it's truly a "tale as old as time."
Because Campbell discovered the Hero's Journey. He didn't make it up. Neither did those older myths. He realized as an anthropologist, that every culture all around the globe had the same story beats in all their myths.
Sure, some myths, and some movies, use 10 of the 17, or even just 5. But throughout human history, around the world, these story beats keep showing up. In cultures that had nothing to do with one another.
The Hero's Journey is a concept innate to being human.
And if remembering these 17 steps may seem a little daunting, fear not. Make sure to check out Dan Harmon's abridged 8-step variation of the Hero's Journey monomyth. Same structure, just made more digestible.
Dan Harmon’s Story Circle
Practically speaking, the Hero’s Journey is an excellent tool for structuring an outline in a clear and familiar way. It has the power to make your script much more powerful and emotionally resonant.
It’s circular, allowing for repeat adventures (which works well if you're learning how to write a TV pilot ) and each aspect drives the hero to the next. From the Goddess, the Hero finds temptation. From reconciling with the father, the Hero is now prepared for the final boon.
Story Circle • 8 Proven Steps to Better Stories
Using a Hero’s Journey worksheet can help you write a treatment or create a well-structured outline , which is a valuable tool for creating a strong first draft.
By putting in the 17 steps of the Hero’s Journey before building the outline, you can ensure that the writing process will flow smoothly and efficiently. Let us know in the comments how the monomyth has helped you craft a story that escalates with every beat to an exciting climax.
Up Next: Dan Harmon's Story Circle →
Write and produce your scripts all in one place..
Write and collaborate on your scripts FREE . Create script breakdowns, sides, schedules, storyboards, call sheets and more.
Summed up in a brilliant way. This proves once again that I was right to study English and then go where my passion lays: Film and Video, including on Instagram (@moritzxbauer) and Youtube. At University I wrote a term paper on “Archetypes of mythical heroism on the example of Aragorn in Lord of the Rings”. Campbell’s Journey of the Hero has been one of my main references. I have never seen the structure being adapted so well to film in general.
None of these include the hero's journey of Buffy Summers in BtVS. As a result, it's hard to take these essays as seriously as one might otherwise.
I love this!! It's going to help so much with writing my book, thank you!
Thank for for the brilliant template. It will help me as a catholic priest to examine the journey of disciples in the Bible for deeper understanding through the contemporary literary lens.
Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Pricing & Plans
- Product Updates
- Featured On
- StudioBinder Partners
- The Ultimate Guide to Call Sheets (with FREE Call Sheet Template)
- How to Break Down a Script (with FREE Script Breakdown Sheet)
- The Only Shot List Template You Need — with Free Download
- Managing Your Film Budget Cashflow & PO Log (Free Template)
- A Better Film Crew List Template Booking Sheet
- Best Storyboard Softwares (with free Storyboard Templates)
- Movie Magic Scheduling
- Gorilla Software
- Storyboard That
A visual medium requires visual methods. Master the art of visual storytelling with our FREE video series on directing and filmmaking techniques.
We’re in a golden age of TV writing and development. More and more people are flocking to the small screen to find daily entertainment. So how can you break put from the pack and get your idea onto the small screen? We’re here to help.
- Making It: From Pre-Production to Screen
- Is Film School Worth It — Why You Should or Shouldn’t Go
- How to Write a Poem — A Step-by-Step Guide
- What is a Character Flaw — And Why Writers Love Them
- How to Become a Movie Critic — Career Tips Explained
- What is an Indie Film — Definition & History Explained
- 299 Facebook
- 238 Pinterest
- 12 LinkedIn
Receive Big Ideas to Your Inbox
Great adventures: five examples of a hero’s journey.
- March 2, 2020
- TEDxMileHigh Admin
- Art & Design
It’s the common thread woven throughout all storytelling. A lens that can be applied to any film or work of literature where each story will look the same. This arc of character and plot development is called the hero’s journey, and it’s everywhere.
In part one of this series , we learned what the hero’s journey is and the steps a character must take in order to fulfill their quest. We also learned that this story arc is relatable to us because our lives follow a similar pattern. If you still aren’t convinced that the hero’s journey permeates the fictional world, here are five great examples of a hero’s journey from different classics.
Spoiler Alert: If you are unfamiliar with any of these books or movies, skip them! We discuss the entirety of the story, including the end.
Examples of a Hero’s Journey in Five Stories
This 2009 sci-fi blockbuster became the top-grossing film of all time just 47 days after it premiered. Its success is largely due to the incredible Computer-Generated Imagery (CGI) characters and visual effects that are vibrantly convincing. Underlying messages and morals such as the importance of a peoples’ culture and land conservation accompany the film. While all of these elements play a role in the resounding praise of this film, there’s another reason people loved the film: the main character followed a typical hero’s journey.
Jake Sully starts out as a paraplegic former Marine. He is chosen to be a bodyguard for a research team on a search for a new energy source on the planet Pandora. While on their mission, Sully meets Neytiri, a native of Pandora, and is quickly accepted by her and her people. Sully is then faced with the moral choice to continue his work with the team he came with, and thus destroy the sacred native land, or join the native tribes and fight back against his own people. In the end, he helps save the land and its people and makes a permanent transition from his human body to the able-bodied avatar.
Sully’s time on Pandora is the perfect example of a hero’s journey:
- Separation: He is called to his adventure as a bodyguard, separating himself from his otherwise ordinary life
- Initiation: The initiation stage involves his meeting Neytiri and his introduction to her native tribe, and his moral dilemma of helping the natives of Pandora or staying with his team
- Return: His return is marked by the triumph of the natives. He returns to the tribe, physically changed from a human to one of their own, and mentally a new being with a new purpose
2. Marvel’s Spiderman
Another dominating movie franchise is Marvel’s The Avengers and the superhero spin-offs that it consists of. The movies have been a force to be reckoned with in the box office. However, each character had their start as a part of a comic book. Perhaps one of the most classic of this comic-book-hero-turned-movie-star is Spiderman.
The most recent adaptation of this beloved character is in the Marvel Avenger movies and the spin-off hits. In case there is any question that he is a hero, here is his journey in three steps:
- Separation: After the iconic spider bite, Peter Parker discovers his spider-like powers, prompting his new superhero life. He needs to adapt to life as a teenager with superpowers and fight crime at the same time
- Initiation: Tony Stark (a.k.a. Iron Man) and the other Avenger superheroes recruit him to help them in their battle against their extraterrestrial enemies
- Return: In the end, Spiderman returns as Peter Parker to his normal high school life, but is changed by the knowledge of his bigger responsibility as a superhero
Marvel’s Avenger version of Spiderman follows the classic hero’s journey, but we can see a major emphasis on the introduction of a mentor throughout Parker’s adventure. Iron Man serves as a father-like figure and helps Parker not only navigate his newfound superpowers but also how to harness them and use them for good.
3. The Wizard of Oz
A beloved novel-turned-film story that includes wicked witches, ruby slippers, and flying monkeys. This film is known for its brilliant use of color to separate real life from the fantasy world of Oz, as well as its iconic song “Somewhere Over the Rainbow.” Dorothy’s journey, however, is different from other examples of a hero’s journey because she is a woman. (In part one we learned about the difference between a hero and heroine’s journey, and Dorothy’s yellow-brick-road path embodies a classic example.)
- Separation: After the twister drops her house in the magical land of Oz, and coincidentally on top of the Wicked Witch of the East, all Dorothy wants is to return home to Kansas
- Initiation: On her adventure, she meets three iconic friends, the scarecrow, the tin man, and the lion. They ultimately help her defeat her enemy, the Wicked Witch of the West and find the Emerald City
- Return: Dorothy returns home to her family in Kansas only to realize she’s been on an incredible independent adventure
Like Spiderman, Dorothy also has a mentor: Glenda. She advises Dorothy to seek the Wizard of Oz at the end of the yellow brick road.
The key to a heroine’s journey is overcoming society’s expectations of women . Dorothy does this several times throughout the film, like when she longs for adventure when the expectation is that she lives on her family’s farm. Or the expectation that her new, male friends will help her when she ultimately helps them. Finally, when Dorothy returns home on her own, proving she doesn’t need to rely on her uncles or anyone else to get what she wants.
The other stages of Dorothy’s quest make it one of the many examples of a hero’s journey, but it is this power that she finds as a woman that distinguishes her as a heroine.
4. To Kill A Mockingbird
This Pulitzer-Prize winning novel is at once a coming-of-age story and an attack of racism in the depression-ridden South. The main character and heroine, Scout Finch, grows up conflicted between how she feels and how other people think she should feel.
- Separation: When Atticus, Scout’s father, and a prominent lawyer, agrees to defend a black man in court, the implications are felt by the entire family. The two kids are alienated at school for their father’s decision
- Initiation: Their initiation stage takes up the bulk of the story. Atticus remains a prominent mentor to Scout and her conflicted societal views. The elusive Boo Radley remains a friend and helper although never showing his face. The conflict of this novel is woven throughout the story. Scout struggles to understand the racial views of those around her. There is also major discontent from the Maycomb townspeople surrounding Atticus’s decision to defend a black man
- Return: In the end, Scout finally puts a face to the name when Boo Radley saves her and her brother from a man who disapproved of their father’s case in court. She also realizes that regardless of what other people think, it’s better to do the right thing than cave into societal pressures
Scout can be seen as a heroine on her journey because she defies the expectations of her as a young girl. She also disregards what society thinks of her interactions with black people. She sees no problem with her father defending a black man in court. Although she can feel the discontent from those around her, Scout understands that a person deserves equal treatment despite their race, and she spends most of the novel making that point.
Disney characters and movies follow the hero’s journey.
- Separation: Aladdin lives as a poor “street-rat” until he fatefully meets the Genie in the Cave of Wonders. With the Genie’s help, Aladdin is transformed from poor bread-stealer to Prince Ali in order to win the heart of Princess Jasmine
- Initiation: Aladdin is confronted with not only Jafar, the hand to the Sultan but also the moral struggle of living a lie in order to impress the person he loves
- Return: In the end, Aladdin realizes no magical genie power can truly give him what he wants. After defeating Jafar, he admits to lying about who he is and why he felt he needed to be someone he wasn’t
The emphasis of the return in Aladdin’s hero journey is what is important. He met the Genie and was pushed into this magical adventure as Prince Ali. With the Genie at his side as his mentor, he is able to defeat Jafar, but he realizes the Genie can’t help him with everything. The lesson Aladdin learns about being himself in order to get what he wants is important. It proves that he has had what he needed all along—that is all he will ever need.
The Moral of the Story
From comic books to blockbusters, Pulitzer-Prize novels to classic films, these works have seen varying levels of success. Some were the biggest movies of all time and some were classic novels that are still read generations later. Despite the details in each piece, all of these stories follow the same narrative archetype—the arc of the hero’s journey.
These examples of a hero’s journey are five of many, but they are also proof that this story arc can be applied to any piece of film or literature. I encourage you to apply this arc to any and all of your favorite stories—including your own life.
Get our most powerful and mind-blowing talks sent directly to your inbox.
Browse by category.
- Health & Science
- Social Issues
- Social Science
- TEDxMileHigh
- Volunteering
Related Posts

Hemangiosarcoma: What Every Dog Owner Needs to Know
As one of the most aggressive cancers seen in dogs, hemangiosarcoma grows and spreads rapidly, often without showing clear signs until it’s quite advanced. What

Cognitive Decline in Dogs and Cats: Managing Pet Brain Health
As our beloved furry companions age, some cognitive decline is to be expected. But when pets begin to exhibit signs of accelerated cognitive decline, they

Pet Dental Care: What You Need To Know
When it comes to taking care of our pets, dental care is usually the last thing we think of. Why is that? Well, there are
TED x Milehigh presented by:

HOSPITALITY

Follow Us On Instagram @tedxmilehigh
Join the milehigh conversation..
- Svg Vector Icons : http://www.onlinewebfonts.com/icon
Stay Connected
Spark your curiosity with talks and inside event updates sent directly to your inbox..
- Translators
- Graphic Designers
Please enter the email address you used for your account. Your sign in information will be sent to your email address after it has been verified.
The Hero's Journey: Stages, Steps, and Examples

Remember when you were younger, probably around middle school age, and your teacher introduced the Greek mythology lesson? It was such an exciting time of reading books like Rick Riordan's Percy Jackson & The Olympians: The Lightning Thief . Maybe you fell in love with Percy, a lovable and relatable young boy struggling with his identity. Or maybe you were a part of the dystopian crave and fell in love with Katniss Everdeen from Suzanne Collins' The Hunger Games . Either way, this may have been your first introduction to the hero's journey (we're sure you've seen the templates). After all, the hero's journey is all around us!
If you fell in love with reading a hero's journey archetype and want to try to create your own modern hero, then you've come to the perfect place. We're going to explore the crucial steps of a hero's journey and what they entail, so you can have a template through which to write your own story. Your questions act as our call to action (you'll understand what we mean by that shortly). But first, let's define a hero's journey. After all, how can we possibly evaluate the steps of a hero's journey if we don't even have a solid definition?
The hero's journey
A hero ventures forth from the world of common day into a region of supernatural wonder: fabulous forces are there encountered and a decisive victory is won: The hero comes back from this mysterious adventure with the power to bestow boons on his fellow man. The Hero With a Thousand Faces by Joseph Campbell
The hero's journey is the story of a hero who leaves the ordinary world to go on an adventure full of peril. On it, the hero will gain both adversaries and allies, and will face a great evil. The hero will also face his shadow self, which is perhaps the most frightening antagonist of all.
Campbell references 17 total steps in the hero's journey. Wait a minute, 17 steps? That seems like a lot. Don't worry! Depending on who you ask, the number of steps and what those steps look like will differ, though they all follow a similar template. The hero's journey is commonly accepted to have 12 main steps. To make it even simpler on you, these steps can actually be broken down into three stages: the departure, the initiation, and the return.
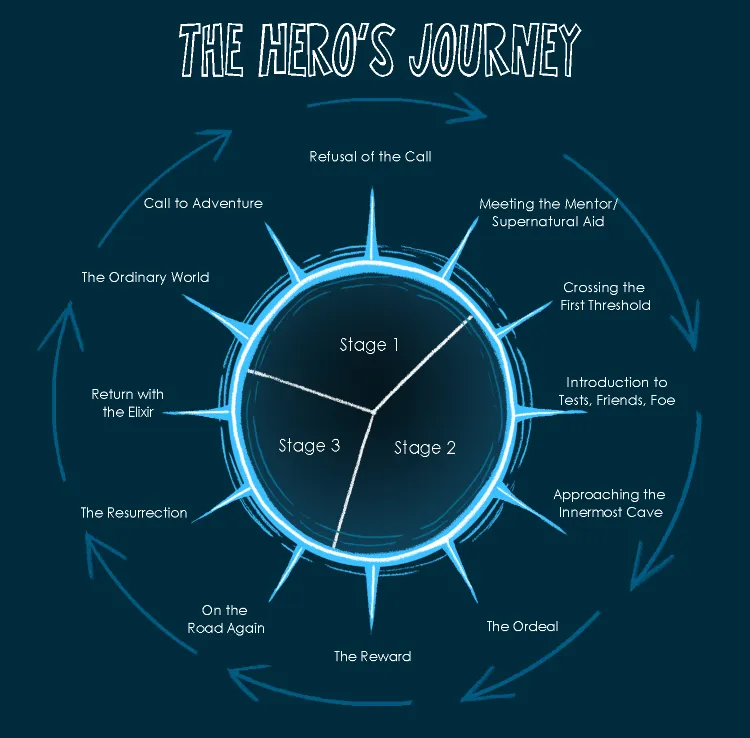
Stage 1: the departure

The departure is just as you might expect. This is the stage where the protagonist is introduced, typically in a modern, realistic setting, and we are introduced to some struggles the protagonist may be experiencing or questions they may have about their own identity. This stage can be broken into our first four steps.
- The ordinary world : As we said, we are first introduced to our protagonist and soon-to-be hero in the reality we know. It is just as the first step is listed: the ordinary world. There is no magic, mayhem, or supernatural creatures evident in this ordinary world. It is the world the protagonist has known all their life.
- Call to adventure : This is one of the steps you may be most familiar with, as it's one of the most commonly known phrases in literature. Regardless of what genre you are writing, your hero has a call to action. After all, there must be a reason why the protagonist leaves the mundane, comfortable lifestyle they've lived up until now. This is the moment where the journey or quest is initiated: a problem, challenge, or quest is presented to the protagonist, and they must decide to leave behind their ordinary lives to face new challenges. Whether the protagonist is immediately threatened, a family member is threatened, or they see something they shouldn't have, it is up to the protagonist to respond to the call.
- Refusal of the call : Wow, isn't it so cool that the hero was discovered by some other world (or they discovered it!) and now they get to embark on this awesome journey? Yes, well, sometimes. Despite how amazing it may seem to be called to accept a quest (hence the reason why this archetype is so popular in literature), the protagonist may not be feeling that excitement. In fact, it's likely that the protagonist is feeling nervous, anxious, scared, hesitant, and thus, resistant to the call at first (don't worry, they'll give in eventually).
- Meeting the mentor/supernatural aid : Okay, so the protagonist is done refusing the call. Maybe they've gotten over their fears, or maybe something happened that makes it impossible for them to continue to deny their inevitable quest. Yay! Now it's time for our protagonist to meet their mentor. The mentor can be supernatural or not, but they act as a teacher, trainer, and instructor for the protagonist. After all, the protagonist is going to need some serious guidance once they've been booted out of their ordinary world. This step involves a lot of trust, though, as the protagonist may barely know their mentor. This step also involves the passing on of certain tools and equipment the protagonist may need to succeed on their journey. These can be special powers or physical instruments.
Stage 2: the initiation

Now that you've spent a decent chunk of time introducing your protagonist (and hero!) and their conflict, it's time to head into the second stage of the hero's journey: the initiation. Before you do this, though, ensure you've checked off the first four items on the previous list. It is crucial that you meet these criteria for a successful hero's journey. After all, the hero can't be truly initiated into their new world if you have not established their old world, their main conflict, and the introduction of their next steps.
This next stage will take up the largest portion of your story. You should fill it with lots of new characters, settings, and trials and tests for your protagonist to endure. This is also a stage where you should focus a lot on character development for your protagonist. No person is going to go through a massive journey and end up the same person they once were when everything is said and done. Take this time to think about how you want your protagonist to change and what it's going to take to accomplish that change.
- Crossing the first threshold : This is the point at which the hero decides to embark on the adventure and cross over into the unknown, leaving his or her ordinary world behind. This is called the threshold because there is something or someone acting as a literal barrier between the protagonist's ordinary world and their new world. Beyond the threshold lies trials and tribulations and potential risks and dangers. Once the protagonist takes that first step beyond this threshold, there is no returning to the life they once knew. This is where the hero's actual journey truly begins.
- Introduction to tests, friends, and foe : This is the step of the story where the cast of characters expands and a new setting, the new world, is introduced. The protagonist may be lost in their new world, so they must evaluate the new people around them to identify potential allies, enemies, or morally ambiguous characters. Trust is established or denied. Just like anyone would struggle with encountering anew environment, the protagonist will endure some struggles of their own, but this is how they'll determine who is friend and who is foe, establishing other character roles in the process. The rules of the ordinary world do not apply to this new world, so hopefully the protagonist meets some good people who will teach him the new ways of life.
- Approaching the innermost cave : At this point on the hero's journey, they have left all semblance of the ordinary world behind. This step marks the preparation for the main event of the journey. The protagonist may gather materials and even other characters, if they're trustworthy enough, to take on the rest of the steps of the quest with them. The cave acts as a metaphor for what the protagonist is about to endure: risk, danger, darkness, and even potential loss. This step also includes some of the tests leading up to the large test yet, which happens to be the next step in the hero's journey.
- The ordeal : Buckle up, this is about to be a wild ride! That's right, your hero has finally made it to one of the biggest challenges of all. The protagonist is no longer approaching the innermost cave. Rather, the protagonist is now fully in the belly of the beast, and what a beast it is! The ordeal is usually not the climax of the story, but this is the moment where the protagonist truly transforms from an ordinary character into a true hero. It may involve their greatest fear or a physically or mentally demanding task.
- The reward : If your protagonist, now hero, succeeds in their greatest challenge, then they will be given a reward that makes the journey worth so much time, effort, and challenge. If they can succeed, then there is hope for them, that bright light that shines through the top of a dark cave and promises fulfillment and a future. This is what the hero has been fighting for this whole time. As for the reward itself, you should make sure it makes sense in the context of your story. It can be an object, a piece of knowledge, or even something entirely different, so long as its value matches the degree of the journey.
Stage 3: the return

Wahoo, your hero has endured so much and has finally gotten their reward! It's over, right? They can return to their ordinary life and reap the benefits of all their hard work? Wrong! Things are never as easy as they seem, especially in a hero's journey, so why would the road back to the ordinary world be any different for your hero?
- On the road again : This is the turning point, literally. The hero turns back around, hoping to return to their normal life after receiving their reward. But thing's are never that simple, so be sure to make sure that road is blocked. Traffic cones, stoplights, maybe a supernatural villain or catastrophic natural disaster! That should do the trick. If the road back home was easy, we'd be bored, so maintain the stakes with challenges for the hero to face as they make their way back home.
- The resurrection : Congratulations, you've finally reached the climax of your story. Remember how we said the ordeal was the moment where your protagonist transformed from an ordinary character into an actual hero, this is the moment where they can prove to us that they deserve the hero title, after all. The stakes become extremely high, as the hero does not want to fail after having endured so much already. This is the final test for the hero and the final opportunity for the villain or opposing forces to defeat the hero. If the hero comes out on top, then they will finally be able to reach that light at the end of the tunnel.
- Return with the elixir : The hero has finally completed all their challenges and is able to return home with their reward. Their transformation is complete, and they've most likely become a better person because of the journey. Or, if you want to add a twist to this step, you can always have the hero fail to return without they set out to receive, but you better be prepared to write a sequel and a whole other journey!
Following the template

Since we mentioned The Hunger Games at the very beginning, let's use Katniss Everdeen and her hero's journey as a model for this template.
- The ordinary world : Katniss Everdeen is introduced as a citizen on District 12, a poor mining district. She spends her days hunting in the woods to provide food for her family.
- The call to action : Every year, a reaping takes place where a male and female tribute from each district is randomly chosen to take place in the Hunger Games, a fight to the death. During the reaping, Katniss' sister Primrose is selected, so Katniss volunteers to take her place as the female tribute from District 12.
- Refusal of the call : As we mentioned, you may not include all 12 steps of the hero's journey in your own story. Katniss does not actually refuse the call, as she volunteered herself to save her sister. A refusal of the call is slightly seen in Peeta, Katniss' fellow tribute, as he is visibly nervous and shaken up. The nature of this story makes it so that a refusal is impossible.
- Meeting the mentor : Katniss meets Haymitch Abernathy, a previous Hunger Games victor from her District. He is her literal mentor and is meant to teach her how to make allies, get sponsors, and survive in the arena. She also finds a mentor in Cinna, the person in charge of her appearance for promotions.
- Crossing the threshold : Katniss is whisked out of District 12 and on the train to the gaudy, wealthy Capitol.
- Introduction to tests, friends, and foe : Katniss must attempt to learn who to trust while also earning sponsors and impressing the Game Makers. Katniss makes a reluctant alliance with Peeta and admires Rue from District 11. During training, it is evident that the Careers (tributes from the wealthier districts) are enemies.
- Approaching the innermost cave : Katniss enters the physical arena.
- The ordeal : The arena is full of challenges: tracker jackers, mutant wolves, poisonous berries, and other tributes trying to survive. The games themselves are the whole ordeal.
- The reward : Katniss and Peeta are the last tributes standing.
- On the road again : Although Katniss and Peeta have survived, there can only be one winner, and the Capitol wants to force them to select who lives and who dies.
- The resurrection : Katniss' bold attempt at a mutual suicide leads to both of them being allowed to live as victors, lest they become martyrs in front of the whole country.
- Return with the elixir : Katniss and Peeta return to District 12 as victors, allowing them to live lives of wealth and luxury. If you've read the books, you'll know this is nowhere near the end of Katniss' journey.
Reaping the rewards
If you've managed to check off all 12 steps on our hero's journey checklist, then you've got yourself an awesome hero's journey. If you're just starting out on your own journey of writing for a hero, then be sure to follow this template for maximum results. Be the hero in your own journey and remember to never give up as you face those roadblocks and challenges while buckling down and writing a story of your own!
Header photo by Zoltan Tasi .
Related Posts

Creating an Anthology Book Series: A Step-By-Step Guide

How To Write a Swoon-worthy Historical Romance Story
- Book Writing Advice
- All Blog Posts
- Writing Advice
- Academic Writing Advice
- Admissions Writing Advice
- Short Story Advice
- Employment Writing Advice
- Business Writing Advice
- Web Content Advice
- Article Writing Advice
- Magazine Writing Advice
- Grammar Advice
- Dialect Advice
- Editing Advice
- Freelance Advice
- Legal Writing Advice
- Poetry Advice
- Graphic Design Advice
- Logo Design Advice
- Translation Advice
- Blog Reviews
- Short Story Award Winners
- Scholarship Winners

Professional book editing services you can trust

The Dawn of Modern Shonen – How My Hero Academia Revolutionized Shonen Anime With One Bold Choice
- My Hero Academia follows a seasonal release model, providing concise storytelling and longer breaks.
- The seasonal approach allows for better pacing, steady progression, and the necessary time for emotional story arcs.
- The series' success with the seasonal model has influenced other popular anime franchises like Jujutsu Kaisen and Demon Slayer .
My Hero Academia , created by Kohei Horikoshi, is one of the anime industry's most popular series. It is one of the best-selling manga series worldwide and has enjoyed both critical acclaim and an avid fanbase. The series is known for its phenomenal storytelling, its excellent character development with relatable and realistic superheroes and dastardly villains, and its truly unique storyline following a young, "quirkless" boy inheriting powers from his childhood hero.
My Hero Academia offers a refreshing twist on the typical superhero origin story, standing out among other shonen series with a superhero premise. Furthermore, it also changed the landscape for shonen anime as a whole. My Hero Academia was one of the first to operate on a seasonal model.
This means that the series releases shorter and more concise story arcs, rather than being continuously ongoing. The model also allows for longer breaks between seasons of the anime, since there is more flexibility to pause between arcs , which doesn't typically happen in continuous anime like One Piece , that don't stop running.
My Hero Academia Releases Seasonally Rather Than Using A Continuous Release Model
Produced by bones; based on the original manga by kohei horikoshi.
There are, of course, benefits and drawbacks to each model of airing an anime series. One Piece is a great example of the continuously running anime approach. The series has been releasing pretty consistently, with an occasional short week-long break at the most, since the first episode was released on October 20, 1999. A lot of other popular anime series adopted the continuous model, including Naruto, Bleach, and Dragon Ball Z. Due to these massively popular shonen setting the stage, this way of creating an anime became immensely popular, with many other creators following suit and adopting a continuous schedule for their series.
However, M y Hero Academia came along to break that trend and establish a previously unheard-of option for an anime release schedule. It was one of the first big shonen series to try out an alternative model. For example, the first season of the anime ran from April 3, 2016, to June 26, 2016. Instead of continuing weekly like another anime at the time might have done, the show took a break until April 1 of 2017: an almost year-long break. This was radical at the time, since most big shonen properties did not pause for any extended amount of time .
The Seasonal Model Allows For More Concise Storytelling & Better Arcs
The freedom offered by this release schedule helped my hero academia cut out filler.
One of the strongest benefits of the seasonal approach is it offers the opportunity for more concise and to the point storytelling . Without the pressure to release episodes every single week, writers can develop individual arcs more thoughtfully and slowly with lulls in between, rather than keeping a broader story going from week to week without ceasing. Although the creators still must focus on how each arc adds to the wider overall storyline, the seasonal model does allow for more breaks in between to brainstorm new ideas, making the major My Hero Academia battles, triumphs, losses, and character arcs feel paced well.
Following in My Hero Academia's footsteps, countless other award-winning shonen franchises began to try out the seasonal model as well. Series like Chainsaw Man, Demon Slayer, Jujutsu Kaisen, and Spy x Family all began using this perspective to define their anime release schedules. Although all of these beloved series would have been able to release filler without catching too much flak from fans, each of these creators saw the benefits of breaking between seasons in order to create an intentional story that doesn't include filler content, choosing instead to craft one succinct storyline and plot that flows steadily between seasons.
There Are Positives and Negatives With Each Release Model
For series like One Piece and Naruto, the weekly schedule seems to work well and please fans. Filler content is not always a negative and sometimes even drives the plot forward and offers interesting and surprising insight into beloved characters that there is no time to delve into in traditional plot-focused episodes. There is much discourse, both in favor of and against, this type of content, but lighthearted side episodes can provide a nice respite from continual action, and heavier topics like character death. However, not every series will benefit from including these and My Hero Academia is one such example.
The seasonal model has given My Hero Academia incredible pacing . With 25 episodes per season and year-long breaks, Deku's journey is able to progress steadily but not feel rushed, allowing him to grow in his abilities at the right pace. It allows for breaks between darker arcs that include emotionally heavy moments and death, like the Shie Hassaikai arc. These pauses give fans time to process and creators time to ponder what direction to take the next season. Although continuous series will not cease to exist, more shows are taking inspiration from My Hero Academia 's astounding success with the seasonal model.
Watch on Crunchyroll
My Hero Academia
In My Hero Academia, some humans have superpowers called quirks. Izuku Midoriya, nicknamed Deku, is not one of them. Deku has always idolized heroes like the number one hero, All Might, and since he was a child, he has always wanted to be a hero. However, his lack of a quirk has always held him back, but a chance encounter with All Might after discovering a classmate in danger sets Deku on the path to becoming a true hero. My Hero Academia centers around Deku and a class of heroes-in-training at UA. This school shapes young quirk users into future heroes through fake rescue missions, combat training, and other hero-tempering tasks. With young Deku inheriting the "One-For-All" quirk, he will learn what it means to be a true hero while facing off with dastardly supervillains.
Cast Daiki Yamashita, Nobuhiko Okamoto, Christopher R. Sabat, Ayane Sakura, Clifford Chapin, David Matranga, Luci Christian, Kenta Miyake, Aoi Yuki, Yki Kaji, Justin Briner
Release Date April 3, 2016
Genres Superhero, Animation, Action
Website https://www.funimation.com/shows/my-hero-academia/
Franchise My Hero Academia
Production Company Bones
Number of Episodes 113


COMMENTS
4. Meeting the Mentor. The hero has either gone off on an adventure or has been thrust into one-now, they get some sort of guide to take them through this new world. This new guide is a mentor character, and they'll often have something to help our hero out along the journey. Think Gandalf or Hagrid.
Warner Bros.' Magical Journey Through Hogwarts. Image via Warner Bros. The Harry Potter series features not just one, but eight of the movies that best follow the Hero's Journey. From Chris ...
Examples of the hero's journey. Examples of the hero's journey can be found in many works of literature and mythology. Some examples include: The Odyssey by Homer; The Left Hand of Darkness by Ursula K. Le Guin; The Lord of the Rings by J.R.R. Tolkien; The Hunger Games by Suzanne Collins; The Lion, the Witch, and the Wardrobe by C.S. Lewis
The very first hero's journey arc was created by Joseph Campbell in 1949. It contained the following 17 steps: The Call to Adventure: The hero receives a call or a reason to go on a journey. Refusal of the Call: The hero does not accept the quest. They worry about their own abilities or fear the journey itself.
The Hero's Journey is a common story structure for modeling both plot points and character development. A protagonist embarks on an adventure into the unknown. They learn lessons, overcome adversity, defeat evil, and return home transformed. Joseph Campbell, a scholar of literature, popularized the monomyth in his influential work The Hero ...
An ultimate battle that tests the hero's resolve. A triumphant return home. If this sounds familiar, that's because this exact narrative template has inspired countless stories from ancient myths to modern television shows and movies. This template is known as the "monomyth"—or, colloquially, the hero's journey.
Consider the iconic "Star Wars" series, a shining example of the Hero's Journey. Luke Skywalker's evolution from a farm boy to a Jedi mirrors the stages of the monomyth, striking a chord ...
This ultimate Hero's Journey writing guide will define and explore all quintessential elements of the Hero's Journey—character archetypes, themes, symbolism, the three act structure, as well as 12 stages of the Hero's Journey. We'll even provide a downloadable plot template, tips for writing the Hero's Journey, and writing prompts ...
The Hero's Journey: Use this structure when you want to tell a story of personal growth, transformation, and adventure. It works well for epic tales, fantasy, and science fiction, but it can be adapted to other genres as well. Three-Act Structure: This is a versatile structure suitable for a wide range of genres, from drama to comedy to action.
More modern examples include The Hobbit by J.R.R. Tolkien, and Suzanne Collins' The Hunger Games. What is The Hero's Journey? The Hero's Journey is a three-act plot structure that divides into twelve stages with a specific purpose and function within the narrative. The reason The Hero's Journey is the most popular is that it combines ...
9. Reward (Seizing the Sword) In which the Hero sees light at the end of the tunnel. Our Hero's been through a lot. However, the fruits of their labor are now at hand — if they can just reach out and grab them! The "reward" is the object or knowledge the Hero has fought throughout the entire journey to hold.
May 1, 2023 by 30 DayBooks. Every captivating story, from ancient myths to modern blockbusters, shares a common narrative structure that resonates with audiences across generations and cultures. This powerful storytelling framework is known as the hero's journey, a concept rooted in the groundbreaking work of renowned mythologist and author ...
6. Girl Waits with Gun by Amy Stewart. "Amy Stewart" via wikipedia, public domain. Based on the true story of one of the US' first female sheriffs, Girls Waits with Gun tells the story of Constance Kopp and her two sisters. It's a hero's journey story that, like Kopp herself, breaks the mold of the genre.
Reviewing hero's journey examples can simplify this concept and aid in understanding. Explore each step of the journey and clear examples.
The 12 Stages of the Hero's Journey (as outlined by Christopher Vogler) While Joseph Campbell originally outlined 17 stages of the monomyth in his book, screenwriter Christopher Vogler simplified it into 12 stages in a popular guidebook for writers. Known as the hero's journey model, these 12 steps are: Ordinary World. Call to Adventure.
Example: Grizzly Man (2005) Directed by Werner Herzog, this documentary explores the life and death of Timothy Treadwell, who lived among grizzly bears in Alaska. The film is a character study and examination of nature, presenting real-life events without following a fictional hero's journey.
Examples of The Hero's Journey in Film 'The Matrix' Warner Bros. Many iconic films have embraced the Hero's Journey structure to great effect. Here are a few examples: Star Wars: George Lucas drew heavily from Joseph Campbell's work when creating the Star Wars saga. Luke Skywalker's journey from a farm boy on Tatooine to a Jedi Knight follows ...
The Hero's Journey Home 12. Refusal of Return. Upon a successful completion of the Hero's Journey, and a transformation into a different person, the Hero has a "refusal to return." The Shire seems so boring now and the last thing Harry wants is to go back to that drawer under the stairs. And, oftentimes, the return can be just as dangerous.
Examples of a Hero's Journey in Five Stories. 1. Avatar. This 2009 sci-fi blockbuster became the top-grossing film of all time just 47 days after it premiered. Its success is largely due to the incredible Computer-Generated Imagery (CGI) characters and visual effects that are vibrantly convincing.
The examples below are: Interview with a Vampire. The Hunger Games. Interstellar. Harry Potter and the Philosopher's Stone. We hope to add more as time goes on. For each story we identify how each of the stages of the Hero's Journey is represented.
Movie Examples Showing the Hero's Journey. 1. The Lord of the Rings Trilogy (2001-2003) The Lord of the Ring Trilogy (2001-2003) Official Supertrailer - Elijah Wood, Ian McKellan Movie HD. Watch on. This classic high fantasy epic is one of the most recognized depictions of the hero's journey in fiction.
The hero's journey is commonly accepted to have 12 main steps. To make it even simpler on you, these steps can actually be broken down into three stages: the departure, the initiation, and the return. The hero's journey is usually defined as having three stages subdivided into 12 steps total.
Illustration of the hero's journey. In narratology and comparative mythology, the hero's journey, also known as the monomyth, is the common template of stories that involve a hero who goes on an adventure, is victorious in a decisive crisis, and comes home changed or transformed.. Earlier figures had proposed similar concepts, including psychoanalyst Otto Rank and amateur anthropologist Lord ...
Lion King Hero's Journey Essay Fight Club' Masculinity Essay Essay on Lennie Death in 'Of Mice and Men' 'The Hunger Games' Hero's Journey Essay Percy Jackson's Hero's Journey Based on a Concept by Joseph Campbell Critical Analysis of Several Stages of Hero's Journey McDonald's Customer Service Essay Essay on Public ...
The seasonal model has given My Hero Academia incredible pacing. With 25 episodes per season and year-long breaks, Deku's journey is able to progress steadily but not feel rushed, allowing him to ...